Colon Cancer
- Most common type of GI cancer.
- Second highest cause of cancer occurrence and death
in US In 2012,
- Second most common cause of cancer in women
- Third most common in men
- Fourth most common cause of cancer death
In 2015 (KSA),
- The most common cancer among men
- Third commonest among women
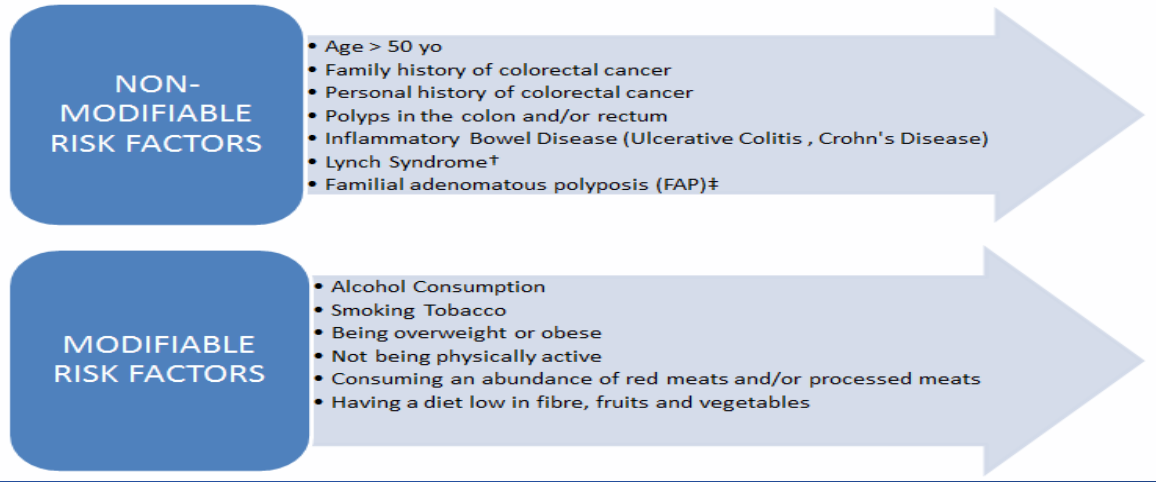
Etiology:
Most cases of colon cancer are sporadic.
It is a multifactorial disease process
- Genetic factors
- Environmental
- Inflammation
Genetic factor
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP):
- Autosomal dominant disorder
- Mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene.
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC)
- Called (Lynch syndrome)
- Autosomal dominant disorder
- Mutations in the DNA mismatch repair proteins.
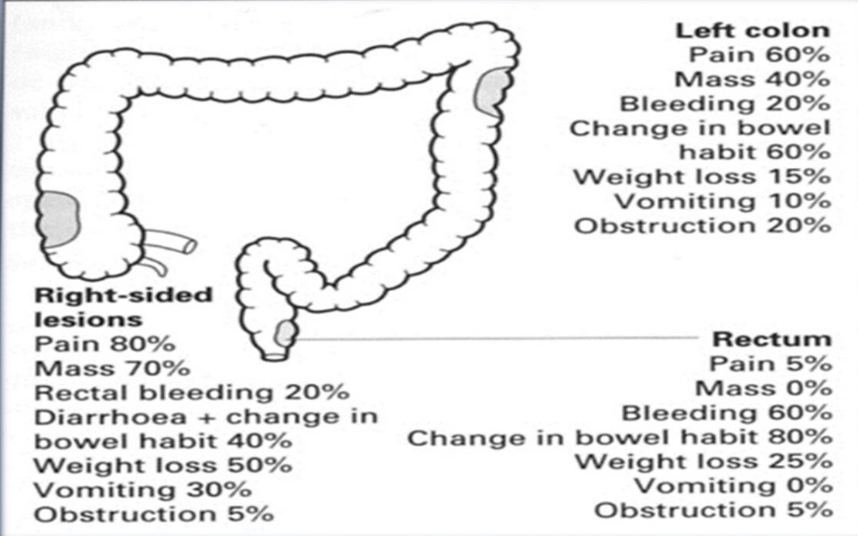
Signs and symptoms:
- Screening procedures
- Depends on the location
Common symptoms:
- Rectal bleeding
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Abdominal pain
- Change in bowel habits
- Intestinal obstruction or perforation
Physical findings may include the following:
- Early disease: Nonspecific findings (fatigue, weight loss) or none at all
- Advanced disease: Abdominal tenderness, palpable abdominal mass, hepatomegaly, ascites
Diagnosis
-
Laboratory studies
- CBC- LFT- CEA
-
Imaging studies:
- Abdominal X-ray
- Contrast study (Barium study with double contrast)
- Abdomen CT/MRI
- Positron emission tomography, including fusion PET-CT scan
-
Colonoscopy+Bx
-
Metastatic workup
Diagnosis Criteria
The Amsterdam criteria: Diagnostic criteria to identify families likely to have Lynch syndrome, known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC).
Bethesda guidelines
- Created by National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Recommendations for individuals with Lynch syndrome
Management
- Early disease better outcome
- Surgery is the only curative modality for localized colon cancer (stage I-III).
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Surgical options include the following:
- Right hemicolectomy: For lesions in the cecum and right colon
- Extended right hemicolectomy: For lesions in the proximal or middle transverse colon
- Left hemicolectomy: For lesions in the splenic flexure and left colon
- Sigmoid colectomy: For sigmoid colon lesions
- Total abdominal colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis