Disorders of the adrenal glands
- Cushing’s disease
- Cushing’s Syndrome ----------------------------→
- Hyperaldosteronism “Conn’s Syndrome”
- Addison’s Disease
- Pheochromocytoma
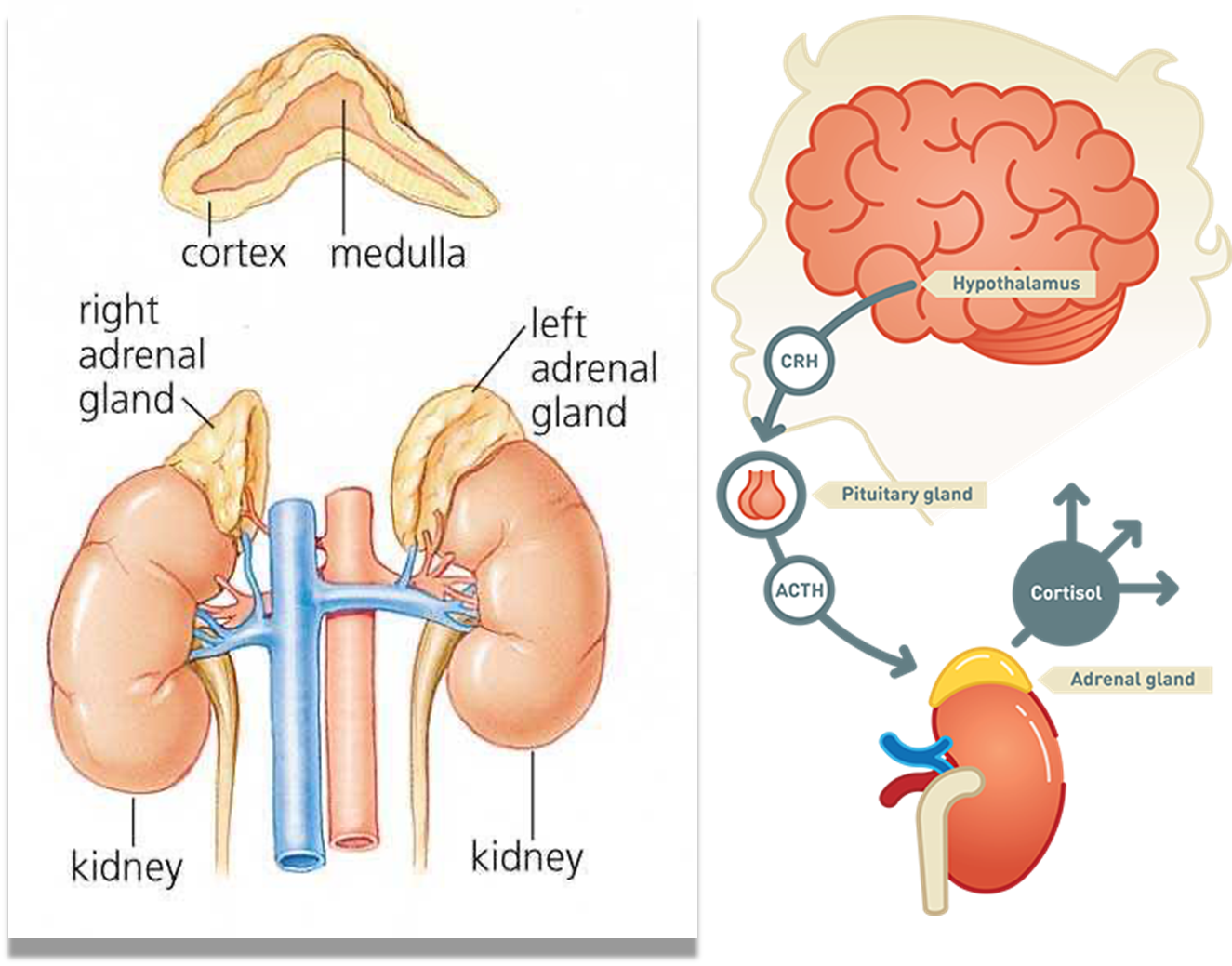
Adrenal glands
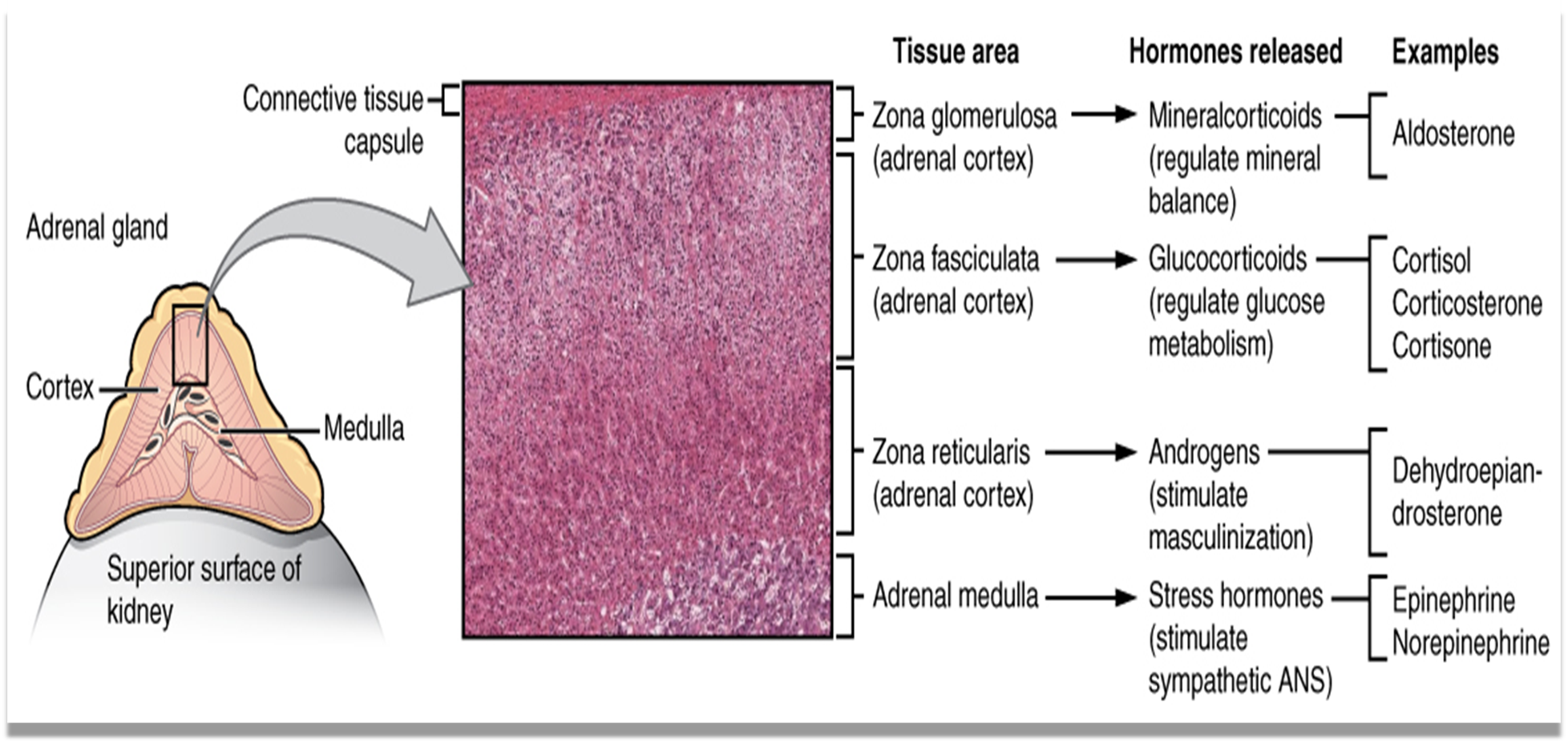
Also known as suprarenal glands Endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones Each gland has an outer cortex and an inner medulla
The adrenal cortex is divided into 3 zones:
- Zona glomerulosa
- Zona fasciculata
- Zona reticularis
Mineralocorticoids:
- Zona glomerulosa
- Produces aldosterone
- Helps in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolytes balance
- Na retention
- Water retention
- K+ excretion
Glucocorticoids:
- Zona fasciculata
- Cortisol and cortisone
- Helps in the regulation of the metabolism and immune system suppression
- CORTISOL is responsible for control & metabolism of:
- A. CHO (carbohydrates)
- Increases glucose formation
- Increases glucose release
- B. FATS:
- Control of fat metabolism
- Stimulates fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue
- C. PROTEINS:
- Control of protein metabolism
- Stimulates protein synthesis in liver & protein breakdown in tissues
- D. Others:
- Inflammatory and allergic response
- Immune system therefore increases the risk of infection
- A. CHO (carbohydrates)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone ACTH
- Produced in the anterior pituitary gland
- Individual biorhythms
- Highest in the early morning
- Gradually decrease on the rest of the day
- Stress- Increases cortisol production
ANDROGENS:
- Zona reticularis
- Produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs
- Hormones which increases male characteristics via release of testosterone
Adrenal medulla: It produces catecholamines (Epinephrine, and Norepinephrine)
Catecholamines produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.