- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) Pril’s
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) Sartans
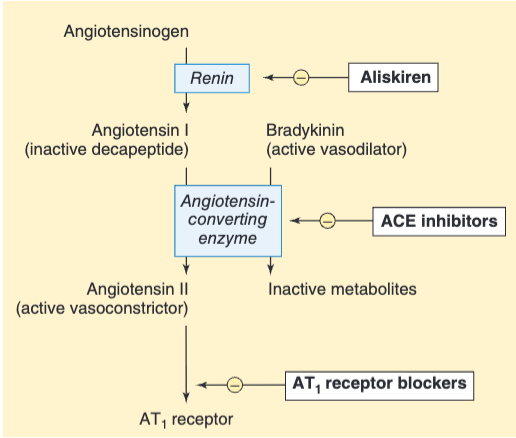
RENNIN ANGIOTENSIN ALDESTERON SYSTEM RENIN:
It is a proteolytic enzyme secreted by the kidney into the blood stream. Stimuli that increase renin secretion: Sodium depletion, diuretics, hypotension, hemorrhage, upright posture, dehydration, constriction of renal artery, heart failure and Cirrhosis
- A1 (Can be converted by all tissues) ⇒ A2
- (Kinase, Cathepsin helps ACE to convert 1 to 2
- Bradykinenin RR lowers A2
- ACEE, ARBS
Actions of Angiotensins
- Angiotensin I (precursor of angiotensin II): It has no pharmacological action.
- Angiotensin II: It acts on two receptors; AT1 and AT2 receptors
Its action on AT1 receptor produces the following:
CVS:
- Arteriolar constriction leading to increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure (40 times as active as norepinephrine).
- Angiotensin II produces positive inotropic and chronotropic effects which are primarily due to central and peripheral sympathetic stimulation. Endocrine:
- Increase secretion and synthesis of aldosterone which causes Na and water retention.
- Facilitate catecholamine synthesis and release.
- Increase pituitary vasopressin and ACTH.
Renal:
- Suppress renin release
- V.C of renal efferent arterioles, increases proximal tubular Na+ reabsorption
C.N.S
- Increase H2O intake and vasopressin secretion.
- Stimulate central sympathetic discharge.
Its action on AT2 receptor produces the following:
- Antiproliferation.
- Apoptosis (normal cell death).
- Vasodilatation and increase local bradykinin.
Inhibitors of the renin-Ang system:
-
Inhibitors of renin release: Beta blockers carvidelol, labetalol, bucindolol, celiprolol, dilevalol α-methyldopa (Adrenergic Neuron Blocker) , clonidine (Central a2 stimulant)
-
Inhibitors of plasma renin activity: aliskrine.
-
Inhibitors of Ang-2 formation: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)(pril)
-
Blockers of AT receptors: saralasin, losartan, valsartan