EPIDEMIOLOGY
In K.S.A, more than 25% of the adult population has HTN ( saudi medical journal, 2007)
In the U.S., 29% of the adults have HTN
Incidence is rising throughout the world ( ? Due to lifestyle)
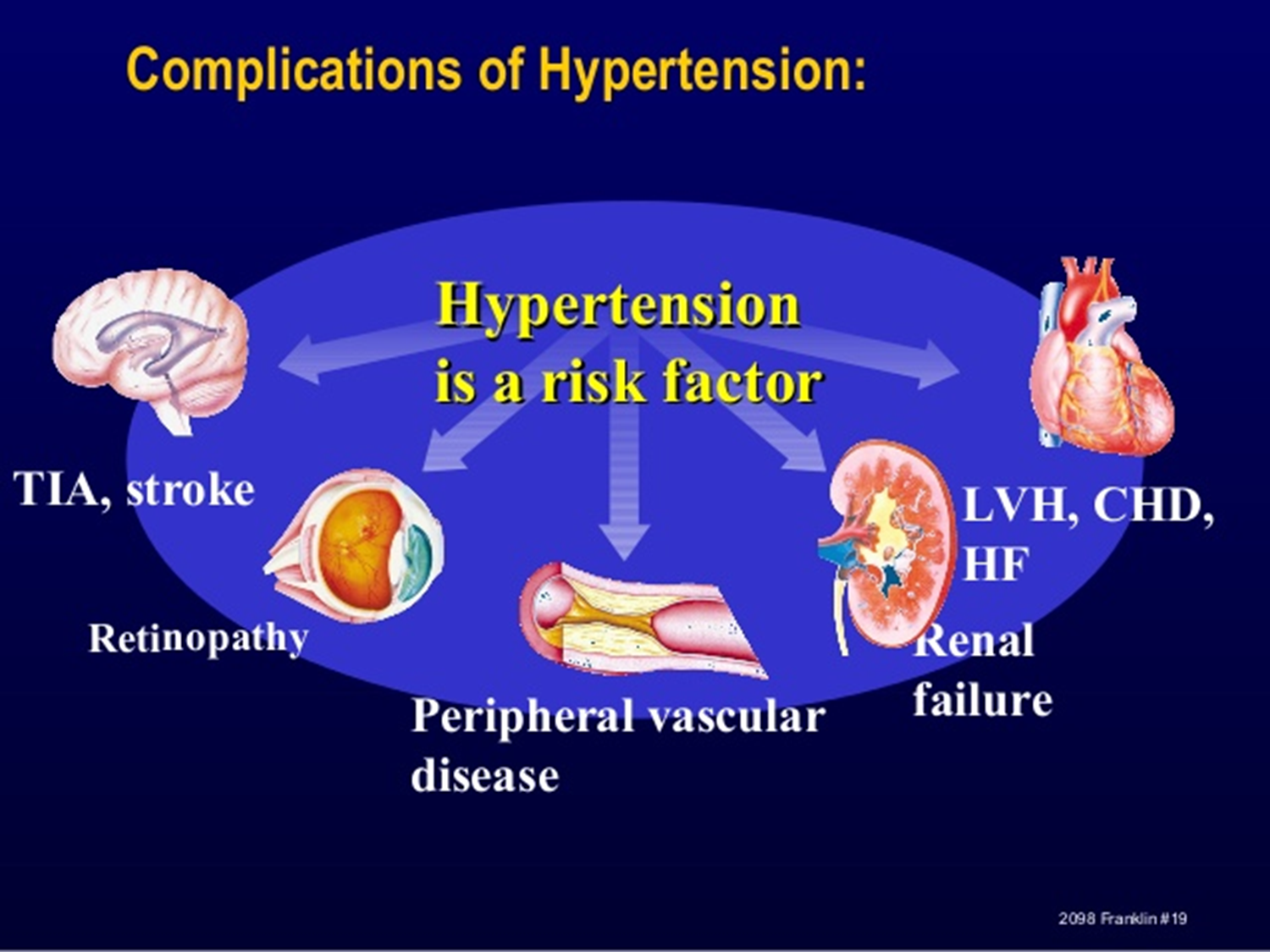
WHY IS HTN HARMFUL ?
STAGES OF HTN
- Elevated B.P. : Systolic between 120-130
- Stage 1 HTN : Systolic between 130-140 and/or diastolic b/w 80 & 90
- Stage 2 : Systolic 140 or more and/or diastolic 90 or more
Hypertensive Crisis: (Hypertensive urgency // Hypertensive Emergency) Systolic usually more than 180 and diastolic more than 120
TYPES OF HTN
- Primary hypertension- (no known cause) also called essential HTN
- Secondary Hypertension- (Secondary to an underlying disease)
S/S of HTN
Very non-specific
- Asymptomatic
- Headache, dizziness, body pain
- Sec. HTN: features of the underlying disease
- Severe rise in BP can present as angina/MI, CHF, stroke/TIA, altered mental status Hypertensive encephalopathy ⇒ Hypertensive crisis
Physical Exam
Do a detailed examination at the first visit.
- Check the pulses, cardiac examination
- Examine for any S/S of stroke
- Examine the eyes for retinopathy
- Examine the heart for murmurs, CHF
- Auscultate the abdomen for renal artery bruit ( occurs in renal artery stenosis)
- Look for features of Cushing’s, acromegaly etc. if you suspect these.
HYPERTENSIVE RETINOPATHY Y
Divided into 4 grades , based on severity
- Grade 1: Retinal vessels become less clear
- Grade 2: A-V nipping
- Grade 3: Edema, hemorrhages, Copper wiring
- Grade 4: Optic disc edema, silver wiring
Diagnosis of hypertension
Routine investigations
- CBC, urea, creatinine, electrolytes, lipid profile, ECG, blood sugar, urinalysis
- If secondary HTN is suspected ⇒ order further tests accordingly
- ECG may show left ventricular hypertrophy
- High creatinine ⇒ suspect renal pathology