Case 1 Z
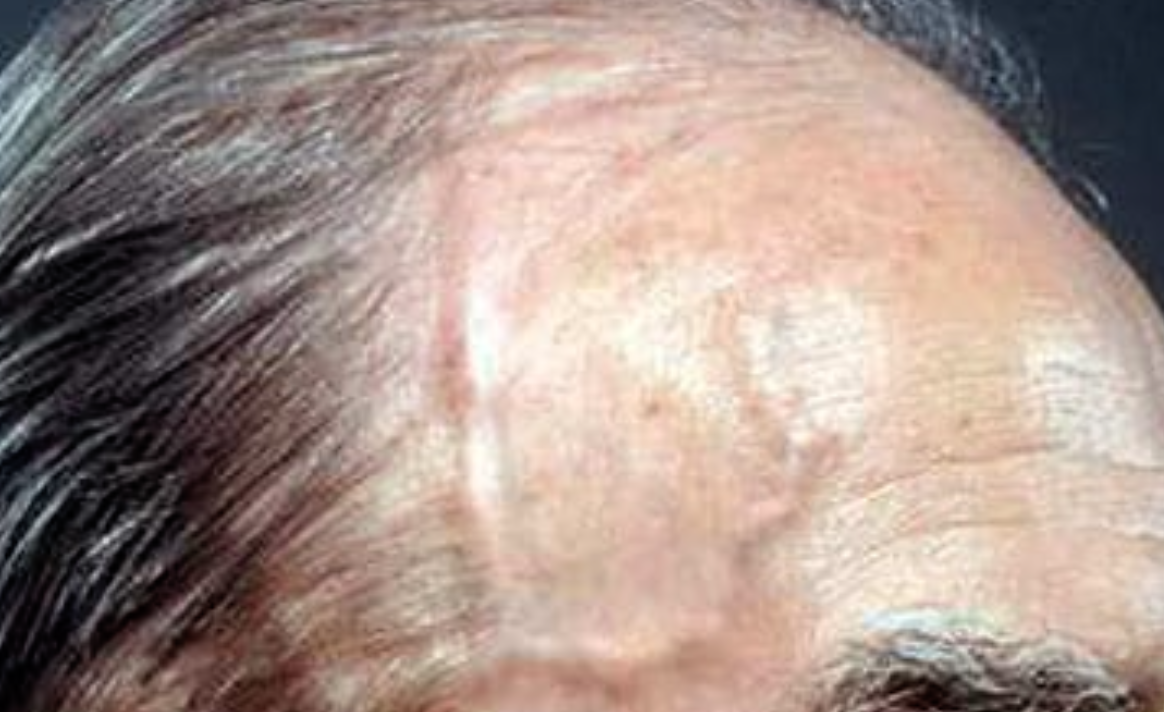 A 70 years old male presented with a new onset headache and loss of
vision for 72 hrs. He also complained of jaw claudication on chewing and
talking.
A 70 years old male presented with a new onset headache and loss of
vision for 72 hrs. He also complained of jaw claudication on chewing and
talking.
-
Mention 3 expected features of the temporal artery which may be present in this condition?
- Weak or absent pulse,
- artery tenderness or enlarged and
- beaded appearance of the artery
-
Mention 1 blood test which you will do during diagnostic work up?
- ESR
- CRP
-
Which imaging technique can be helpful in diagnosis?
- Doppler US
-
What will you do for a definitive diagnosis?
- Temporal artery biopsy
-
Mention 2 neurological complications of this condition?
- Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (blindness) - acute vision loss
- Diplopia (due to 3rd, 4th, or 6th nerve palsy)
- New onset Headache
- Jaw claudication
-
What is the treatment of this condition?
- Corticosteroid
Case 2
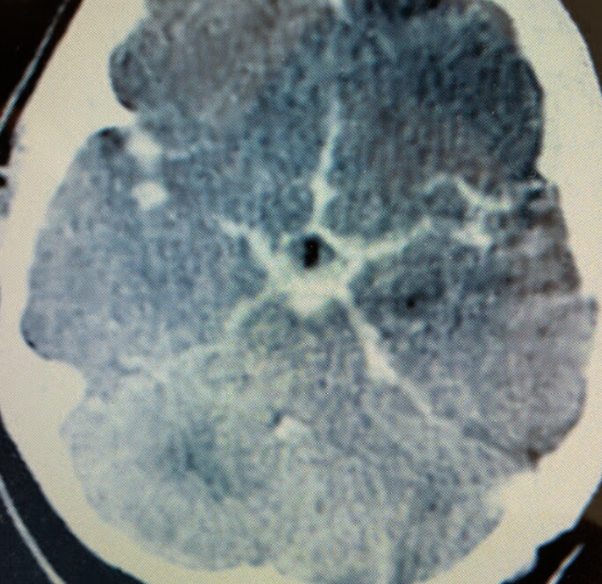 What’s ur finding ?
