Z 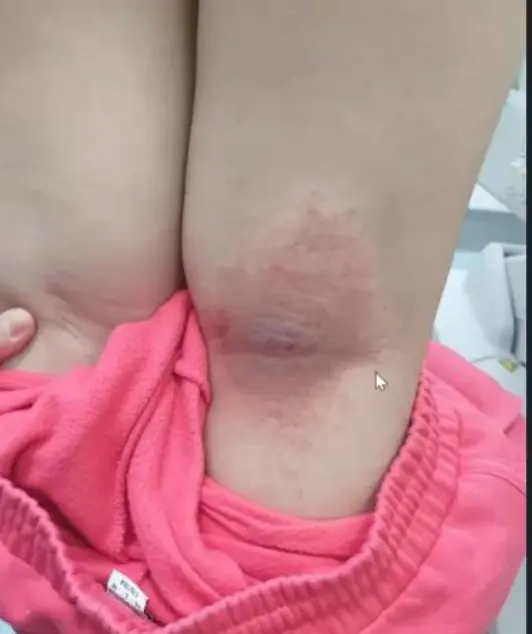
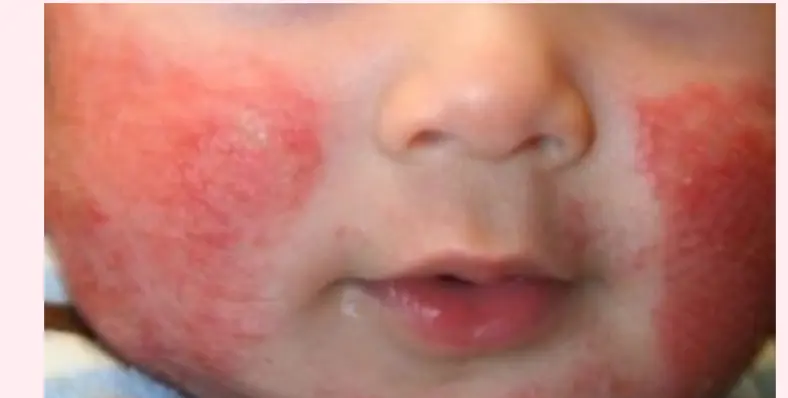 Subacute adult atopic Dermatitis.
Subacute adult atopic Dermatitis.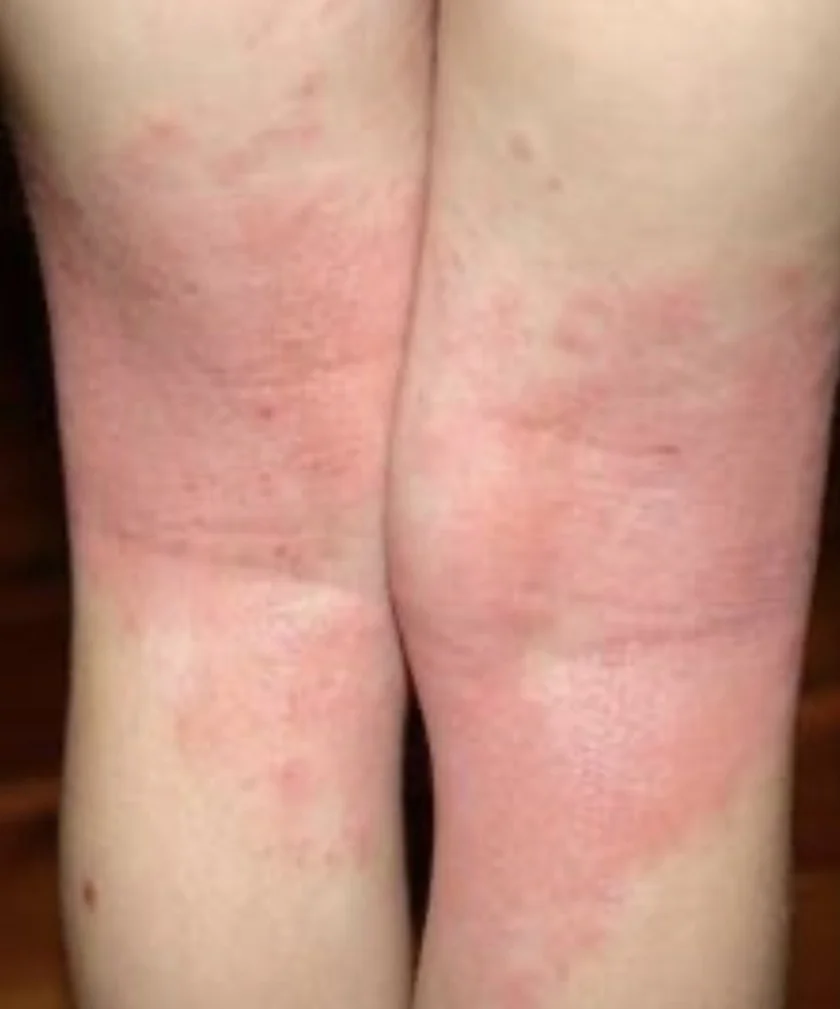
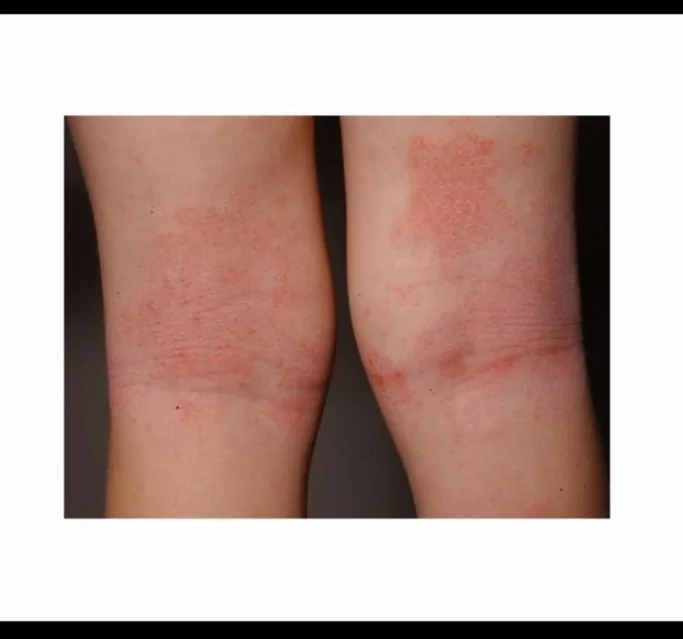
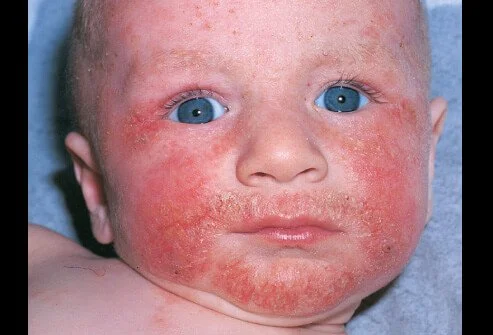
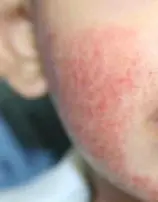
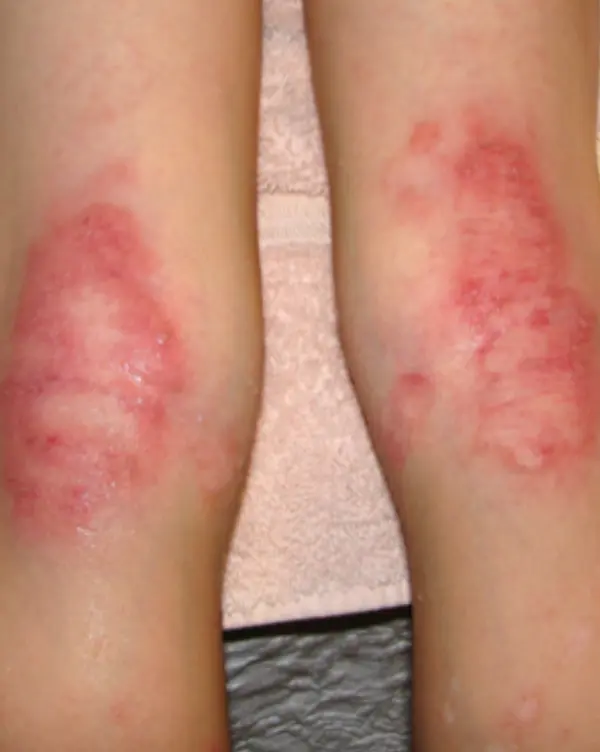
