Renal trauma
Blunt trauma, particularly road traffic accidents and contact sports, are the mechanisms of injury. Loin pain and hematuria are the major presenting features. CT is the preferred imaging investigation.
Imaging appearances: Renal and ureteral injury:
-
CT with IV contrast of the abdomen/pelvis: to assess renal and accompanying injuries or intraabdominal fluid retention
-
Urethrocystography: if CT is unavailable
CT findings - Low-grade renal injury e.g. Subcapsular hematoma ,parenchymal contusion & renal laceration
- High-grade renal injury Renal vein or artery injury & Shattered kidney with loss of identifiable renal anatomy
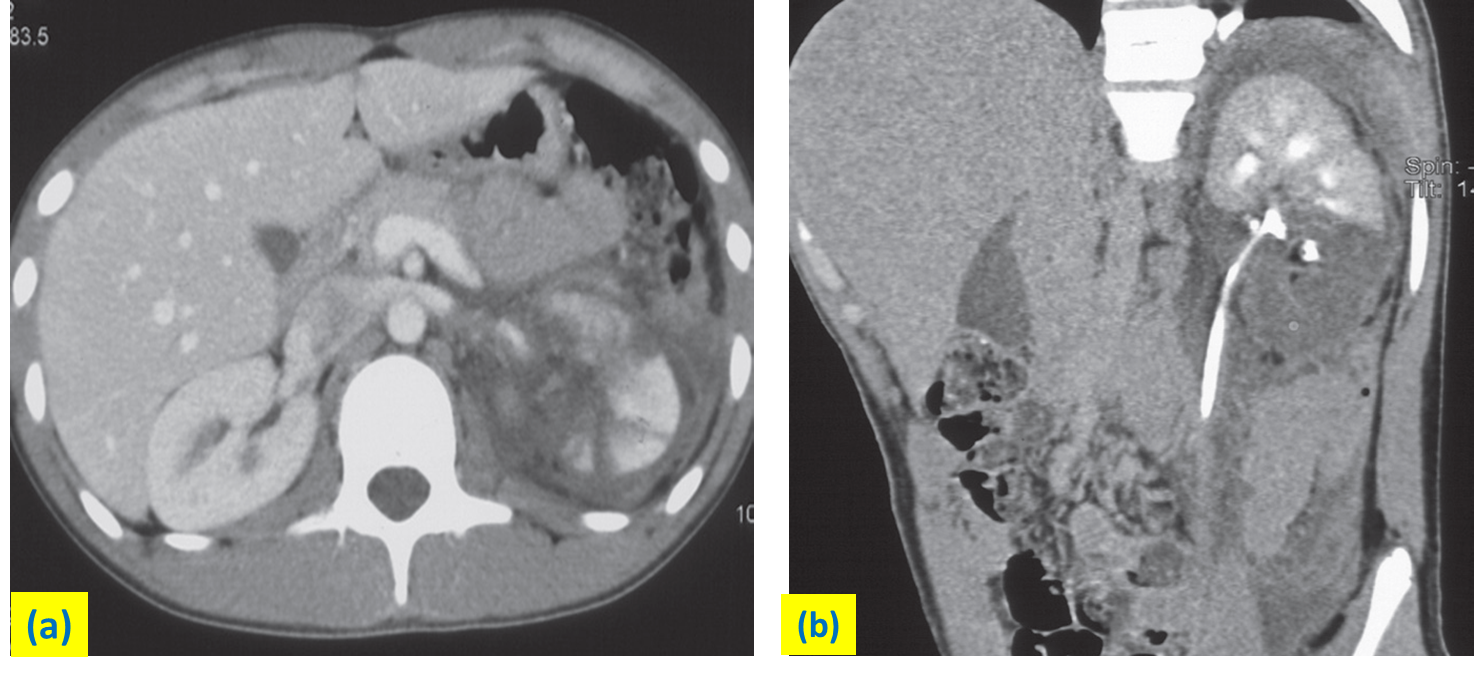
(a) Axial CT demonstrating reduced perfusion in the midpole of the left kidney. Fluid is seen in the perinephric tissues.
(b) Delayed oblique sagittal reformat demonstrating contrast in the collecting system and confirming no leak of contrast.