Metastatic disease have any of the following:
- Vertebral metastases (94%)
- Intradural extramedullary metastases(5%)
- Intramedually metastases (1%).
Plain radiography:
Is used to show erosion of the pedicles or the vertebral body.
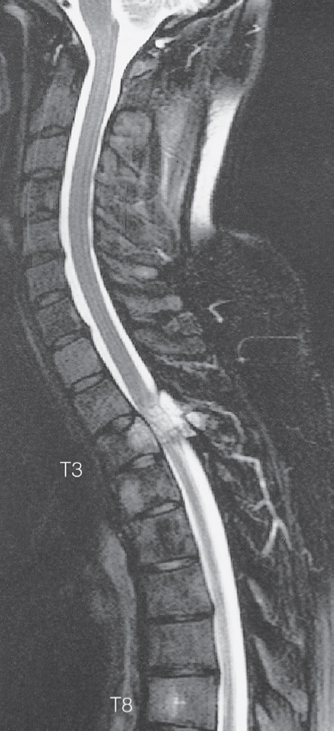
Spinal cord compression. - T2-weighted MRI scan
showing metastases from a breast carcinoma in the body and pedicle of T3 causing compression of the spinal cord.
MRI:
Is very sensitive in detecting vertebral metastasis.
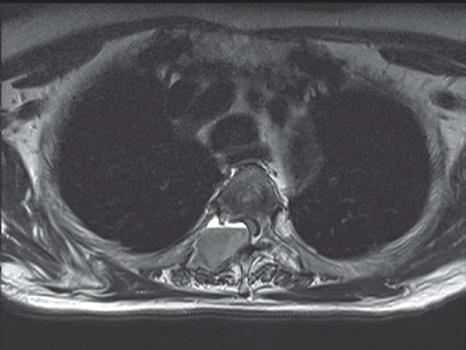
Axial T1-weighted image
showing a breast cancer metastasis
arising from the right pedicle and causing extradural compression of the cord.
Scintigraphy:
Very sensitive in detecting bone metastasis.
Metastasises
Osteoblastic metastasis→
- increase in radiographic density
- e.g.: prostate cancer, small cell lung cancer
Osteolytic metastasis →
- decrease in radiographic density
- e.g.: multiple myeloma, thyroid cancer, kidney cancer, melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer
Mixed metastasis:
- e.g.: breast cancer, gastrointestinal cancer