Definition:
It is a common type of anemia caused by insufficient dietary intake and absorption of iron, and/or loss from bleeding which can originate from a range of sources such as the intestinal, uterine or urinary tract.
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
- As the name implies, iron deficiency anemia is due to insufficient iron.
- Without enough iron, the body can’t produce enough of a substance in red blood cells that enables them to carry oxygen (hemoglobin).
- As a result, iron deficiency anemia may leave a patient tired and short of breath.
AETIOLOGY (IDA)
- Inadequate intake of iron & of food, which enhances iron absorption.
- High intake of inhibitors of iron absorption.
- Hookworm infestation.
- Blood loss (heavy menses & use of aspirin & NSAID).
- High fertility rate in women.
- Low iron stores in newborns.
DIAGNOSIS OF IDA
-
Clinically
- ➢ Symptoms: fatigue, dizziness, palpitations
- ➢ Signs: pallor, smooth tongue, Koilonychia, splenomegaly.
-
Laboratory
- Stainable iron in bone marrow
- Response to iron supplements
Diagnosis of IDA
- Mild anemia may have no or very limited symptoms.
- As hematocrit approaches 30%: fatigue and poor exercise tolerance
- As hematocrit lowers to 25%: tachycardia, palpitations, dyspnea on exertion, and pallor.
- More severe anemia results in:
- lightheadedness
- confusion
- syncope
- chest pain
- A systolic ejection murmur (“flow” murmur).
- Symptoms specific to iron deficiency are rare:
- brittle nails
- spoon-shaped nails
- glossitis
- pica.
- Iron deficiency anemia as a specific diagnosis is determined by laboratory findings, not symptoms.
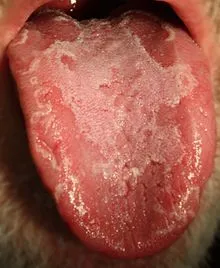
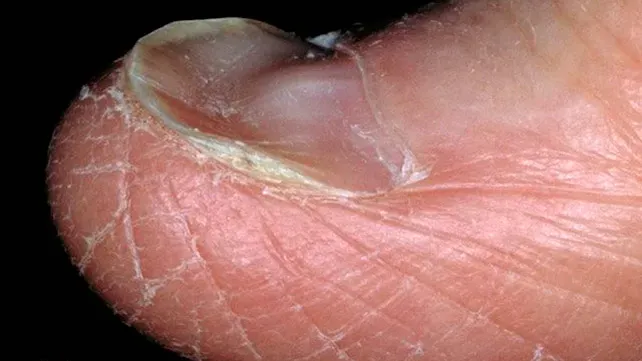
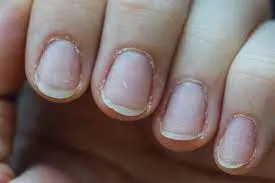
LAB FINDINGS IN IDA
- Microcytic hypochromic anaemia
- Low Hb level (< 11.0 g/dl)
- Low MCV, MCH, MCHC
- Low serum ferritin
- High RDW more than 16% denoting anisocytosis
- High iron binding capacity
Normal Blood Film
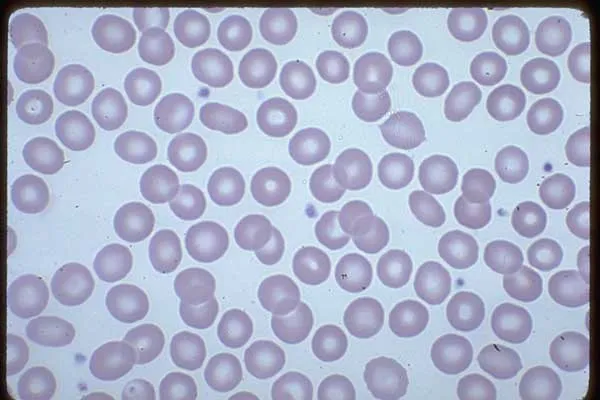
Treatment
- Oral administration of simple ferrous salt:
- 6 - 10 mg / kg / day of elemental iron.
- Parenteral iron is seldom indicated.
- Severely anemic children with HB level
- < 4 gm / dl may be given blood transfusion.
- Dietary education.
- Treat the underlying cause.
Prevention
-
Adequate diet include vegetables rich in iron, meat and vitamins for full term infants.
-
Administration of iron (2 mg/kg) from the age of 2 months for low birth weight and premature infants.