SURGERY
-
risk of cancer in some women is increased substantially over the normal risk (but does not approach 100%),
-
counseling that explains the benefits and risks of prophylactic mastectomy?
-
Genetic tests for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations provide valuable information
Most common presentation is with a breast lump or lumpiness, which is usually painless.
Any discrete lump, no matter how small or mobile, can be cancer
Risk factors:
- Age- rises with age
- Early menarche and late menopause
- Age at 1st pregnancy > 40
- Nulliparous women
- HRT (Hormone replacement therapy)
- Obesity
- Exposure to radiation
- Diet (saturated fat)
- Genetic factor (BRCA 1, BRCA 2)- 50-60 % of hereditary ca.
- Previous benign disease (atypical hyperplasia)
Types of breast cancer
Management
I. MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER- DCIS
-
Localized disease (<4cm):-
- “Wide local excision” with normal healthy tissue all round the margins + Radiotherapy (except for very small lesions)
-
Larger (>4cm) or widespread disease:
- “mastectomy”
II. MANAGEMENT OF INVASIVE BREAST CANCER
-
Operable: T1-T3, N0,N1,M0
-
Local therapy (surgery) +
-
systemic therapy (Chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy)
Breast Cancer in Pregnancy
-
1-2% present during pregnancy
-
Diagnosis is often delayed
-
1st & 2nd trimester: Mastectomy, chemotherapy can be given (small risk to the fetus), RT after delivery.
-
3rd trimester: Surgery or delivering baby early (32 weeks) followed by treatment of breast cancer.
Management of Advanced & Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Average survival 20-30 months
- Effective symptom control with minimal side effects.
- No evidence that treating metastatic disease improves survival.
- Surgery only for fungating lesions.
- Chemotherapy, hormone therapy, anti-HER2
IMAGING
Mammography in breast cancer (medio-lateral) Mammography (right breast; mediolateral oblique view) A high-density mass with an indistinct margin and containing microcalcifications projects in the upper breast. The features of this lesion are highly suspicious for malignancy.
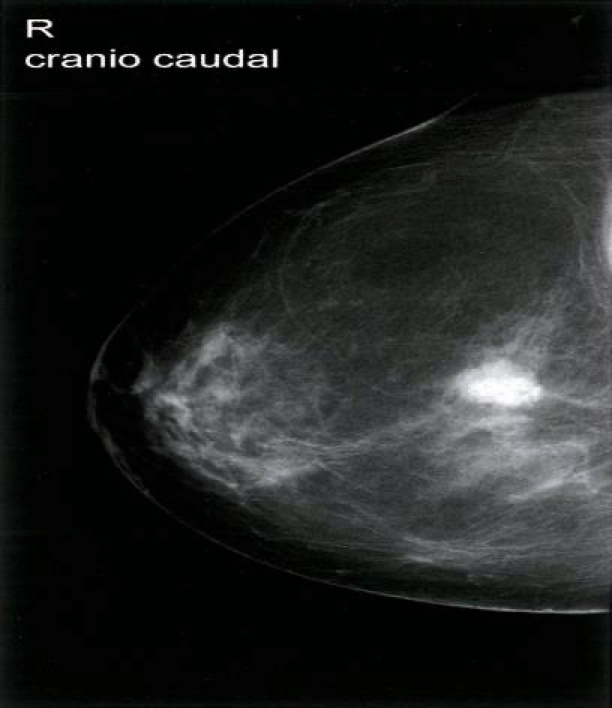
Suspicious breast mass (Craniocaudal) - Mammography (right breast; craniocaudal view) A mass with suspicious features, including high density and indistinct margins, is visible in the posterior third of the breast.
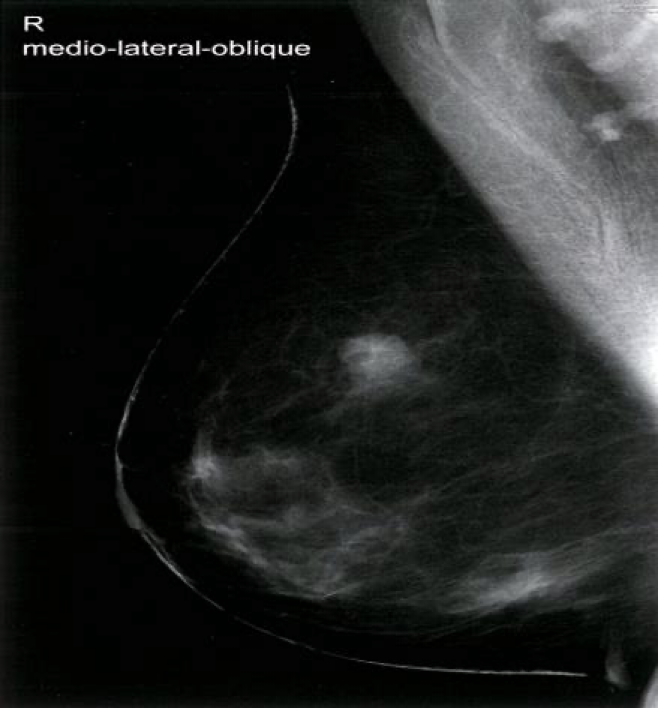 In postmenopausal women and women ≥ 30 years of age with a suspicious breast mass, mammography is preferred over ultrasound Z . In premenopausal women < 30 years of age, ultrasound is preferred Z , because the higher density of breast tissue decreases the diagnostic power of mammography.
