https://next.amboss.com/us/search?q=thyroid+hormone+synthesis&v=overview
Chemistry Disorders Investigations of Thyroid hormones
What are thyroid hormones in the body?
1- Thyroxine (T4): produced exclusively by the thyroid gland (t1/2: 7 days)
2- T3: (t1/2: one day) - 20% is produced in the thyroid gland - 80% is produced from T4 in the liver, kidney & muscles by deiodinase of outer ring (as 80% of T4 is converted to T3 in extra thyroid tissues) - T3 is the biologically active form of thyroid hormones (as it is has 10 times more affinity more than T4 for thyroid receptors)
3- Reverse T3 (rT3): - Produced outside thyroid from T4 by deiodination of inner ring. - rT3 is biologically inactive.
General actions of thyroid hormones
1- Major effect of T3 & T4 is to enhance general protein synthesis essential for growth. T3 enhances transcription of growth hormone (GH) itself. (anabolic effects of T3). However, very high T3 levels in blood causes inhibition of protein synthesis (catabolic)
2- Thyroid hormones are essential for normal physical, mental & reproductive development in humans. Intrauterine or neonatal hypothyroidism causes cretinism in which there is physical & mental retardation.
3- Thyroid hormones have metabolic actions that regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids & protein. basal Metabolic rate (BMR) is increased.
-
Biosynthesis of thyroid hormones
-
Transport of thyroid hormones in blood
-
Regulation and control of thyroid function
-
Thyroid Function Test
Pathology
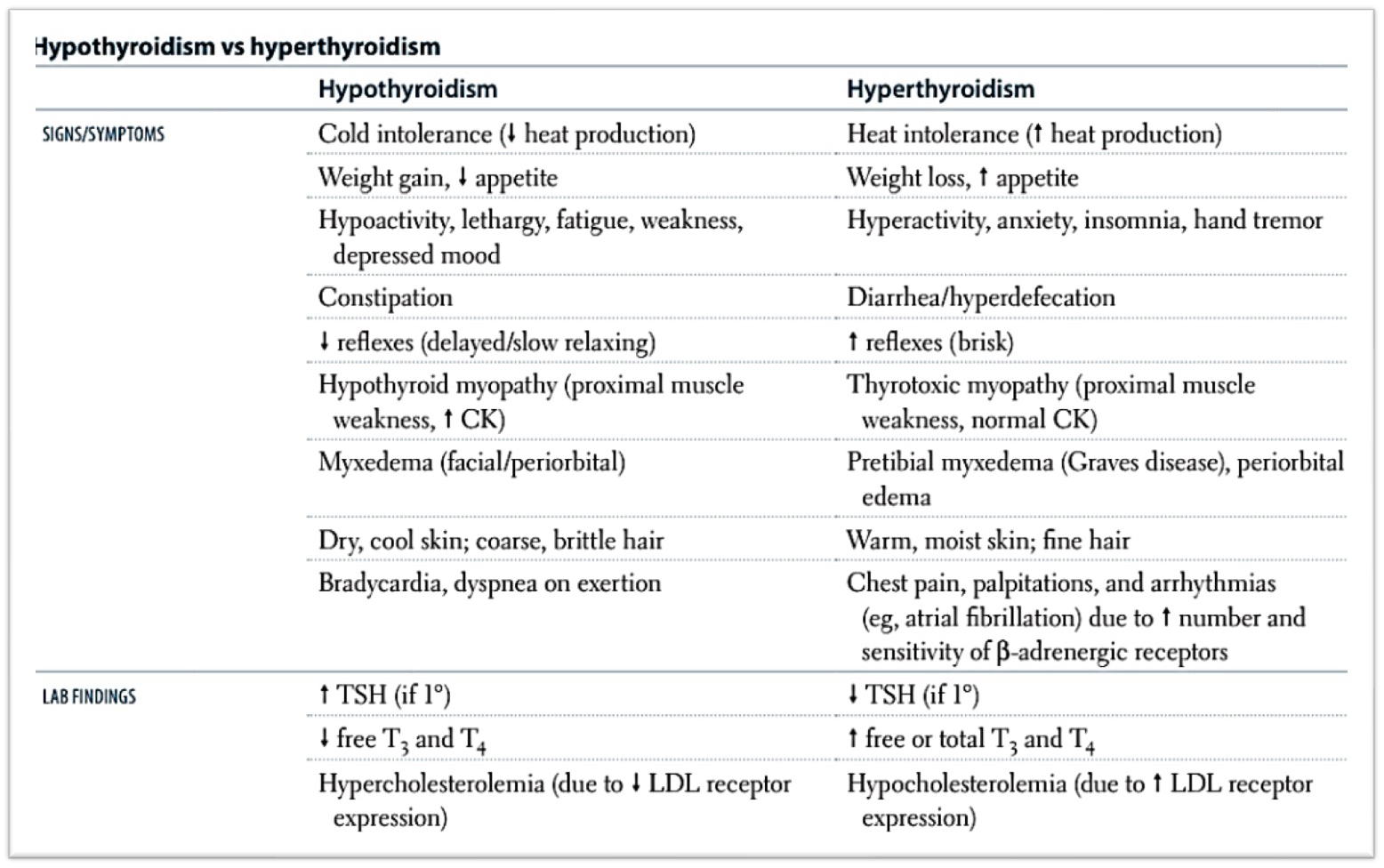
1. Hyperthyroidism
2. Hypothyroidism