Ankylosing spondylitis is a spondyloarthropathy, which as the name suggests, results in fusion (ankylosis) of the spine and sacroiliac (SI) joints, although involvement is also seen in large and small joints.
X-ray
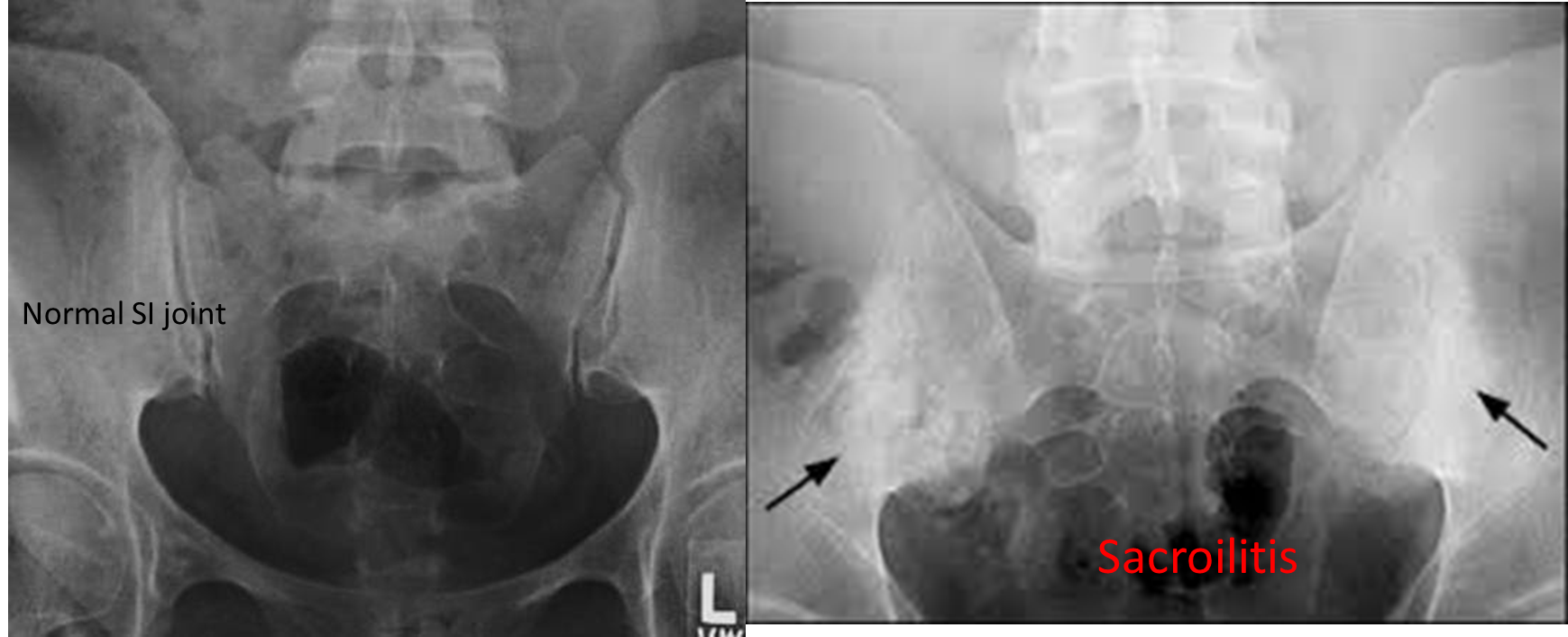
A. Sacroiliac joints (PA view) Characteristic findings (usually symmetrical) Signs of sacroiliitis; first sign: - Erosion and sclerosis of the sacroiliac joints
- Ankylosis: fusion of the articular surfaces
B. Spine (AP and lateral views) Characteristic findings
- Loss of lumbar lordosis: abnormal straightening of the spine
- Ankylosis of costosternal and costovertebral joints
- Dagger sign: A radiodense line running through the center of vertebral bodies on AP view Caused by ossification of vertebral ligaments
