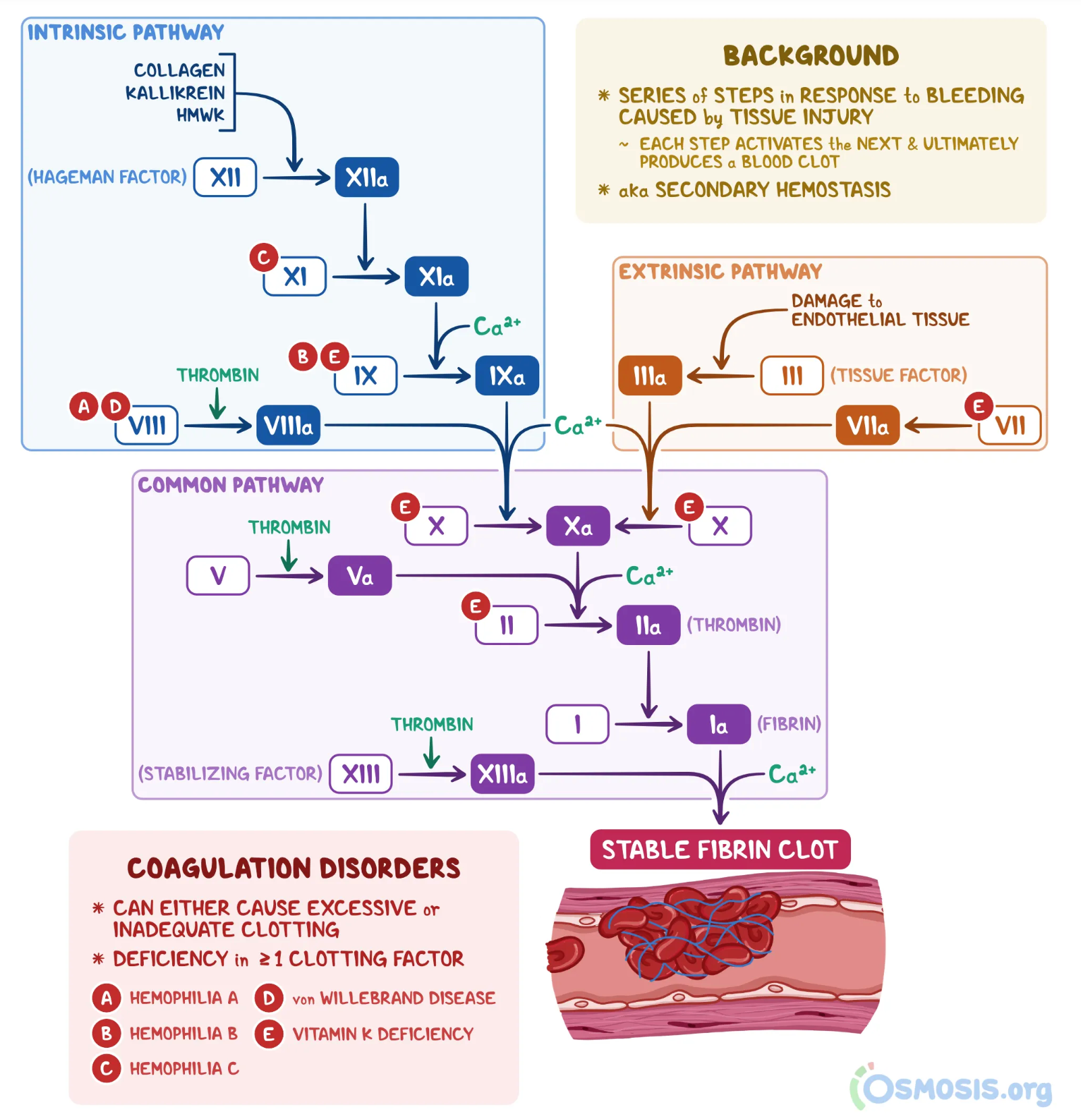
Steps of Primary Hemostasis
-
Endothelial Injury: Vasoconstriction mediated by neural reflex & endothelin released from damaged endothelial cells.
-
Exposure: Subendothelial collagen exposed binds to the von Willebrand factor (vWF) released from damaged endothelial cells.
-
Adhesion: Then; Platelets bind to the vWF via GpIB receptors on the platelets, activating platelets.
-
Activation: Platelets undergo a conformational change and release calcium, ADP, and thromboxane A2. ADP binds to P2Y12 receptors on adjacent platelets & induces expression of GpIIB/IIIA receptors, mediating the final step.
-
Aggregation: Finally, after GpIIB/IIIA expression on the platelets, fibrinogen binds these receptors and aggregates platelets together, forming a platelet plug.
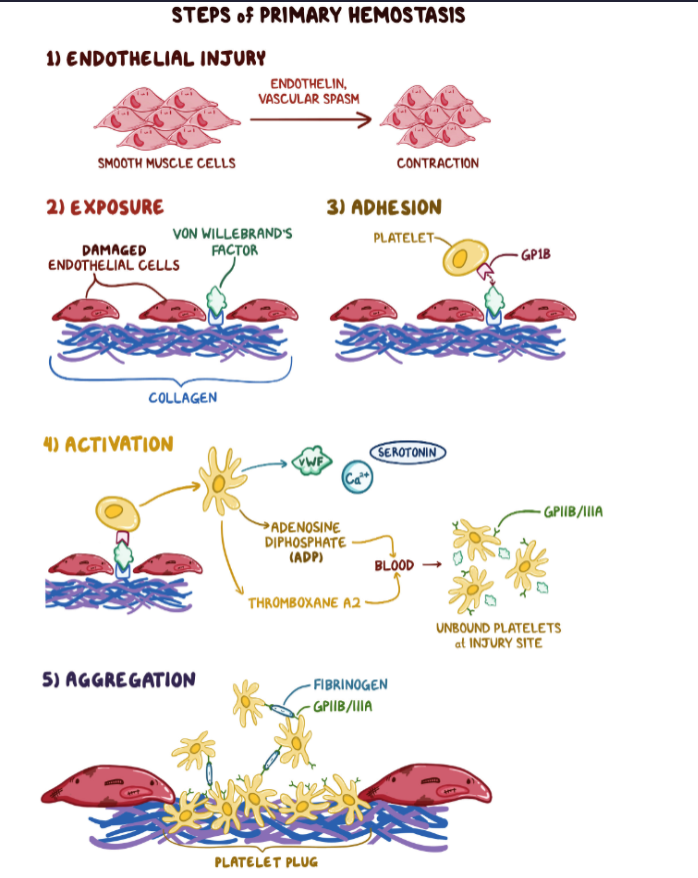
Question on Primary Hemostasis
An investigation is done on hemostasis to determine the steps involved in preventing blood loss after injury. Which of the following is true regarding primary hemostasis?
A. After an endothelial injury, vasodilation mediated by neural reflex occurs immediately.
B. ADP released from activated platelets binds to P2Y12 receptors on adjacent platelets, causing increased expression of Gp2B/3A.
D. Calcium released from platelets binds to P2Y12 receptors on adjacent platelets, causing increased expression of Gp2b/3A.
E. Adhesion of platelets to the site of injury is mediated by binding to von Willebrand factor (vWF) via GpIIB/IIIA receptors
F. Fibrinogen mediates platelet aggregation via GpIB receptors