In postmenopausal women and women ≥ 30 years of age with a suspicious breast mass, mammography is preferred over ultrasound Z . In premenopausal women < 30 years of age, ultrasound is preferred Z , because the higher density of breast tissue decreases the diagnostic power of mammography.
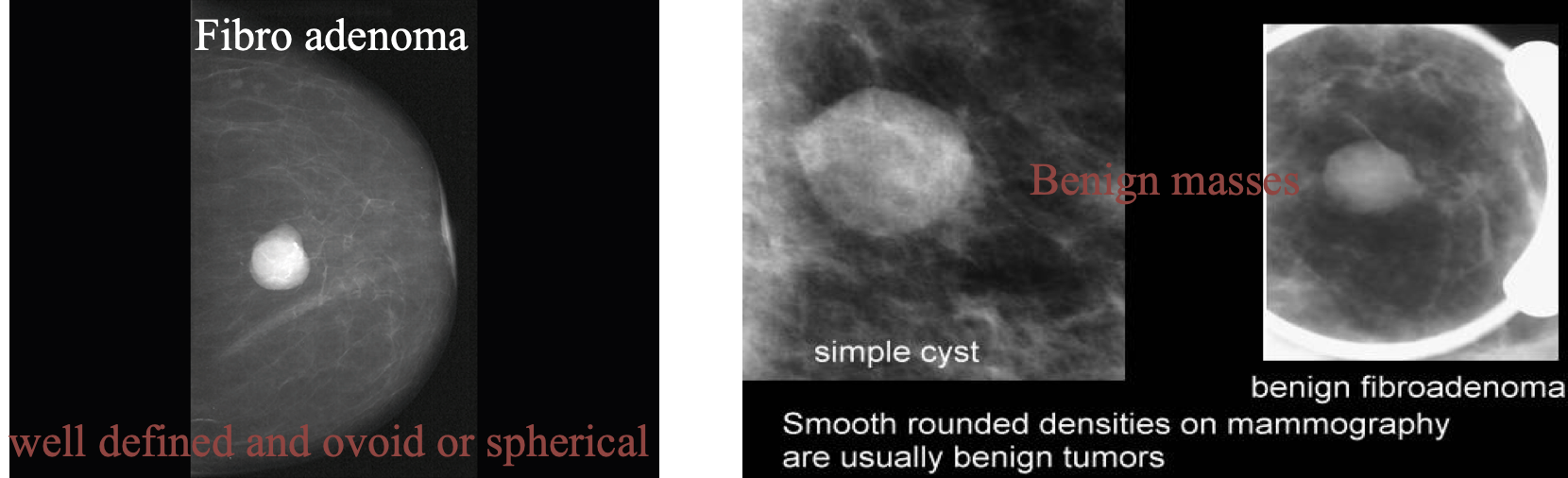
 Ultrasound image of a benign breast lesion. There is a very well-defined hypoechoic ovoid mass typical of a benign fibroadenoma.
Ultrasound image of a benign breast lesion. There is a very well-defined hypoechoic ovoid mass typical of a benign fibroadenoma.