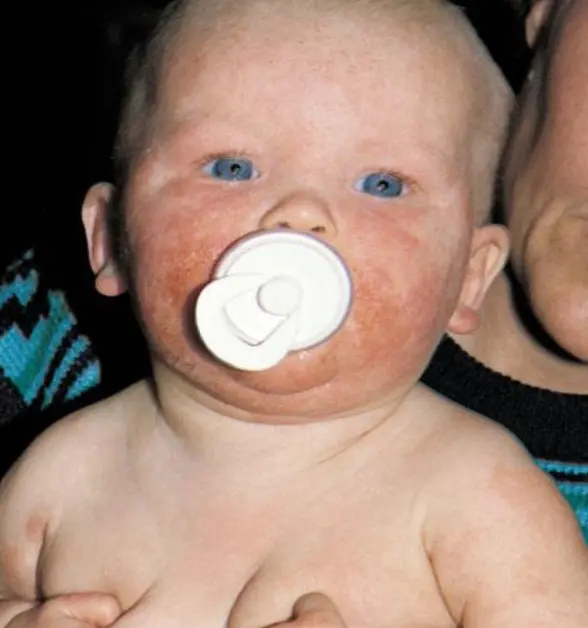
Atopic Dermatitis CS-OSPE
Diagnosis: Atopic Dermatitis (including Infantile phase subacute and Childhood phases)
Context/Description: Cases involve patients (e.g., a 2-year-old kid, Ali from 5 months to 15 years old, a one-year child) suffering from very itchy skin lesions, often with redness, on the face or other areas, experiencing severe bouts.
