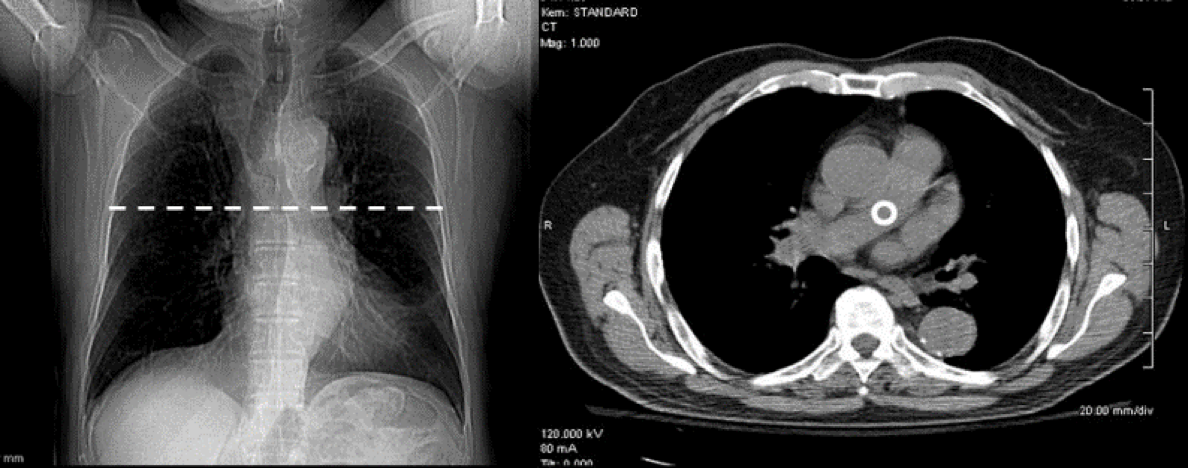
Computerized (or computed) tomography (CT scan) is an imaging technique that employs a rotating x-ray generator and multiple detectors to produce a large number of cross-sectional images on several planes.
Unlike traditional radiography, which produces projectional images of structures superimposed on each other, CT visualizes slices of the patient only a few millimeters thick, eliminating the problem of superimposition.
A CT scan is used to define normal and abnormal structures in the body and/or assist in procedures by helping to accurately guide the placement of instruments or treatment planning.
Z The advantages of CT scan besides allowing for image manipulation and 3D reconstruction include shorter study time and lower cost than MRI and higher resolution than projectional radiography,
while disadvantages include lower resolution than MRI and exposure to ionizing radiation.
Interpretation: - Hypodensity: an area of tissue with lower density (appears darker) than normal or surrounding tissue - Hyperdensity: an area of tissue with higher density (appears brighter ) than normal or surrounding tissue - Isodensity: an area of tissue with the same density (appears with the same brightness) as surrounding tissue or reference structure
CT is usually performed in the axial plane, but it is possible to reconstruct excellent images in other planes, e.g. coronal , sagittal or oblique, and even three-dimensional (3D) images
If blood vessels are bright, indicates high contrast
Hounsfield scale: An index used to quantify the radiodensity of materials imaged by CT.
A CT scan produces a greyscale image, with high-density material appearing bright (e.g., bone) and low-density material appearing dark (e.g., fat).
The shades of gray are described in terms of Hounsfield units (HU), also referred to as CT numbers,
Z on a scale with water as the reference point (0 HU). Higher-density materials have values above 0 (e.g., bone: 1000–1500 HU),
while lower-density materials have a value below 0 (e.g., Fat; air: -1000 HU).