IM
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
(UTI)
BY: PROFESSOR SALIH BIN SALIH
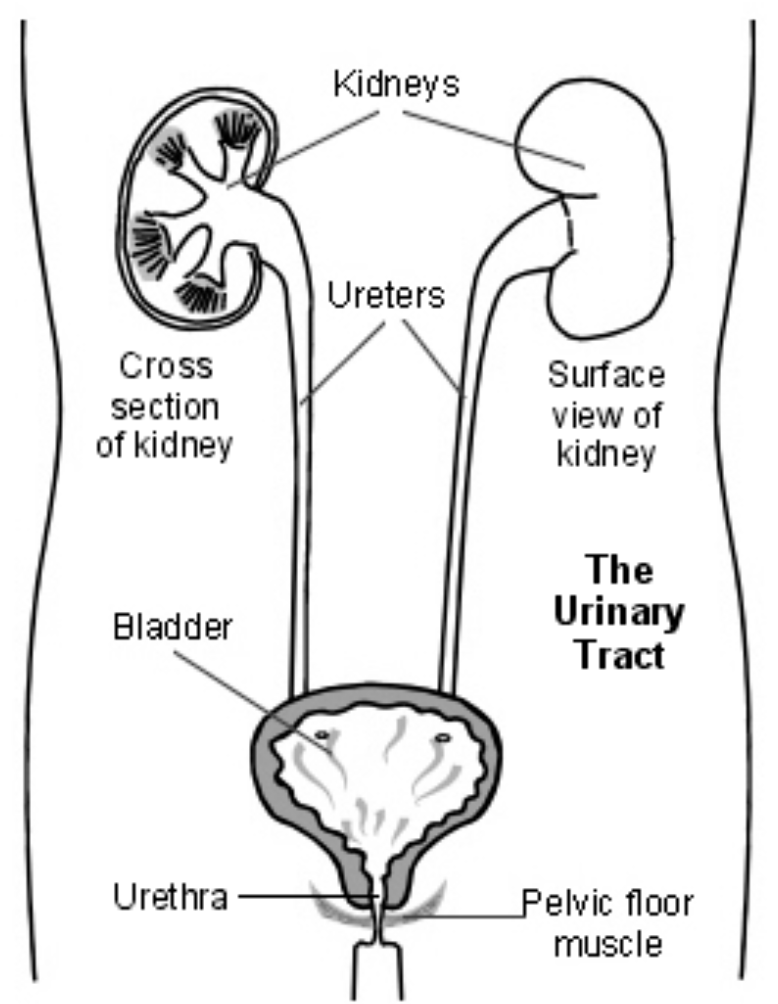
URINARY TRACT
UTI
-
Pyelonephritis (infec. In the kidney)
-
Cystitis
-
Urethritis
-
prostatitis
-
COMMONEST IS CYSTITIS & URETHRITIS, specially in women
-
Cystitis is uncommon in young men.
NATURAL DEFENCES
Factors which prevent infection naturally
- Free flow of urine (no obstruction)
- Acidic urine (acidity kills bacteria)
- Complete bladder emptying (no stasis).
- Remember, stasis of urine is bad.
- Urinary tract epithelium secretes substances which are anti-bacterial.
- ANY BREAK IN THIS CHAIN CAN CAUSE UTI
RISK FACTORS
- Female gender
- Old age (even males)
- DM
- Structural abnormality of urinary tract (causes stasis) eg. diverticulum in the bladder or ureter
- Obstruction of the urinary tract (stone, BPH)
- Pregnancy (causes urine stasis)
- Foley’s catheter
WHAT IS COMPLICATED UTI?
If UTI occurs in the presence of any of these: a) Anatomical abnormality in the urinary tract b) Stones in the tract c) DM d) Poor immunity (eg HIV, patient on long term ______?) e) Presence of Foley’s catheter
If no, then its called an uncomplicated UTI
Pediatrics
Urinary Tract Infections
Most UTIs are bacterial infections of the mucosal surface of the urinary tract.
- The infection may occur anywhere from the urethra to the renal parenchyma.
