History
Framework
- Demographics (Name, Age, Gender, Nationality, Martial, Residency)
- Chief of complaint (Cause of hospitalization + days)
- HOPI (OPERATES NON PAIN | SOCRATES PAIN)
- B-Symptoms
- Systemic Review
- Past history (medical, surgical, medication, allergies, family, social)
- summary
- differential + justify differential
- investigations - appropriate
- treatment - suggestive
Introduction, explain, Permission, Assure privacy, chap. Greetings im Mohammed 5th year medical student; could you tell me your name..“amm ahmad”. im here to take your full history, may i proceed? =-
call nurse, assure privacy.
1) Demographics
Age
- Young Age—indirect
- Old Age—direct
Sex
- Most common hernia in females—indirect inguinal hernia & obturator hernia
- Most common hernia in males—indirect
- Femoral hernia most common among—females
- Direct hernia never occurs in females and children
Occupation: Most common in strenuous labor, Weight lifters.
residency, nationality, martial status…
2) Chief of Complaint
…
3) HOPI
OPERATES OR SOCRATES
I- Site
- From groin to scrotum (hernia)
- From scrotum to groin (hydrocele and varicocele)
II- Onset/Progression
Duration Suddenly/gradually, When first noticed?
III- Character
IV- Radiation
V- Associated Symptoms
Associated with pain: Usually painless, Any other lump/ swelling
Pain in inguinal hernia is usually in the region of the umbilicus due to drag in the root of mesentery as bowel enters the sac
Para-umbilical associated with right inguinal hernia consistent with a generalised collagen disorder
VI- Timing/Episode
- Does it disappear completely, does it become smaller/ larger?
VII- Relieving/ Exacerbating Factors
-
Aggravating factors:
- On straining
- On standing
- On coughing
-
Relieving factors:
- By lying down
- Manually by himself
VIII- Severity
1-10 Grading with Limitations - cant walk, work, or think
4) B Symptoms
…
5) Systemic Review
- Difficulty in micturition
- Difficulty in defecation
6) Past Hx
Past medical / Surgical / Family
- Chronic bronchitis/asthma/TB/DM/HTN/IHD/TB
- Previous surgery
- History of connective tissue disorders in family.
History of appendicectomy: Ilioinguinal or iliohypogastric nerve if damaged by grid iron incision or during keeping the drain; Direct Hernia Occurs
If ilioinguinal nerve is cut in the inguinal canal, direct hernia never occurs Because the nerve supplies the abdominal muscles before entering the cana
Medications / Allergies
Social im going to ask some specific question to reach to diagnosis, may i?
-
Occupation,
-
Travel,
-
kids,
-
smoking
- ⇒ leads to chronic bronchitis = cough = prone hernia
- Collagen deficiency occurs in smokers.
-
alcohol,
-
drugs,
-
sexual activity
7) Summary
8) Differential, Impression, most likely diagnosis
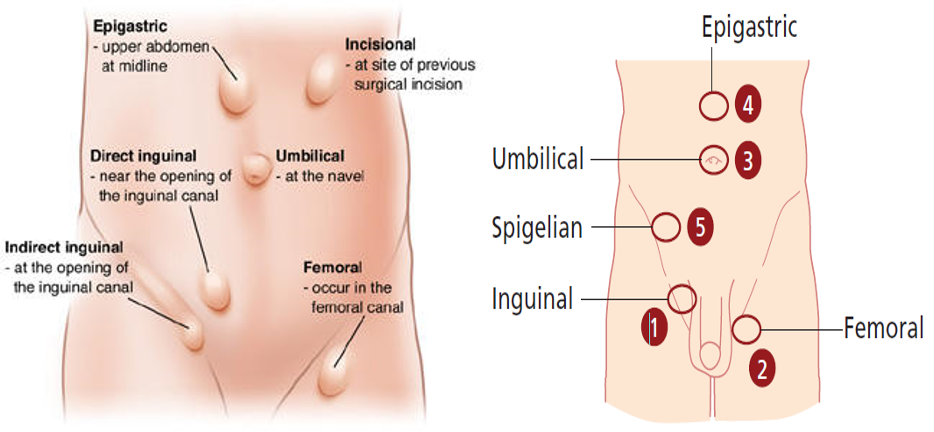
- Groin hernias: Inguinal (direct/ indirect) , femoral hernia
- Umbilical & Para-umbilical hernia
- Epigastric hernia
- Incisional hernia
9) Investigations
I. Routine
- Hemoglobin
- Bleeding time/Clotting time
- Total count, differential count, ESR
- Urine—albumin, sugar deposits
- Blood—urea, sugar
- Blood grouping/typing—for irreducible hernia/huge hernia
II. Anesthetic Purpose
- X-ray chest (Chronic TB, Asthma—precipitate hernia)
- ECG all leads
III. USG Abdomen and Pelvis
- In old age group—to find benign prostate hyperplasia calculate post-voidal residual urine. If >100 ml it is significant
- To find any mas
10) Treatment Plan
A. Treat the precipitating cause of hernia first e.g.
- Benign prostate hypertrophy
- Tuberculosis
- Stop smoking
B. Conservative management is indicated only in cases of very old man with direct hernia; since there is no chance of obstruction.
