ENT
Sinusitis
Infection of the sinuses
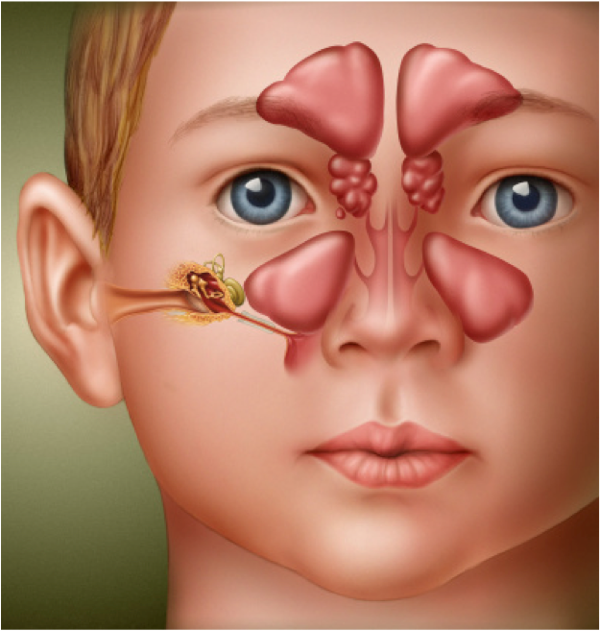
Sinusitis: 4 Paranasal Sinuses
Inflammation of one or more sinuses:
- Frontal
- Maxillary
- Ethmoid
- Sphenoid
Development of Sinuses
- Maxillary and ethmoid sinuses present at birth.
- Frontal sinus developed by age 5.
- Sphenoid sinus last to develop, by age 8-10.
Normal Sinus
Sinus health depends on:
- Mucous secretion of normal viscosity, volume, and composition.
- Normal mucociliary flow to prevent mucous stasis and subsequent infection.
- Open sinus ostia to allow adequate drainage and aeration.
Physiologic Importance of Sinuses
- Provide mucus to upper airways.
- Lubrication.
- Vehicle for trapping viruses, bacteria, and foreign material for removal.
- Give characteristics to voice.
- Lessen skull weight.
- Involved with olfaction.
Ostiomeatal Complex
- Ostiomeatal complex is the area under the middle meatus (airspace) into which the anterior ethmoid, frontal, and maxillary sinuses drain.
- Posterior ethmoids drain into the upper meatus.
- It is the functional relationship between the space and the ostia that drain into it.
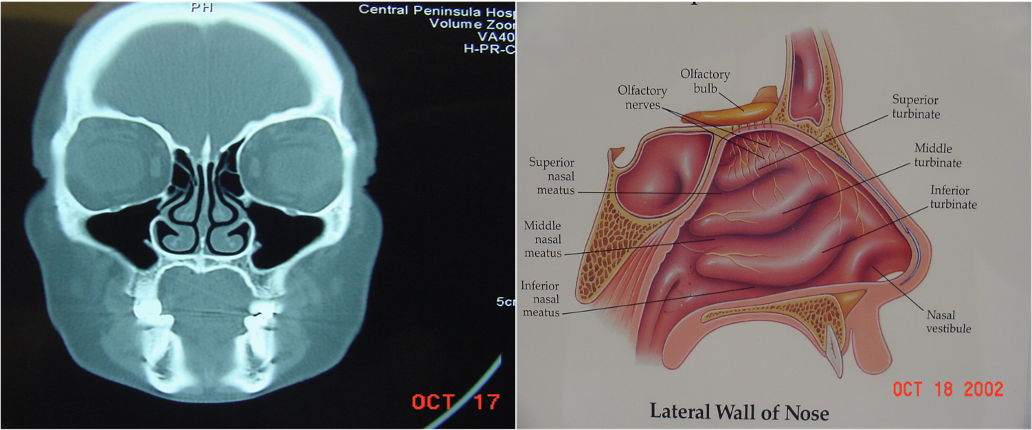
Lateral Wall of Nose
Sinusitis Classification
- Acute Sinusitis: Infection lasting 4 weeks, symptoms resolve completely.
