Definition: a viral illness in which the symptoms of rhinorrhea & nasal obstruction are prominent.
- Rhinitis,
- rhinosinusitis,
- (rhinoconjunctivitis)
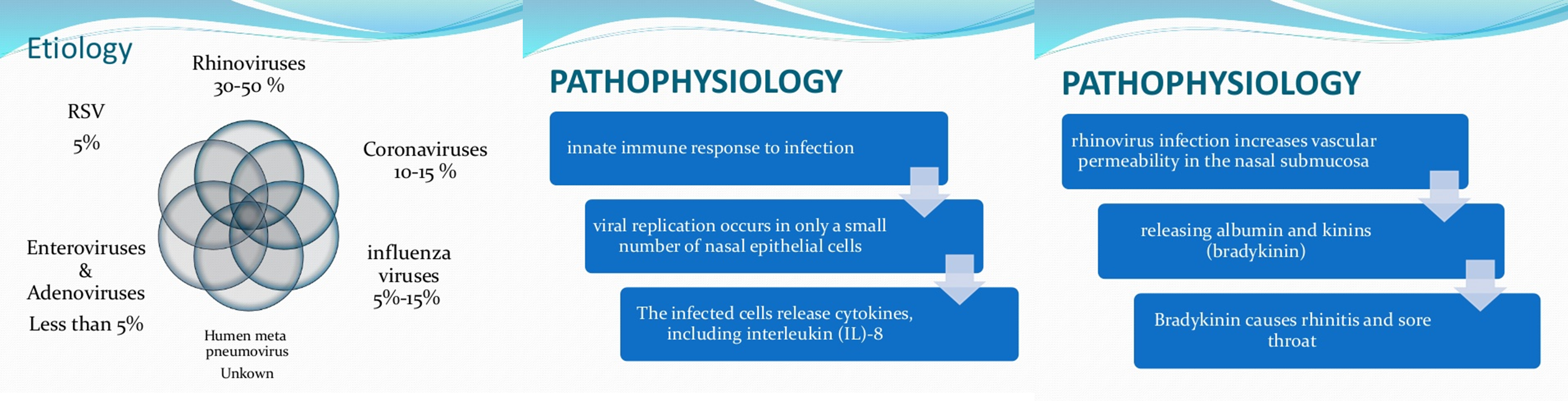
EPIDEMIOL0GY
Colds occur year-round, but the incidence is greatest from the early fall until the late spring.
⇐— Y
Clinical manifestation
The onset of 1-3 days after viral infection.
sore or “scratchy” throat, followed closely by nasal obstruction and nasal discharge
Systemic manifestations:
- Fever, chills, restlessness, bone aches, headache and anorexia
- The usual cold persists for about 1 week, although 10% last for 2wk.
Symptomatic treatment:
-
antiviral ttt ??
-
nasal decongestants: Effective topical adrenergic agents such as xylometazoline, oxymetazoline, or phenylephrine. (Reduced-strength formulations of these medications are available for use in younger children, although they are not approved for use in children <2 yr old)
-
Anti pyretics e.g -----------paracetamol
-
Cough sedatives
-
supportive: hydration, hot drinks…..etc
Children should never take ASA (acetylsalicylic acid) for a viral infection of the respiratory tract. - Reye’s Syndrome
Differential diagnosis :
- Infections: Sinusitis, pharyngitis
- Allergy: allergic rhinitis
- Others……………….
Complications: Y
URT: otitis media, sinusitis and periorbital cellulitis …. LRT: laryngeobronchitis, bronchiolitis and asthma attacks