Scintigraphy: Reserved for the investigation of abnormal thyroid function and in patients with known thyroid carcinoma.
Radioisotopes study
- A radionuclide is injected or given orally.
- Radioisotope taken up by thyroid/parathyroid
- Radiotracer:
- Oral: e.g: I-123, I-131
- I.V : e.g:Tc-99m pertechnetate
Normal thyroid tissue on nuclear medicine thyroid scan: Normal-sized gland with evenly distributed activity
Normal Thyroid Scan
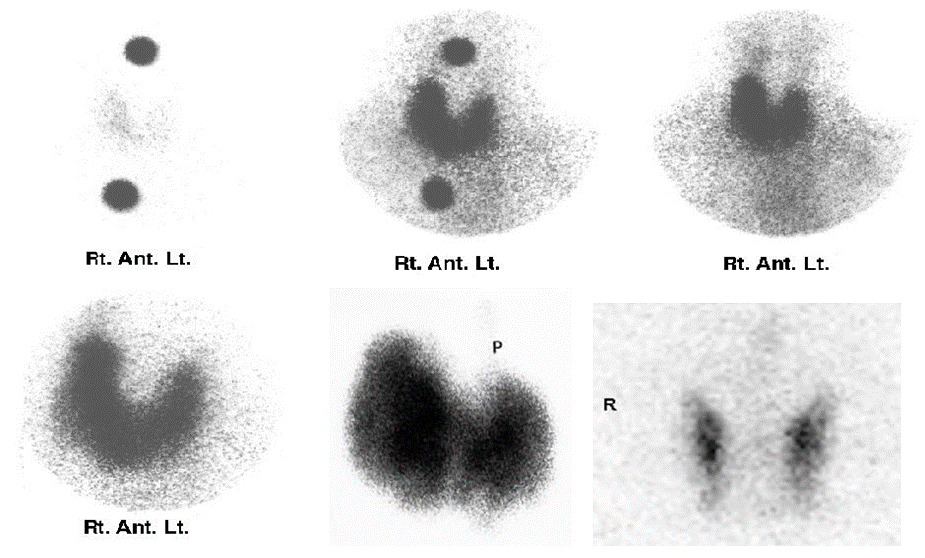
Presentations of Thyroid Scintigraphy
Overview of radioactive iodine uptake patterns in hyperthyroidism
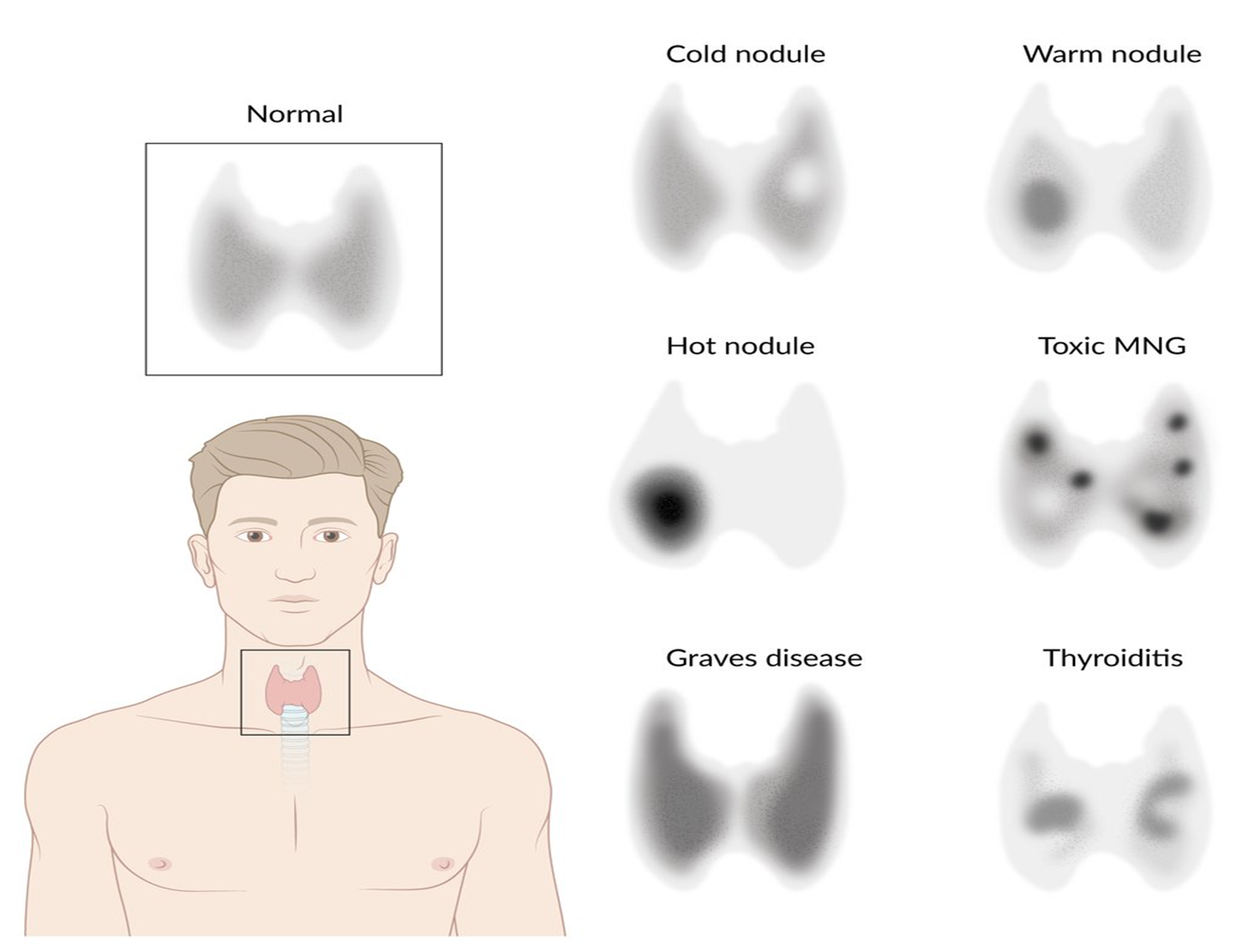
Thyroid scan is usually indicated to see the function
Indications are :
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Graves’ disease
- Hyperplasia
- Functioning nodule
- Thyroid cancer?
- Functioning thyroid or thyroid nodule will show high uptake
- A nodule with high uptake is called hot nodule