C. Truss : is not curative for hernia.
SURGERIES FOR HERNIA
- Indirect Hernia: Adult - Herniotomy + mesh repair, Children- Herniotomy
- Direct Hernia: No sac excision, sac reduced
Examination
-
WIPER
- Wash hands
- Introduce
- Right side of bed
- Explain Procedure
- Permission for examination
- Position & Exposure
-
Preliminary examination
- General Appearance (man, comfortable, comatose, connected device)
- General examination (Vitals, hand/arm/axilla, hair, face, neck, chest, abd,leg)
-
Focused Examination + (correct technique)
- Specific System Exam - IPPA
- Inspection
- Palpation
- Percussion
- Auscultation
- Lesion/Swelling/Ulcer if present - SSSS TTEDC
- Specific System Exam - IPPA
-
Describe correct physical findings
1) WIPER
Exposure | position | privacy | Ask for vitals
- W ash hands (before and after)
- I ntroduce yourself to the patient and seek his or her consent
- P osition the patient correctly.
- E xpose the patient as needed (e.g. ‘Please take off your shirt for me now, if that is all right’)
- R ight side of the bed
Position & Exposure Mid chest to mid thigh
Position standing at first, then supine - examine both sides
Intro
Greet, Introduce (5th year med), assure privacy (curtain, nurse), explain procedure, position (mention good position - supine semisitting) & exposure (from midchest to midthigh - cover genatelia)
2) General Appearance
- Conscious and alert
- features
- connected devices
elderly male with good build lying comfortable to be - connected to cannula - not connected oxygen. (note general exam findings)
“Now i will do focused examination after general apperance, should i do general examination?“
3) General Examination
dont touch patient until needed
-
Hand: organized explaination from distal to proximal
- Clubbing -
- Capillary refill
- Pulse:
- water hammer pulse
-
Vital signs
-
Face & Neck:
-
Abdomen:
- Mass abdomen
- Malgaigne’s bulgings
- Ascites
-
Lower Limb: Edema - thumb
4) Focused Examination
Hernia Focused Examination
Inspection
Standing position
- Groin swellings:
- Does it extend down to scrotum?—Inguinoscrotal
- Is testis separate from swelling?
- Site:
- Femoral—below and lateral to pubic tubercle
- Inguinal—above and medial to pubic tubercle
- Size
- Shape:
- Pyriform—indirect
- Hemispherical—direct
- Retort—femoral
- Extent
- Surface
- Skin over the swelling
- Visible peristalsis
- Cough impulse
- Draining lymph nodes
- Penis
- Urethral meatus
- Opposite scrotum
Palpation
Ask patient if there is any pain before proceeding.
- Temperature
- Tenderness
- Site
- Size
- Shape
- Extent
- Surface
- Skin over
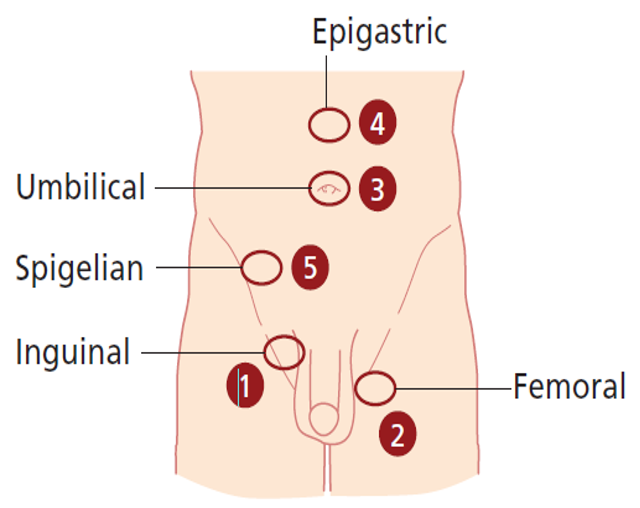
- Get above the swelling: (hernia vs scrotal swelling)
- Is testis separate from swelling?
- Get above the swelling is a classical feature of hydrocele
- Cough impulse
- Consistency:
- Soft elastic—intestine
- Doughy granular—omentum
- Reducibility:
- a. Intestine: Last part is easy to reduce; Initial part is difficult to reduce; gets reduced with gurgling sound.