What’s ur finding ?
Star sign!!
Diagnosis?
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Case 3
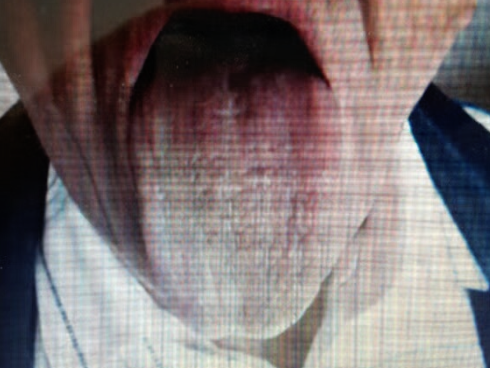 Patient present with slurred speacch and dizziness ?
Patient present with slurred speacch and dizziness ?
A) What is the test u will order ? - CT, MRI, CBC, ECG,
B) What is your diagnosis?
- Stroke / TIA
Case 4
Female pregnant has hypertension + protein urea and recently develop seizures
A) Diagnosis??
Eclampsia
B) Treatment??
C/S
Case 5
 1- Finding:
ptosis both eyes
1- Finding:
ptosis both eyes
2- diagnosis: Myasthenia gravis
Case 6
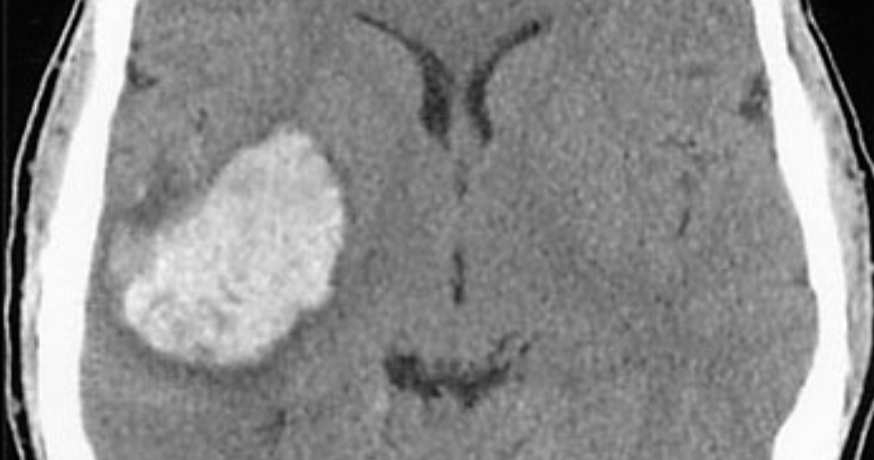 Axial CT scan obtained in a 57-year-old man who presented with left hemiplegia and obtundation.
Axial CT scan obtained in a 57-year-old man who presented with left hemiplegia and obtundation.
Name the site of the lesion?
---basal ganglia---
What is commonest cause of this lesion?
---hypertension---
Case 7 Z
 Describe 2 abnormal findings of the CT?
- a. ---pressure of lf lobe---
- c. ---Hypodense in left lobe---
Describe 2 abnormal findings of the CT?
- a. ---pressure of lf lobe---
- c. ---Hypodense in left lobe---
Name vascular territory involved? - ---medial cerebral artery---
Case 8 Z

- Diagnosis: Cluster Headache
- Treatment: Oxygen mask - Triptans
- Prophylaxis: Lithium
Case 9 Z
 20-year-old male. Severe headache, neck stiffness, photophobia & fever X 1 day. On examination, pain on extending the leg, as shown below:
20-year-old male. Severe headache, neck stiffness, photophobia & fever X 1 day. On examination, pain on extending the leg, as shown below:
Q1: What’s the clinical diagnosis? Meningitis
Q2: Name the 2 most common etiologic agents in this age group (names of bacteria)? Pneumococci, Meningococci
Q3: Which medicine will you give you close contacts of this pt for prophylaxis? Rifampicin | Ceftriaxone in pregnant
Case 10
 Patient complains of unilateral headache off & on since 3 months. She also gets nausea and vision problems just before the headache. Clinical diagnosis is migraine.
Patient complains of unilateral headache off & on since 3 months. She also gets nausea and vision problems just before the headache. Clinical diagnosis is migraine.
Q1: Name any 2 medicines used to treat an acute attack of migraine? Selective serotonin receptor, Ergot alkaloids.
Q2: When should you start prophylactic ttt for migraine? When migraine attacks more than 2 per month, when the attack last more than 24 hours.
Q3: Name any 1 medicine which can be used for migraine prophylaxis? Beta blockers, Tricyclic antidepressant.