Describe the skin condition/Main lesions: An erythematous, ill-defined patch or ill-circumscribed plaque with scaly and excoriation, and Papule, often present in the popliteal area or on the face and cheek.
History/Important Questions:
- Always ask about a history of atopy for the patient or their family. This is the main question to confirm the diagnosis. (asthma, rhinitis, allergies)
- When to suspect food allergy? If young patient.
what are the two important skin functions if impaired patient will develop this lesion ? Z
- A- barrier function
- B- immunological
flag deficiency
Treatment:
- Avoid the trigger
- Anti-histamine
- Emollient
- Topical steroid (e.g., “Hydrocortisone”)
Complications:
- Eczema herpeticum
- Bacterial infection
- Erythroderma
Which of the following is a common associated disease?
- Rhinitis
Which new systemic treatment provides an excellent response in a short time with little side effect?
- Biologics
Two differential diagnoses?
- Contact dermatitis - Seborrheic dermatitis.
The cause of atopic dermatitis is due to function and protein loss. Name the protein and the function?
- Filaggrin – water barrier
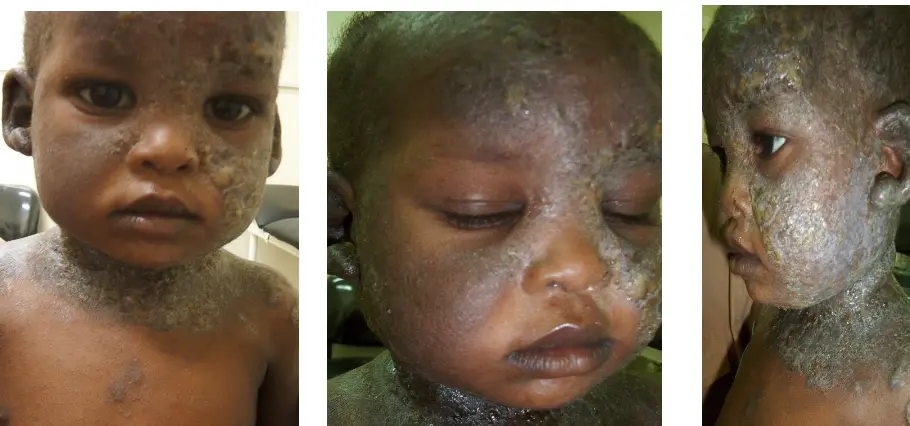 What is the diagnosis?
What is the diagnosis?
- Infantile chronic atopic dermatitis
What is the treatment?
- Withdrawal or avoidance of the triggering substance if identified.
- Emollients: Apply 3 times/day and after bathing to combat dryness.
- Antihistamine: To alleviate itching.
- Topical steroid:
- Hydrocortisone valerate ointment.
- Systemic antibiotic: Such as erythromycin.
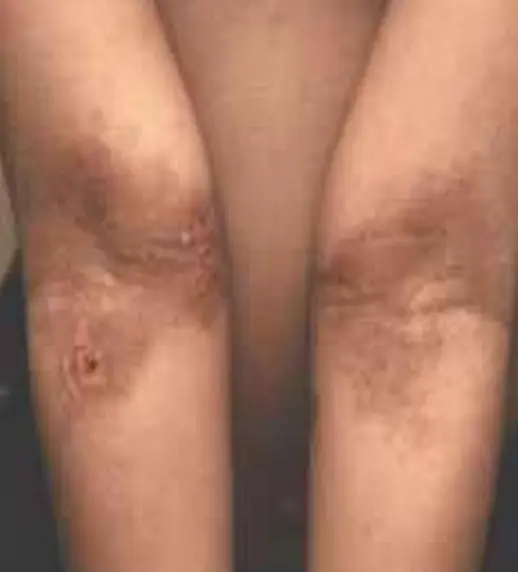 Chronic adult atopic Dermatitis.
Chronic adult atopic Dermatitis.