- b. Omentum: First part easy to reduce, last part is difficult because omentum adheres to fundus of sac.
- Direction of reduction of hernia
- Direct hernia—directly backwards
- Indirect—goes upwards, backwards and laterally
- Ring invagination test
- Only test in hernia; done in lying position.
- Prerequisite:
- ––Swelling should be reducible
- ––Lax of skin should be there for invaginating (so this test could not be done in females)
- Procedure
- Reduce the swelling.
- For right side, invaginate with right little finger into the superficial ring.
- Rotate the little finger medially so that the pulp faces medially.
- Note the direction of entry and site of impulse.
- Look for:
- Strength of superficial ring: Normal ring admits only the tip
- Site of impulse:
- Pulp—direct
- Tip—indirect
- Deep ring occlusion test: (only after complete reduction of hernia)
- After reducing the contents, patient in standing position, occlude the deep ring with thumb. Ask the patient to cough.
- If swelling appears - Direct
- Does not appear – Indirect
- Fallacy of deep ring occlusion test (When will you get the swelling even though it is an indirect hernia by deep ring occlusion test?)
- A. Pantaloon hernia
- B. Wide deep ring (Occlude in such cases with index and middle finger together)
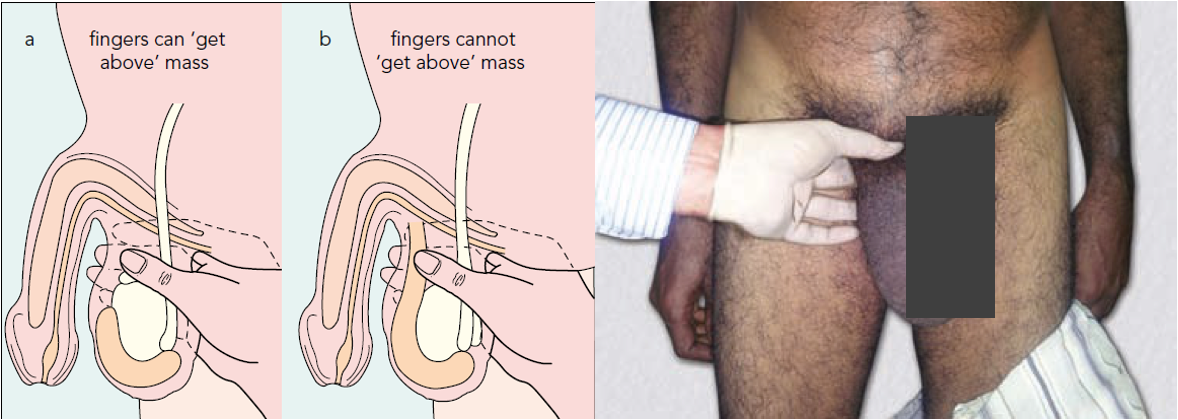
Ring invagination test
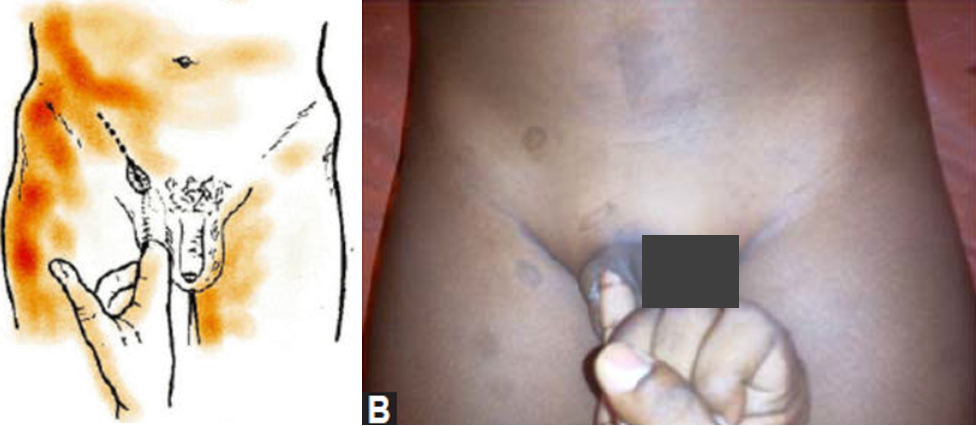
Deep ring occlusion test
Percussion
- Enterocele: Resonant
- Omentum: Dull
Auscultation
Peristaltic sounds occasionally heard.
5) Complete examination with
-
Testis: ‘Traction Test’ to find whether the inguinal swelling is an Encysted Hydrocele of Cord.
-
Epididymis.
