Arterial Conditions
-
Acute Ischemia
-
Chronic Ischemia
-
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
-
Raynaud’s Disease
-
Beurger’s Disease
-
Gangrene
Components of extremities
- Skin & subcutaneous tissue ( lumps, ulcers)
- Arteries
- Veins
- Lymphatics
- Nerves
- Musculo-skeletal system
Systemic inquiry
- Symptoms indicating vascular disease elsewhere
- Chest pain
- Fainting
- Weakness in limbs
- Paresthesia
- Blurring of vision
- Other system inquiry- as in any other patient
Past Medical History
- MI
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Previous episode of claudication
- Dyslipidemia
- Hypertension
Family history
- Genetic predisposition:
- Other family members may
- be suffering from vascular disease
General examination
- ?Obese
- Pulse ,
- Blood pressure
- Full CVS evaluation- heart, carotid, abdominal aorta, peripheral vessels
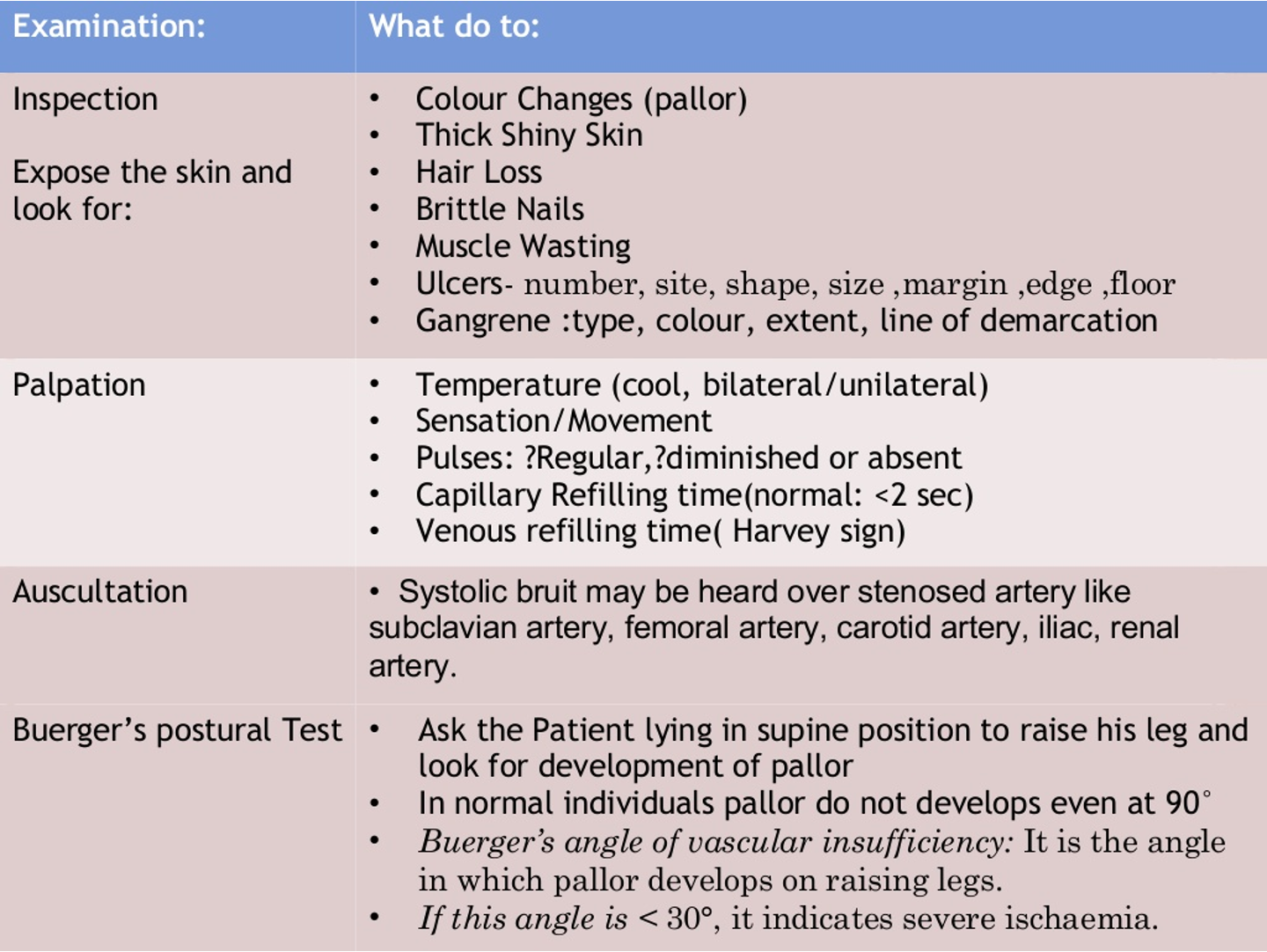
Inspection of the extremity (chronic ischemia)
-
Expose both limbs (lower or upper)
-
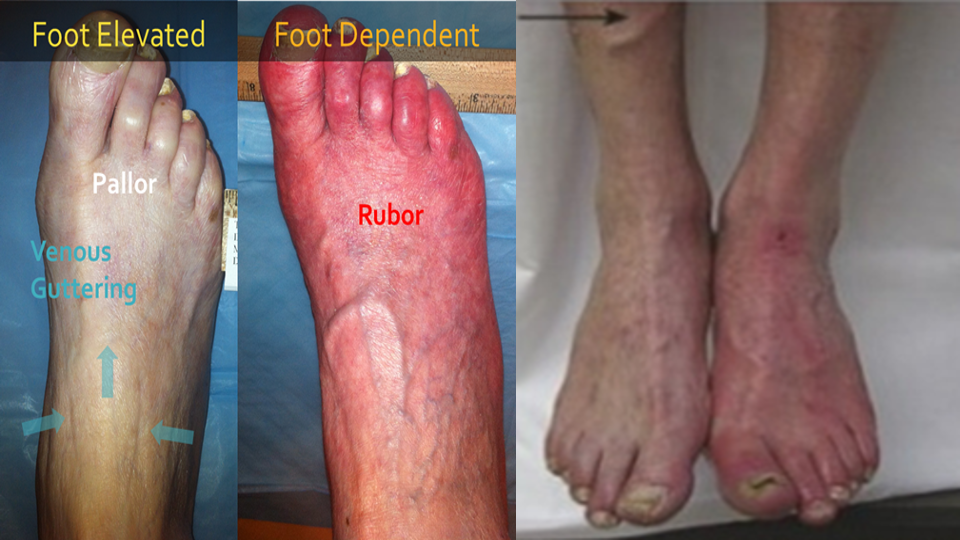
Skin color- shiny skin in ischemia
-
Thickening of nail, loss of leg hair
-
Discoloration ?patches of gangrene
-
Venous filling- empty in ischemia (guttering of veins)
-
Rubor on dependency- red flushed foot returns to normal after some time
-
Muscle wasting
-
Ulceration- tip of toes
-
Pulsatile mass (femoral, popliteal)