- A non functioning thyroid gland or nodule will show low or no uptake
- A nodules with low uptake is called cold nodule
- A hot nodule is usually benign
- A **cold nodule could be malignant **
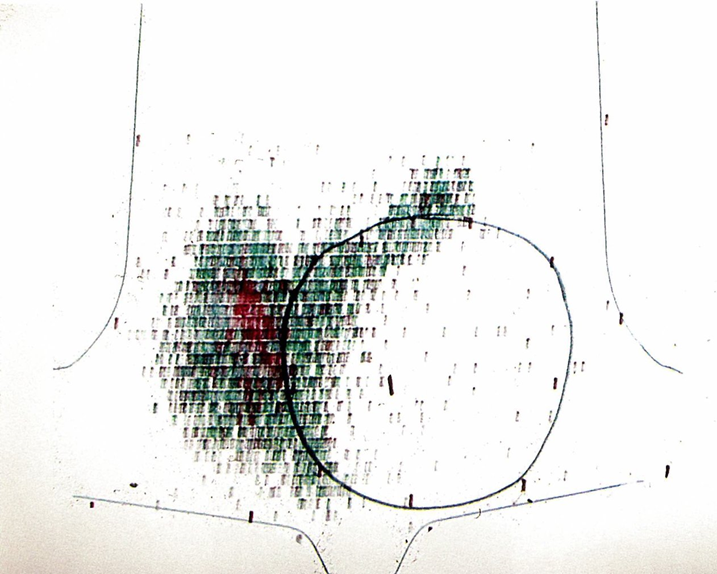
Cold nodule on thyroid scintigraphy
A large cold nodule (black circle) is visible within the left thyroid lobe as an area of decreased radiotracer uptake. Radiotracer uptake by the rest of the thyroid gland appears normal.
A cold nodule is associated with a higher risk of malignancy and warrants further workup (e.g., FNA if there are additional sonographic signs of malignancy on thyroid ultrasound).
Thyroid scan hot nodule
Nuclear medicine thyroid scintigraphy (Tc-99m pertechnetate)
The rounded area in the right thyroid lobe represents a so-called hot thyroid nodule, which shows increased radioisotope uptake compared to the rest of the thyroid gland.
