Dr. Alaidaroos
Presentations
ILOs
Anatomy: anterior abdominal wall, inguinal & femoral canal Rectus sheath hematoma & Desmoid tumor: aetiology, clinical presentation & management Groin & Abdominal wall hernias: aetiology, risk factors, presentation, complications & management
Hesselbach Triangle
Weak spot in anterior abdominal wall through which direct hernia appears.
- Medial: Outer border of rectus abdominis
- Lateral: Inferior epigastric vessels
- Below: Medial part of inguinal ligament
- Floor: Fascia transversalis
- Traversed by medial umbilical fold; (Obliterated Umbilical Artery)
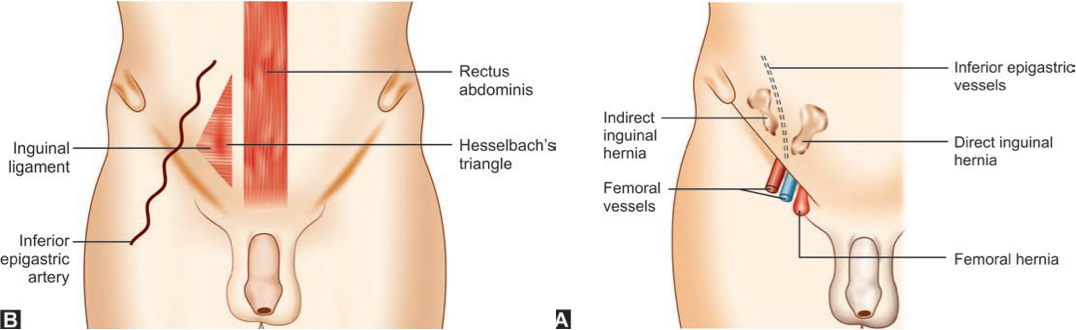
- Traversed by medial umbilical fold; (Obliterated Umbilical Artery)
Inguinal Canal (House of Bassini)
- 3.75 cm length
- Extends from deep ring to superficial ring
- Deep ring is a semioval opening in the fascia transversalis
- Superficial ring is a triangular opening in the external oblique aponeurosis
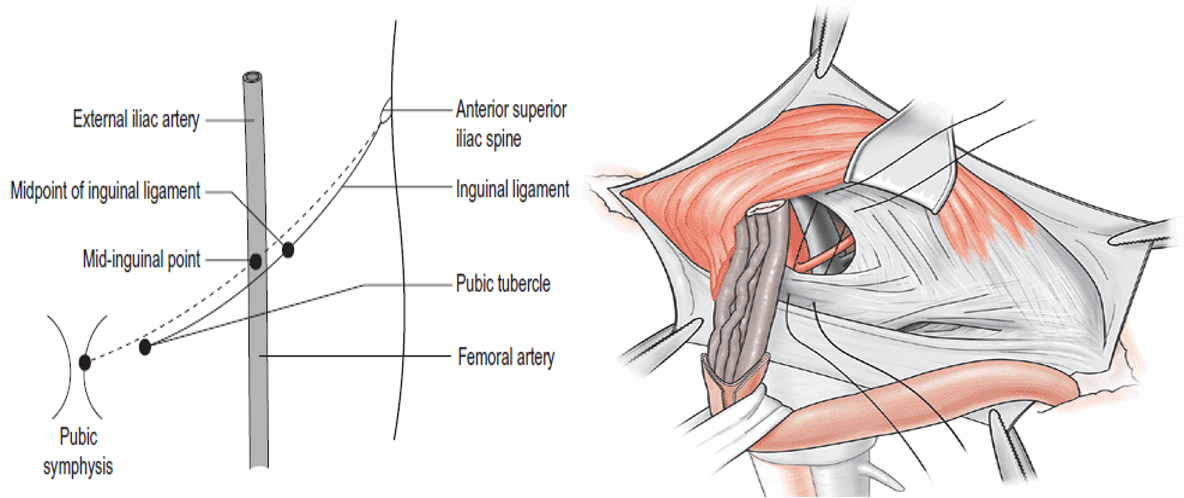
Landmarks
- Deep ring: Half inch above mid point of inguinal ligament (Between anterior superior iliac spine and pubic tubercle) (Remember here: Femoral artery is palpated at Mid inguinal point between ASIS and symphysis pubis)