- Subacute Bacterial Sinusitis: Infection lasting 4 to 12 weeks, resolves completely.
- Chronic Sinusitis: Symptoms lasting more than 12 weeks.
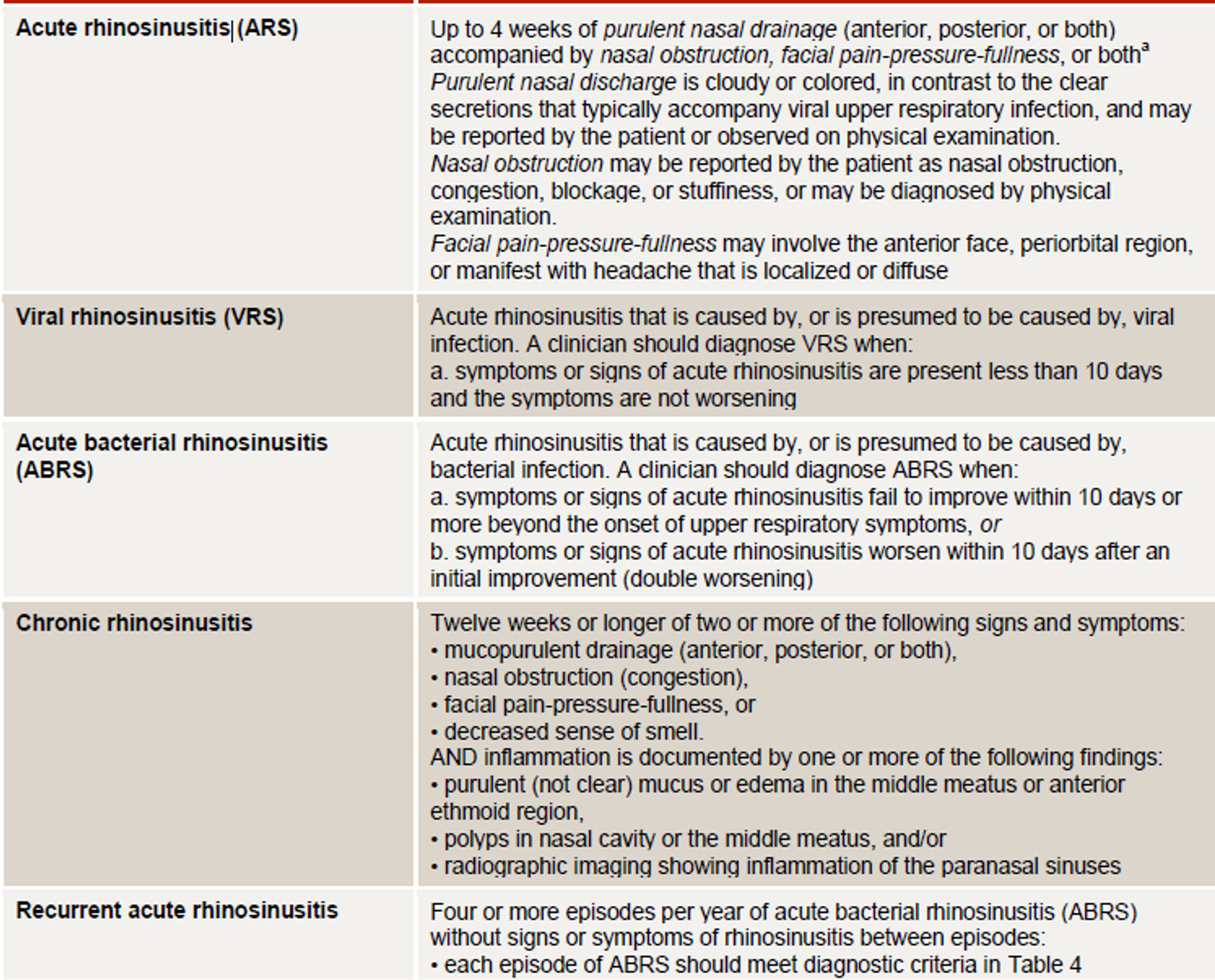
Recurrent Acute Bacterial Sinusitis
- Episodes lasting fewer than 4 weeks and separated by intervals of at least 10 days.
