Surgery
Shock
Cardiogenic Shock
-
Causes:
- Myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, valve dysfunction,
- massive pulmonary embolism,
- cardiac tamponade and tension pneumothorax.
-
A pump failure: Heart becomes unable to maintain adequate cardiac output to meet metabolic requirements.
-
Low output state
-
Normal circulating volume
Management: Cardiogenic Shock
- Myocardial infarction- commonest cause.
- Tension pneumothorax, traumatic cardiac tamponade- trauma.
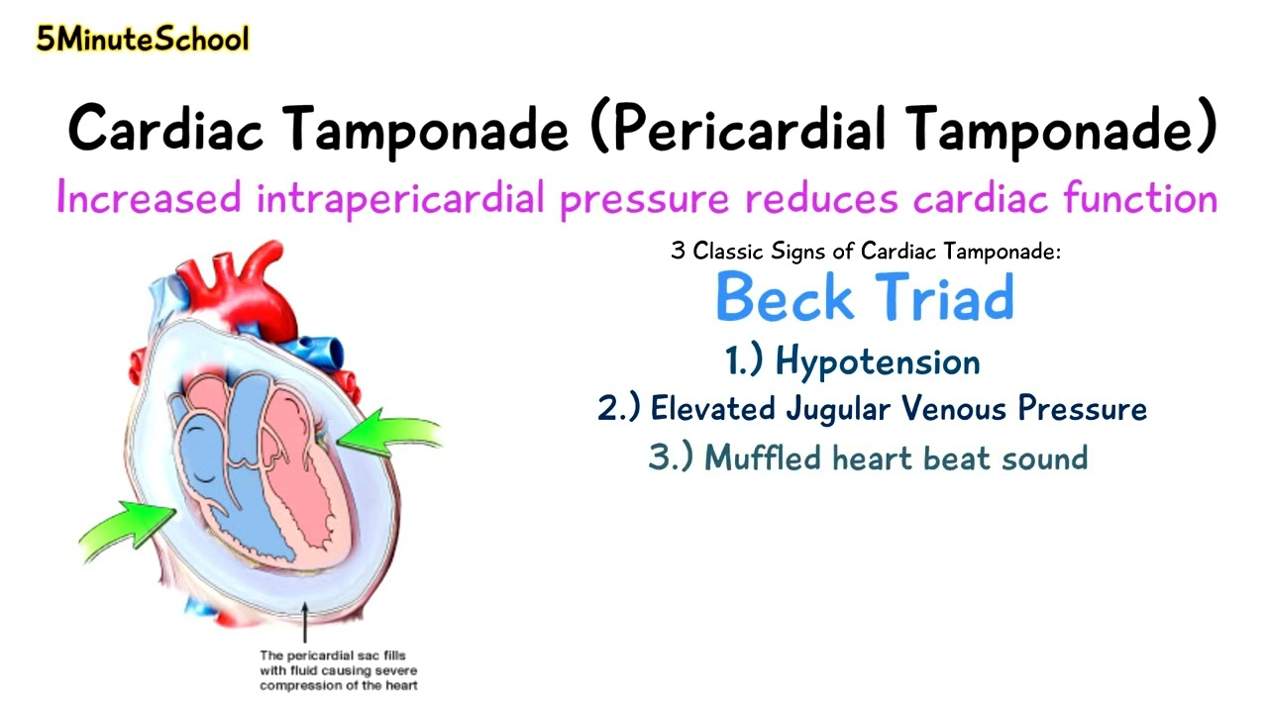
- FEATURES: Hypotension, Distended neck veins , Raised CVP.
- ECG, echocardiography, CXR,ABG, CK-MB, troponin.
- Maintenance of adequate oxygenation.
- Judicious fluid administration to avoid fluid overload.
- Thoracocentesis, pericardiocentesis in trauma.
The patient should have complete bed rest and be monitored in a coronary care unit.
Pain relief with Inj. Morphine or Pethidine HCl.
Pharmacologic support:
-
Inotropes—Like Dopamine and Dobutamine for pump failure.
-
Thrombolytic therapy: with Aspirin and Streptokinase in case of myocardial infarction.
-
Diuretics, cardiac glycosides and ACE inhibitors for patients with heart failure.
-
Temporary cardiac pacing will increase cardiac output and heart rate in bradyarrhythmias.
Truama
Cardiogenic shock
- Tension pneumothorax- most common cause,
- Pericardial tamponade (penetrating trauma),.. Classical Beck’s triad
- Myocardial contusion
Beck’s triad: hypotension, distended neck vein (raised CVP >15 cm H2O, CVP in haemorrhagic shock <5 cmH2O, n=8 to 12 mmHg) muffled heart sound
- Dysrhythmias in contusion
- Ultrasonography : helpful in diagnosis
- Treatment: fluid resuscitation, pericardiocentesis