- Superficial ring: Just above pubic tubercle
- Saphenous opening: 4 cm below and lateral to pubic tubercle
Contents of Inguinal Canal
- Ilioinguinal nerve
- Spermatic cord in male, round ligament in female
round ligaments v spermatic cord
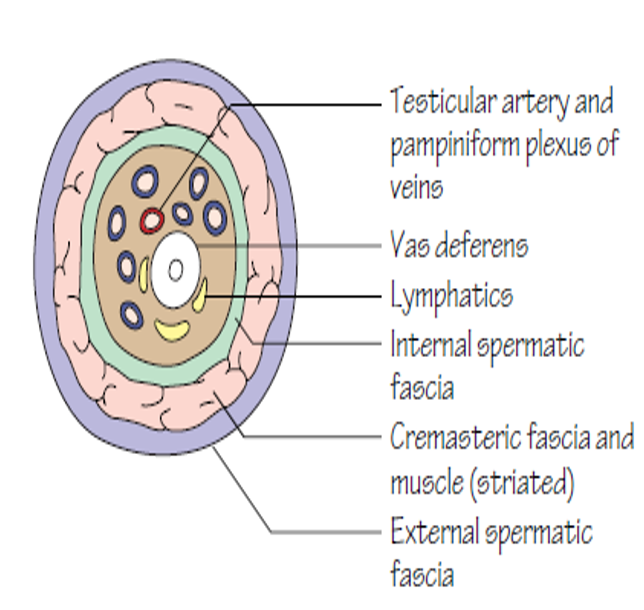
Contents of spermatic cord
- Arteries:
- Testicular Artery
- Artery of Vas
- Artery to Cremaster
- Veins:
- Pampiniform plexus of veins
- Veins corresponding to Arteries
- Lymphatics of testis
- Testicular plexus of sympathetic nerves
- Genital branch of genitofemoral N
- Vas deferens
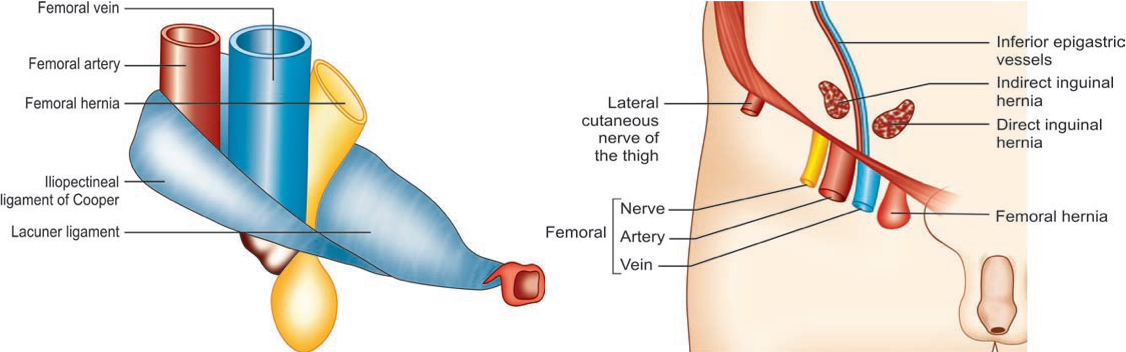
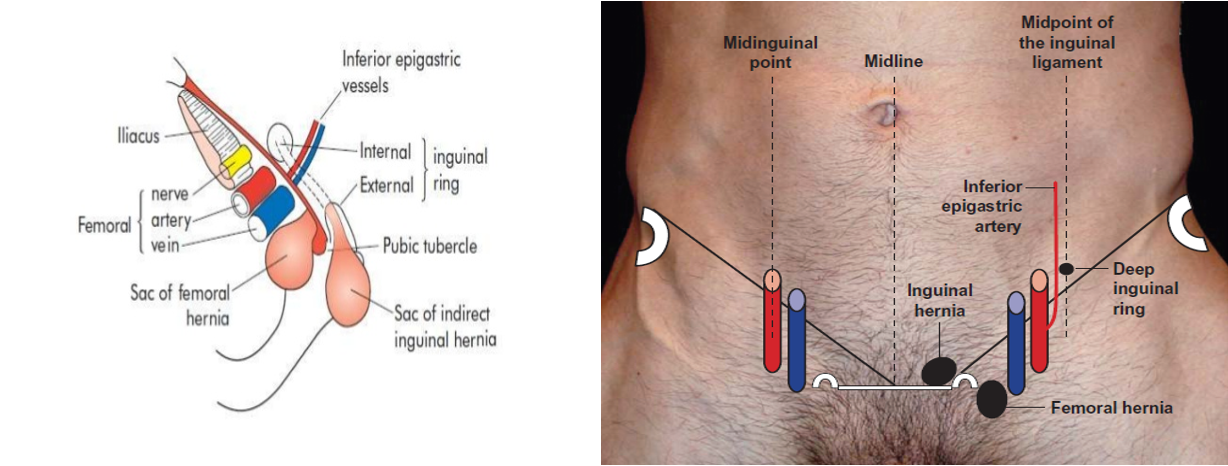
Femoral canal: 2 x 2 cm size
- Medial compartment of femoral sheath
- Base: Femoral ring
- Bounded:
- Anteriorly: inguinal ligament
- Posteriorly: cooper’s ligament
- Medially: lacunar ligament
- Laterally: femoral vein
- Contents:
- Cloquet’s node
- Lymphatics
- Areolar tissue
- Other names:
- Inguinal ligament: Poupart’s
- Lacunar ligament: Gimbernat’s
- Iliopectineal ligament: Cooper’s
- Saphenous opening: Fossa ovalis