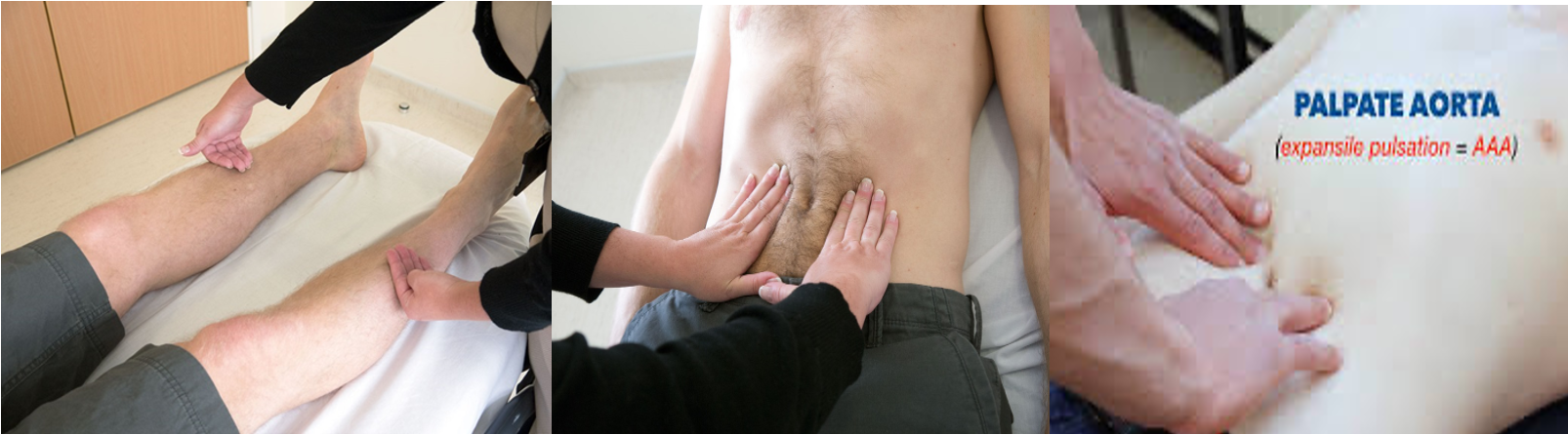
Palpation
Palpation of the extremity
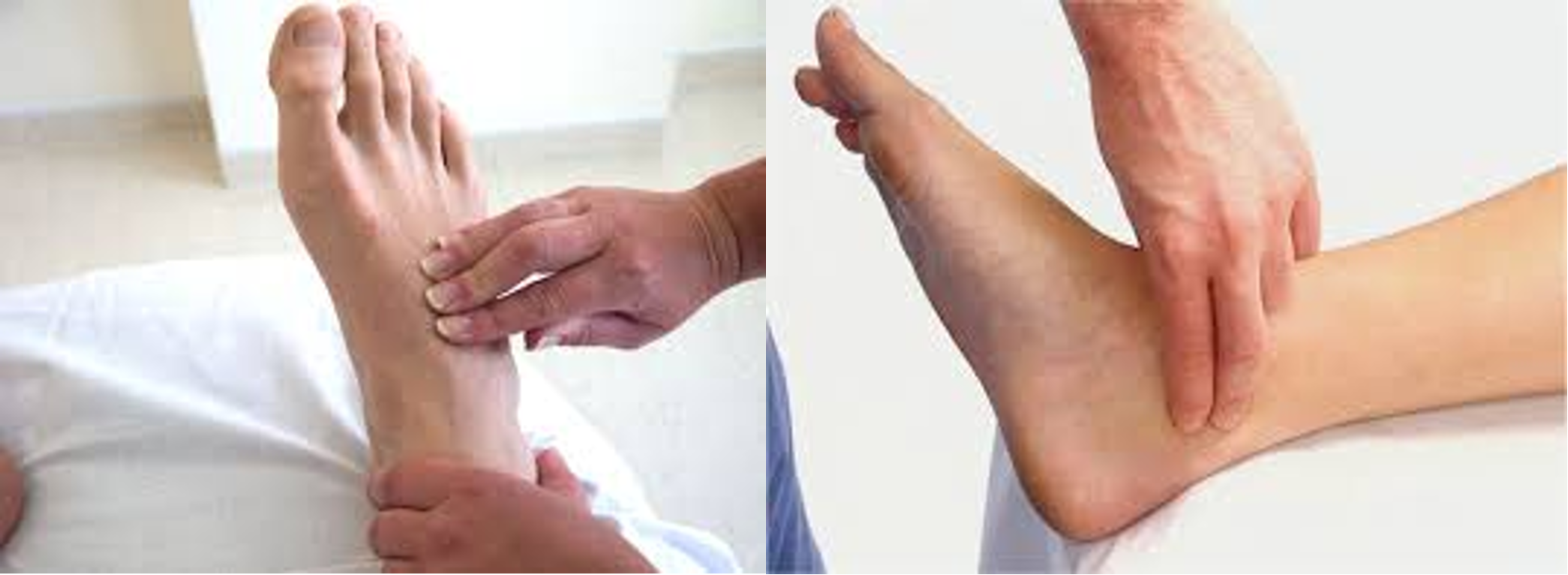
- Temperature- colder limb in ischemia (back of your hand along both limbs)
- Capillary refilling- press tip of nail for 2 secs, normal 2-4 sec.
- Tenderness/ oedema
- Pulses:
- Carotid and abdominal aorta (part of general examination)
- Upper limb:
- Lower limb:
Palpation of Aorta
- Supine position with the knees raised
- Abdominal muscles relaxed
2 is normal
Palpation: Upper limb pulses
- Axillary: in the axilla and medial upper arm.
- Brachial: antecubital fossa immediately medial to the biceps tendon.
- Radial: at wrist anterior to the radius.
- Ulnar: on medial side of the wrist.
