Adverse Effects of Antimicrobial Agents
Overview
The adverse effects associated with the use of antimicrobial agents include multiple categories ranging from mild to severe reactions.
1. Hypersensitivity or Allergic Reactions
Manifestations include:
- Fever
- Skin rash
- Arthralgia
- Cholestatic jaundice
- Hemolysis
Serious reactions:
- Agranulocytosis
- Bone marrow aplasia
- Anaphylactic reaction
Note: Most importantly seen with penicillin which requires confirmation
2. Resistance
Development of antimicrobial resistance is a significant adverse effect that impacts treatment efficacy and public health.
3. Superinfection (Opportunistic Infection)
Definition: Reactions related to alterations in normal body flora
- Occurs when antimicrobial therapy disrupts the normal bacterial balance
- Allows opportunistic organisms to proliferate
- Examples include Pneumocystis and other opportunistic infections
4. Vitamin B Complex Deficiency
Cause: May follow the use of antimicrobials, especially broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Due to inhibition of bacterial flora that normally synthesize these vitamins
- Particularly common with prolonged broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
5. Direct Toxic Reactions (Organ Toxicity)
Characteristics:
- Result from high doses or drug interactions
- Can affect multiple organ systems
Target organ systems:
- Hematopoietic system
- Liver
- Kidney
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Nervous system
- Cardiovascular system
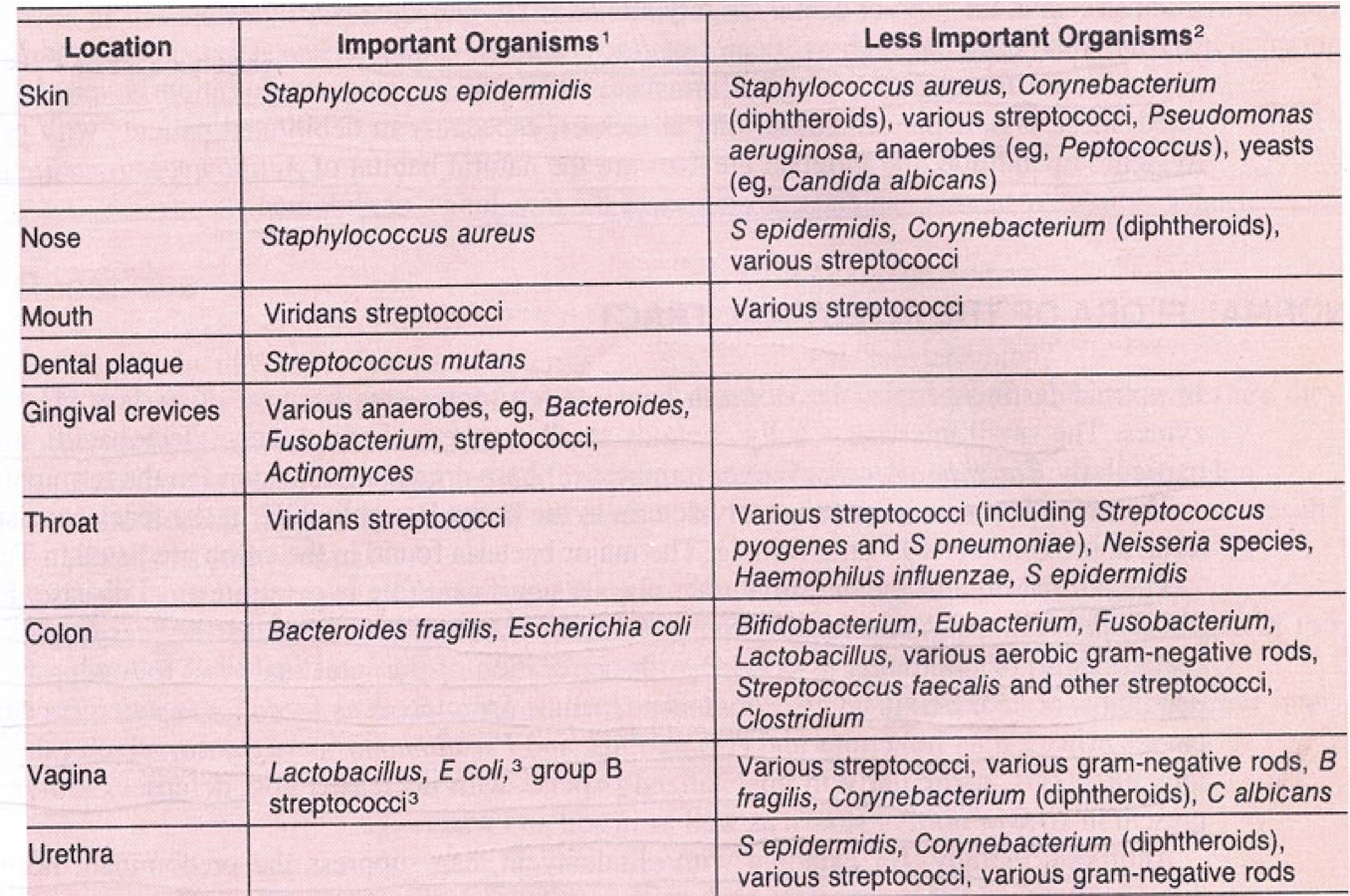
Normal Bacterial Flora
Understanding the normal bacterial flora is essential for recognizing when antimicrobial therapy may cause disruption leading to adverse effects.