Case 11
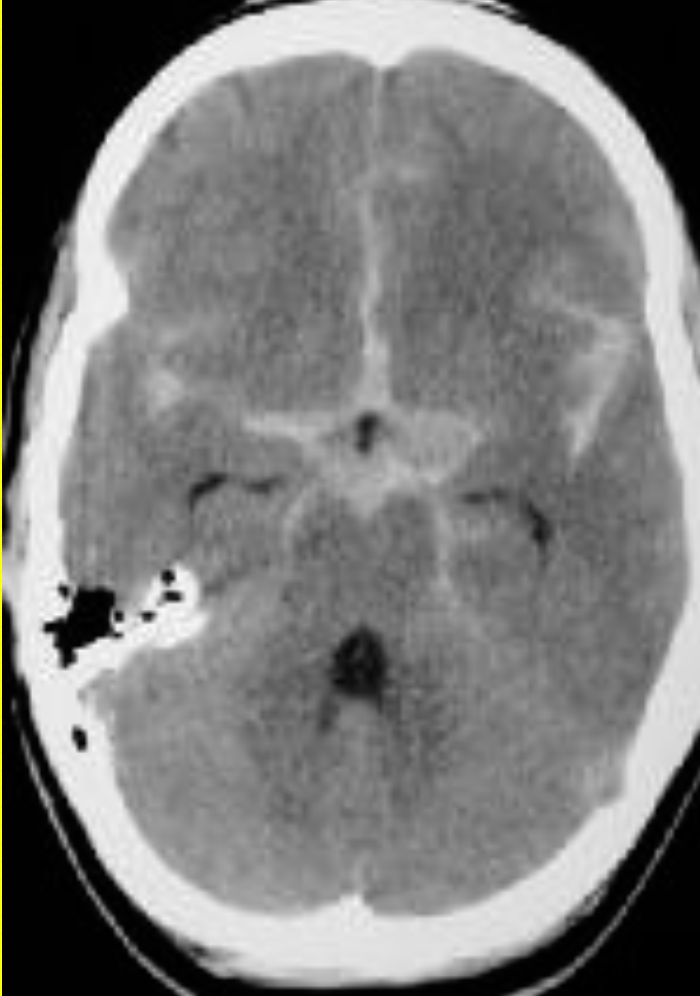
-
Describe 2 abnormal findings of the CT?
a. Left hypodense area occupy the left hemisphere (infarction)
b. Left carinotomy mark -
Name vascular territory involved?
a. Middle cerebral artery
Case 12
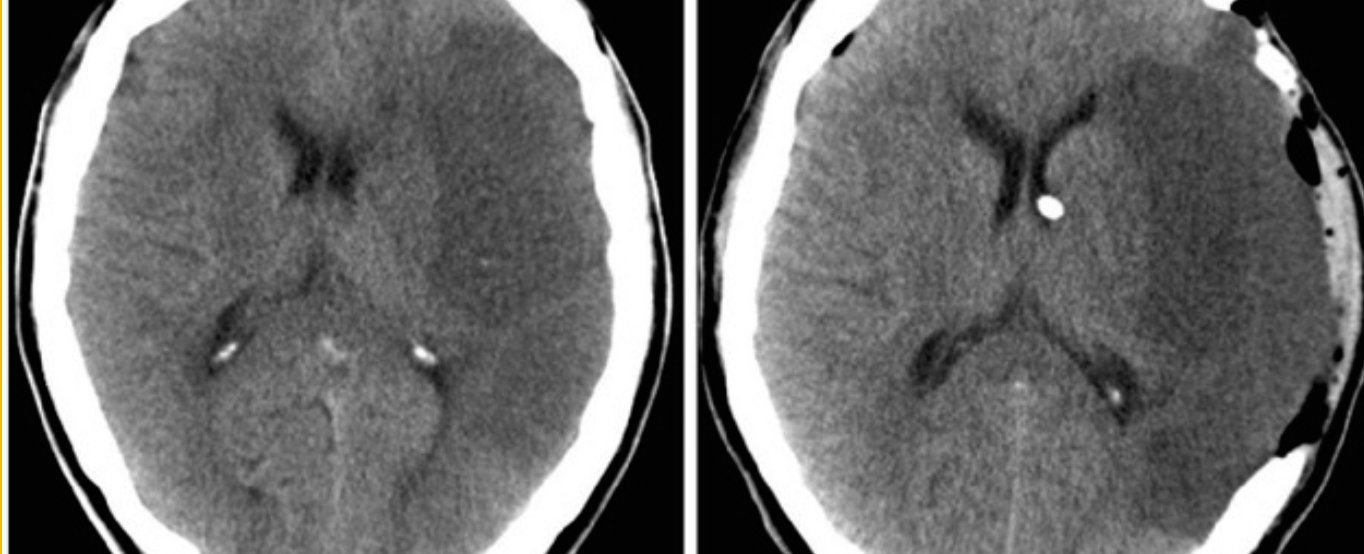
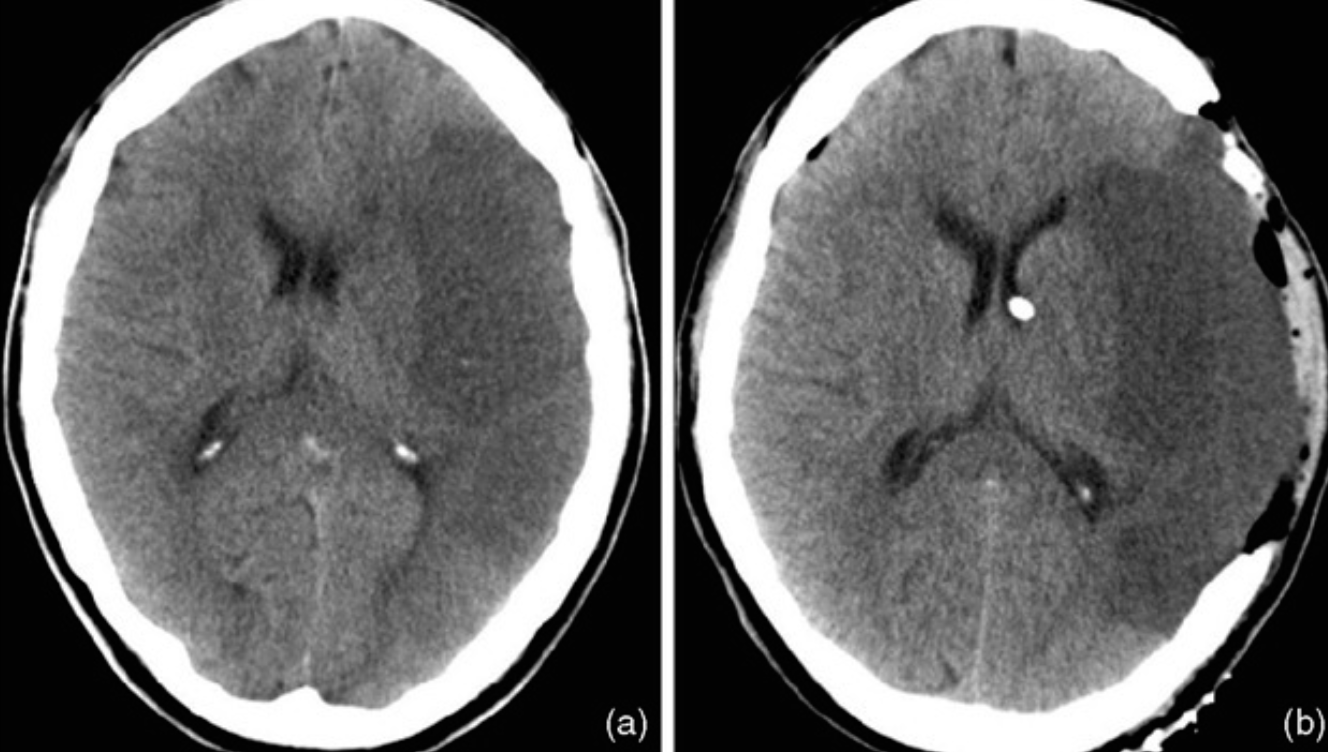
 A 54-year-old woman presented with a sudden onset thunderclap headache and neck pain for 2 days.
A 54-year-old woman presented with a sudden onset thunderclap headache and neck pain for 2 days.
O/E
- Temperature 37°C.
- PR 106 beats/min
- BP 175/106 mm Hg.
- GCS score 14/15
- Pupils- 3 mm diameter, with a light reflex.
- Neck stiffness was ++
-
What is the abnormality in the image shown?
a. Blood mixed with CSF filling the subarachnoid space -
What is the likely diagnosis?
a. Subarachnoid hemorrhage -
What is the abnormality in the image shown?
b. Hyper dinse lesion -
What is the likely diagnosis?
a. Meningitis
58 year old man with slurring of speech and progressive difficulty in swallowing
O/E
Weak jaw and facial muscles, limb weakness with both lower and upper motor neuron signs and tongue muscle atrophy.
-
What investigation is recommended?
Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies, genetic testing for specific motor neuron diseases -
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) or Motor Neuron Disease
Z
A pregnant lady with headache, vomiting and seizure
A 30 year old lady in her third semester of her third pregnancy was noticed to have increased swelling of her feet on her routine antenatal visit.
A week later she developed severe headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and seizure.
Examination
- showed pitting edema legs
- BP was 170/110 mm Hg.
- Urine:
- RBC +
- Protein ++++
-
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pre-eclampsia/Eclampsia -
What is the treatment of choice?
Magnesium sulfate for seizure prevention and blood pressure control, and ultimately delivery of the baby