- Four episodes in 1 year.
Imaging
CT maxillofacial with or without IV contrast Findings may include signs of:
-
Rhinosinusitis: Opacification, mucosal thickening, air-fluid levels, soft tissue swelling.
-
Underlying causes of chronic rhinosinusitis: e.g., anatomic abnormalities, polyposis
MRI with and without IV contrast:
can be used to evaluate for intracranial or intraorbital involvement or to differentiate polyps from tumors
X-ray sinuses
- No longer recommended due to limited sensitivity and specificity
- May show sinus opacification and air-fluid levels.
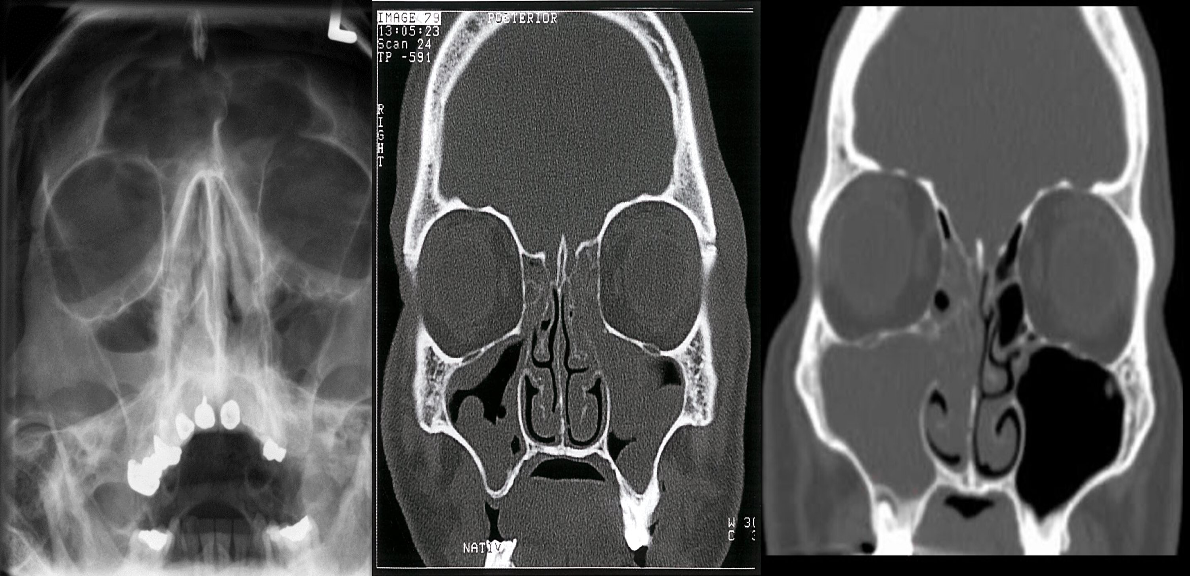 A) X-ray of the paranasal sinuses
A) X-ray of the paranasal sinuses
- An air-fluid level is visible within the right maxillary sinus
- This is a typical radiological feature of sinusitis.
B) Chronic rhinosinusitis CT paranasal sinuses (without contrast; coronal plane) The ethmoid sinuses are opacified and there is lobulated thickening of the walls of the maxillary sinuses. The findings indicate nasal polyps and retention cysts.
C) CT paranasal sinuses (coronal plane) of a patient with acute sinusitis The right maxillary sinus is completely opacified. Extensive soft tissue density material is also present in the ipsilateral nasal cavity and the right ethmoid sinus is nearly completely opacified.