-
Penis:
- Phimosis
- Penile strictures
- Pinhole meatus
-
Regional nodes.
-
Opposite groin.
-
Per-rectal Examination To Rule out:
- Benign Prostate hypertrophy—micturition difficulty
- Malignant obstruction
- Chronic fissure—constipation
6) Summarize Findings, Thank patient
…
Other
Each type can be:
- Reducible: may result in adhesion resulting in irreducible (longstanding)
- Irreducible/ incarcerated;
- Complicated: Obstructed; bowel & strangulated; artery veins
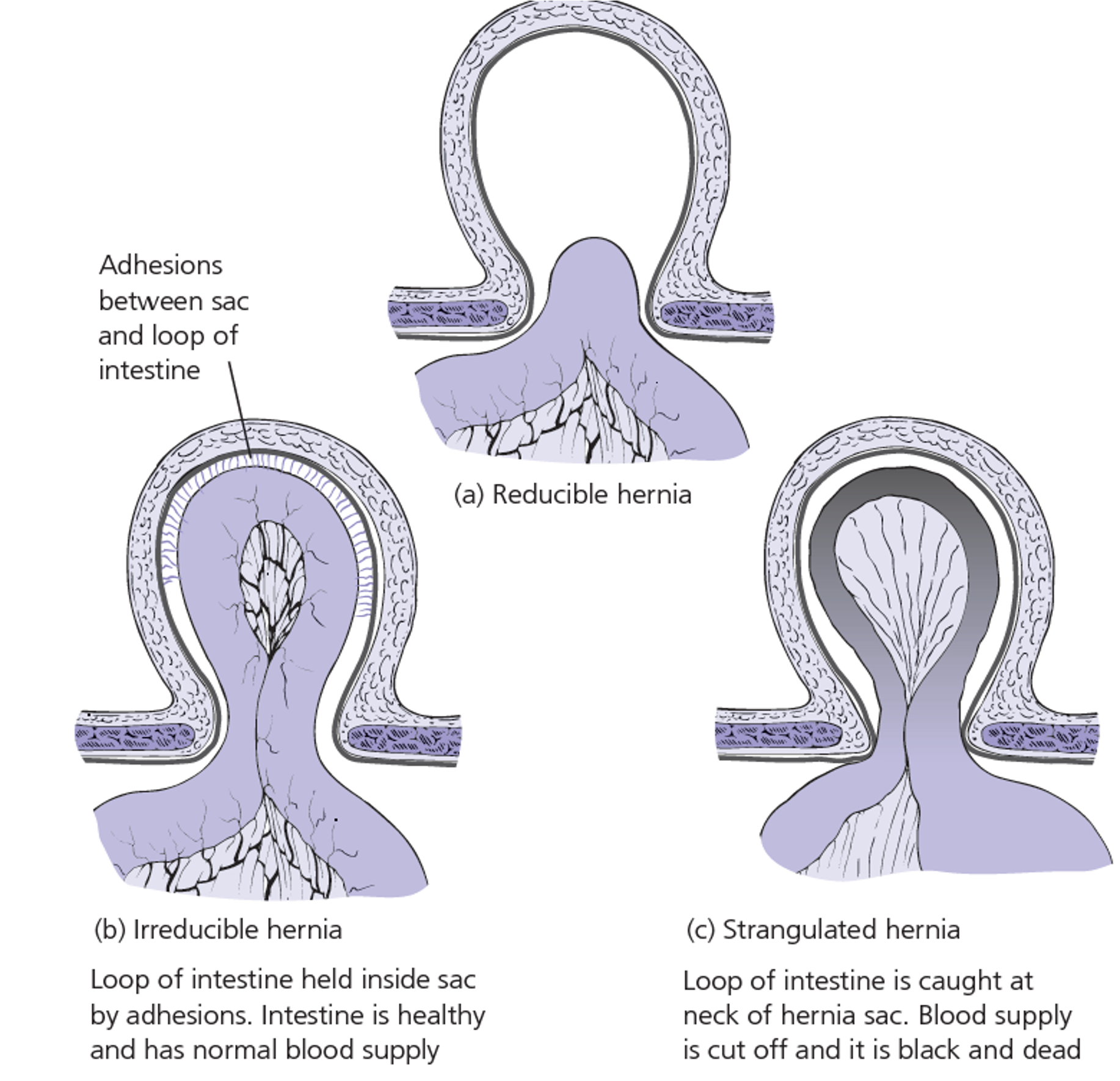
Complications of Hernia
- Incarcerated: Hernia contents are irreducible due to adhesion. May obstruct or strangulate.
- Obstructed: Irreducible hernia presenting with intestinal obstruction.
- Strangulated: When blood supply to the contents is jeopardized in an irreducible hernia.