- A temperature greater than 38.5 °C may help to differentiate acute pyelonephritis from lower tract UTIs.
- The most common organism causing UTI in children is Escherichia coli, accounting for up to 70% of infections.
- Other bacterial pathogens include Pseudomonas aeruginosa (nonenteric Gram-negative), Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, group B Streptococcus (predominantly in neonates).
UTI may involve the kidneys (pyelonephritis), when it is usually associated with fever and systemic involvement, or may be due to cystitis, when there may be no fever. UTI in childhood is important because:
-
Up to half of patients have a structural abnormality of their urinary tract.
-
Pyelonephritis may damage the growing kidney by forming a scar, predisposing to hypertension and to progressive chronic kidney disease if the scarring is bilateral.
Infants
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Lethargy or irritability
- Poor feeding/faltering growth
- Jaundice
- Septicaemia
- Offensive urine
- Febrile seizure (>6 months)
Children
- Dysuria, frequency and urgency
- Abdominal pain or loin tenderness
- Fever with or without rigors (exaggerated shivering)
- Lethargy and anorexia
- Vomiting, diarrhoea
- Haematuria
- Offensive/cloudy urine
- Febrile seizure
- Recurrence of enuresis
A urine sample should be tested in all infants with an unexplained fever >38° C
UTI is the Most Common Cause of Hematuria
Urinary Tract Infection
- Bacteria
FM
Definition of UTI
- A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the kidneys, bladder, or urethra.
- Infectious cystitis is the most common type of UTI, which is caused by a bacterial infection of the bladder.
- Pyelonephritis is an infection of the kidney that often occurs via bacterial ascent.
- Urethritis is an infection causing inflammation of the urethra.
Differential Diagnosis (DD)
- Lower urinary tract infection (LUTI)
- Upper urinary tract infection (UUTI)
- Urethritis
- Urinary tract stones or foreign bodies
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Vulvovaginitis
- Lithium and heavy metal toxicity
if vaginal discharge is present, the probability of bacteriuria (UTI) falls, usually due to candida
Clinical Tips
- Females > males
- UTIs in males ———> STDs
- Old females > young females
- Rare in children ?????
Lower and Upper UTI
- Lower urinary tract infection (LUTI):
- Symptoms suggestive of cystitis (dysuria or frequency without fever, chills, or back pain).
- Upper urinary tract infection (UUTI):
- Symptoms suggestive of pyelonephritis (loin pain, flank tenderness, fever, rigors, or other manifestations of systemic inflammatory response).

Urinary Tract Infection
-
UTI is the most common bacterial infection.
-
Women are more likely to experience UTI than men.
-
Up to 50% of women have had UTI at some time during their life.
-
Recurrent infections are serious. They can cause severe renal disease, even end-stage renal failure.
-
The condition is rare in boys and young men.
-
Invasion and multiplication of microorganisms in the urinary tract.
-
Microorganisms reach the urinary tract via either:
- The urethra “Ascending infection” or
- Bloodstream from a distant source “Hematogenous”.
The majority of urinary tract infections are caused by acending infections from urethra
Risk Factors
-
Aging
-
Females: short urethra, having sexual intercourse, use of contraceptives.
-
Males: prostatic hypertrophy, bacterial prostatitis.
-
Urinary tract obstruction: tumor.
-
Sexual activity
-
Spermicide use
-
Post-menopause: The absence of estrogen (consistent with urogenital atrophy, vaginal atrophy)
-
Positive family history of UTIs
-
History of recurrent UTI
-
Presence of a foreign body
Classification
-
Uncomplicated UTIs include acute cystitis occurring in otherwise healthy, non-pregnant women without functional or anatomical urinary tract abnormalities.
-
Complicated UTIs include infections in patients with functional or structural impairments that reduce the efficacy of antimicrobial therapy.
- The involvement of the kidneys (pyelonephritis) or UTIs occurring in pregnancy are also considered complicated UTIs.
-
Acute UTIs are infections causing acute symptoms in the presence of infected urine.
-
Recurrent UTI is defined as two separate culture-proven episodes of acute UTIs and associated symptoms within 6 months, or more than three UTIs in 12 months.