- Bamboo spine: seen in later stages and is caused by the following Ossification of outer fibers of the annulus fibrosus resulting in ankylosis (fusion) of intervertebral joints
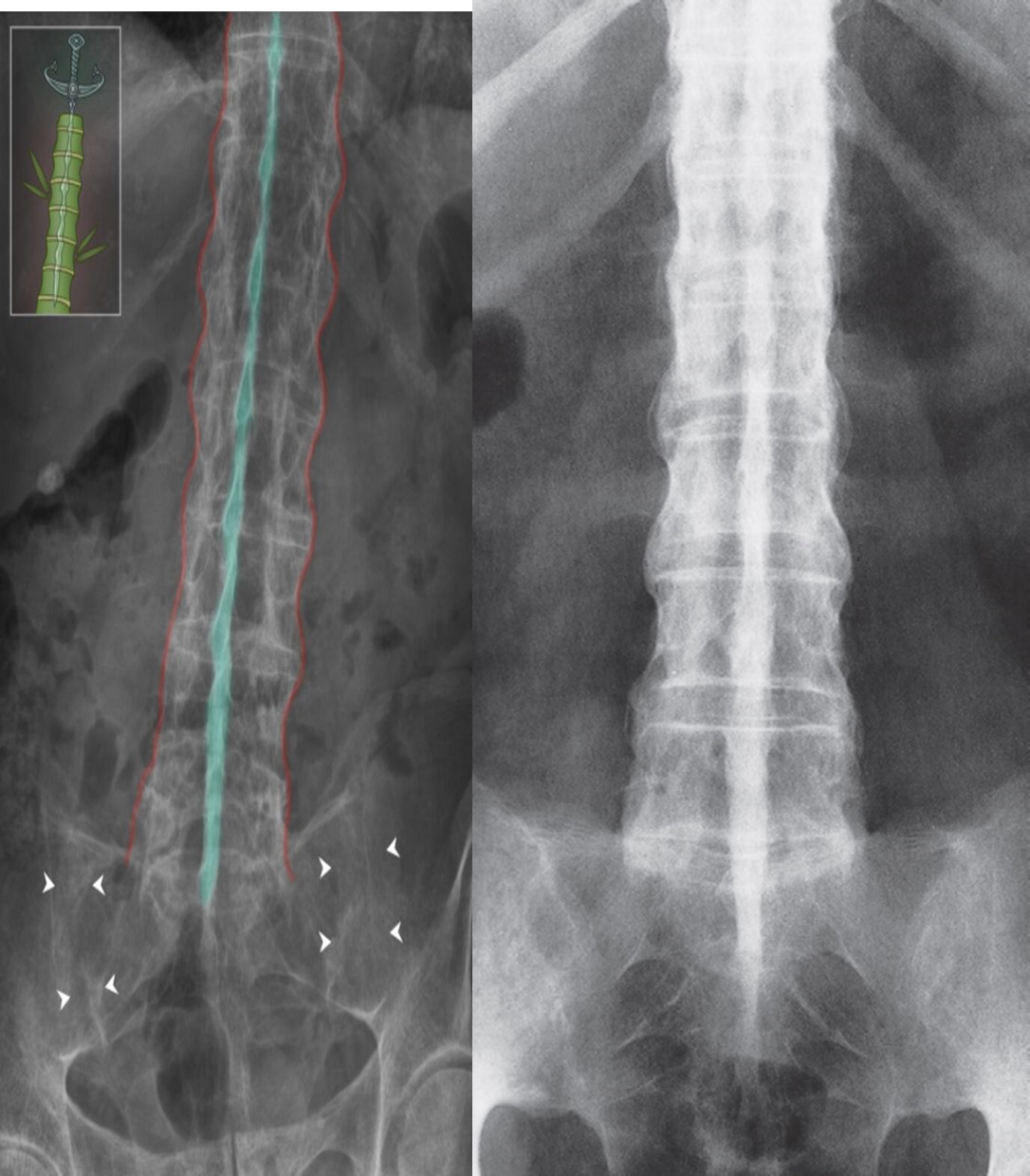
Bamboo spine
Bamboo spine and dagger sign in ankylosing spondylitis
X-ray lumbar spine (AP view)
Marginal syndesmophytes formed by ossification of outer fibers of the annulus fibrosis have caused the spine to resemble a bamboo stem (so-called “bamboo spine”;.
Additional ossification of supraspinous and interspinous ligaments has produced a dense line (dagger sign; green overlay) projecting through the vertebrae. Fusion (ankylosis) across the sacroiliac joints (indicated by arrowheads) can also be seen.