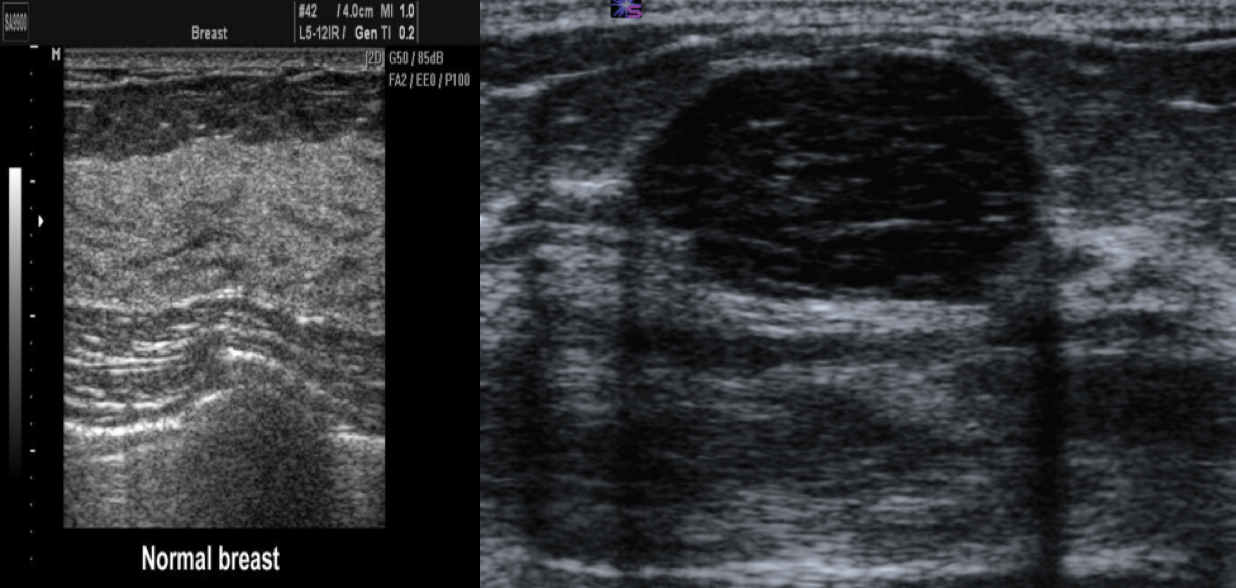
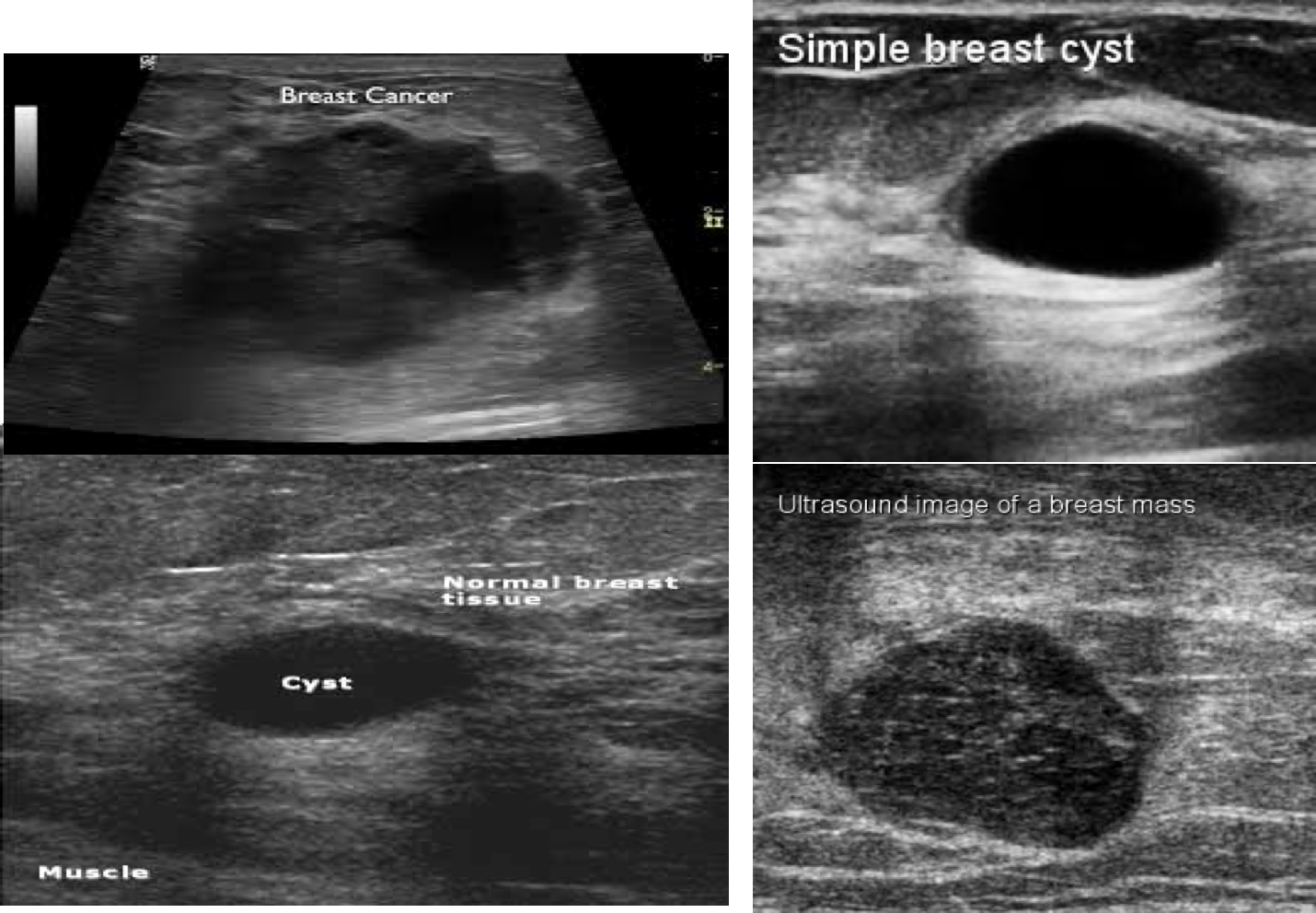
Breast Ultrasound is usually done to differentiate between solid and cystic masses
MRI: Superior modality to: lymph node examination leading to no results from other modalities, except MRI