Lower limb pulses
-
Femoral: At midinguinal point (midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the top of the pubic symphysis
- Midpoint of the inguinal ligament – halfway between the pubic tubercle and the anterior superior iliac spine (the two attachments of the inguinal ligament). The opening to the inguinal canal is located just above this point.
-
Popliteal: Knee flexed to 45 degrees. Foot flat on the examination table. Bimanual technique. Both thumbs are placed on the tibial tuberosity anteriorly and the fingers are placed into the popliteal fossa between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle and compressing it against the posterior aspect of the tibia just below the knee
-
Posterior tibial: 2 cm posterior to the medial malleolus.
-
Dorsalis pedis 1 cm lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon or in the cleft between 1st and 2nd metatarsals (use 3 fingers)
Peripheral scaling
- 0= abbsent
- 1= diminished
- 2= normal
- 3= bounding (aneurysm or AI)
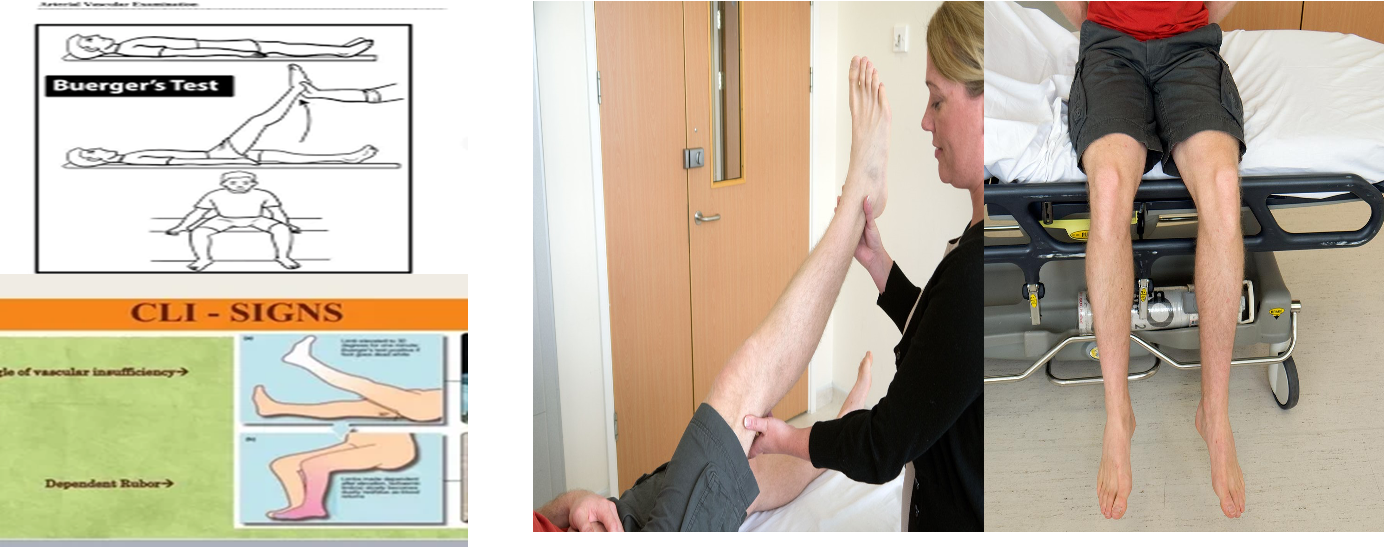
Buerger’s test: Pallor on elevation (vascular angle)
< 30°= severe PAD
- Slowly raise the leg (stopping for few seconds at every 10 degrees) with hand under the heel and notice for skin pallor.
- Rubor on dependency- red flushed foot
- Returns to normal after some time





- A)Stop smoking
- B)Start therapeutic Heparin; if thrombosed - burger is non-sclerotic
- C)Leg stocks - chronic
- D)Avoidance of cold temperature; female raynaud
diagnosed burger
Hemodynamic Noninvasive Tests
- Resting Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
- Exercise ABI
- Segmental pressure measurement
These traditional tests continue to provide a simple, risk-free, and cost-effective approach to establishing the limb ischemia diagnosis as well as to follow up after the procedures.
Exercise ABI
- Confirms the limb ischemia diagnosis
- Assesses the functional severity of claudication
- May “unmask” limb ischemia when resting the ABI is normal
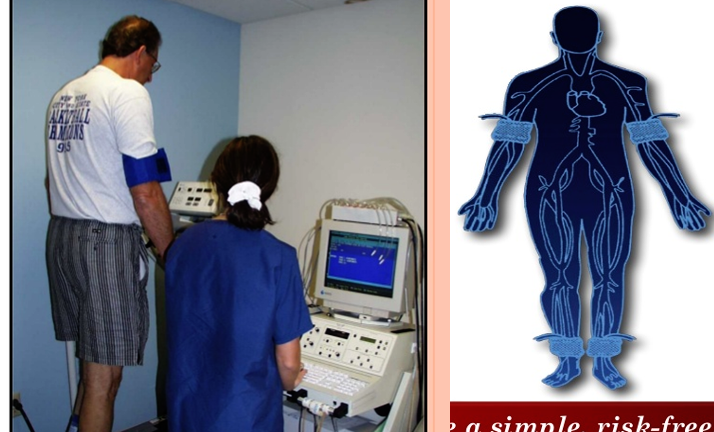
The technique of ankle–brachial pressure index measurement:
Measurement of the posterior tibialis systolic blood pressure. A blood pressure cuff is placed around the calf and the blood pressure is measured with a Doppler probe over the posterior tibialis artery.
Measurement of the brachial systolic blood pressure using a Doppler probe.
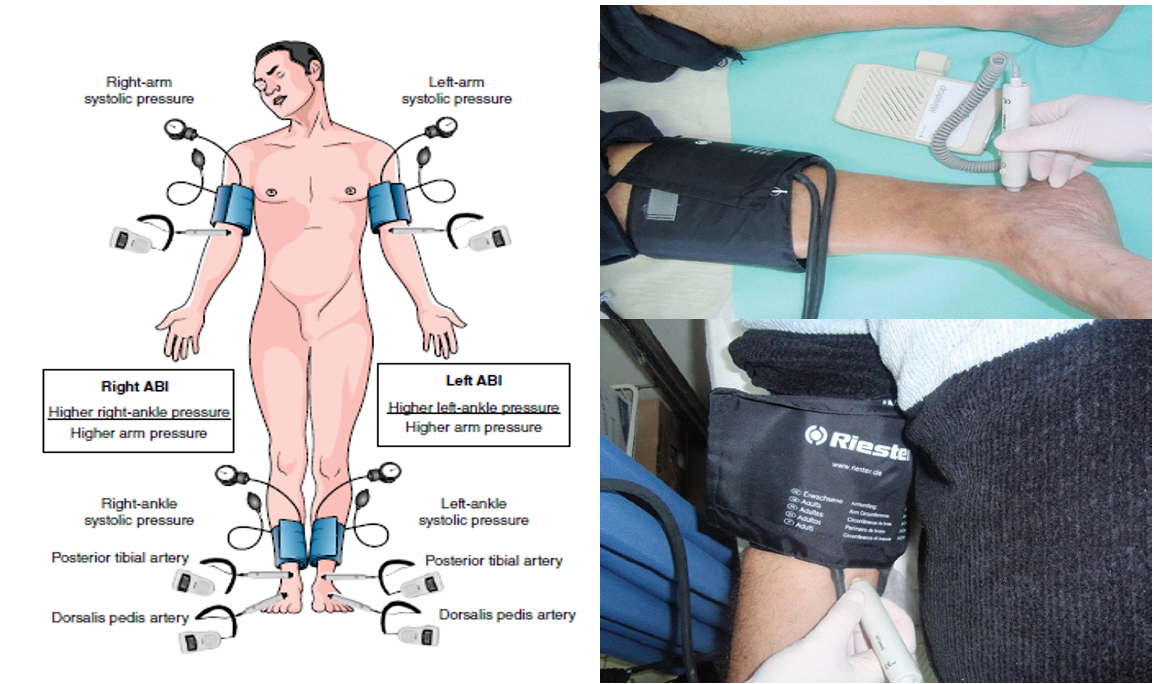
Ankle: brachial index
-
Ankle systolic pressure/ Brachial systolic pressure (Doppler probe)
-
1.2 – Calcified artery -diabetes
-
1.19- 0.95 – Normal
-
O.94- 0.5 – Moderate (intermittent claudication)
-
< 0.5 – Severe disease (rest pain)
