Tension pneumothorax
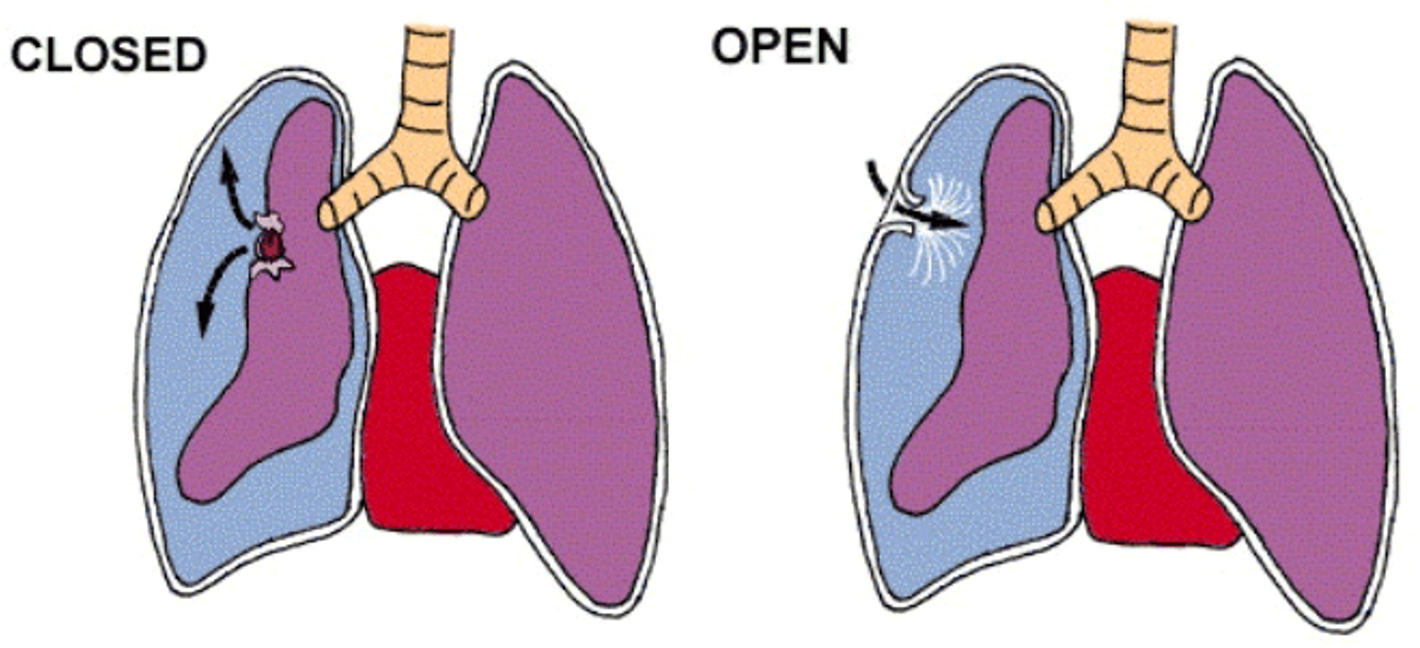
- Traumatic punctured lung wound acts as a one-way valve.
- Each inhalation- additional air accumulate in pleural space.
- Normal negative intrapleural pressure becomes positive.
- Depressing the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm.
- Pushing mediastinal structures to other side.
- Compressing contralateral lung.
- Heart rotated about the superior and inferior vena cava
- Venous return and cardiac output decreased.
- Distending the neck veins.
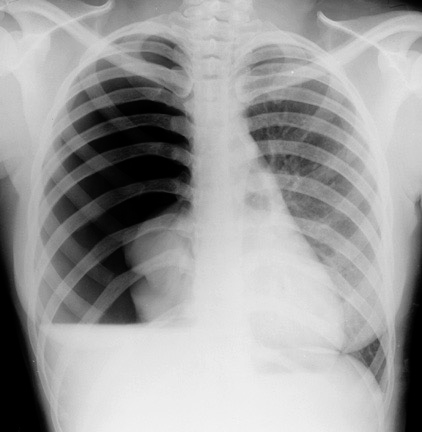
Clinical features
- Tachypnoea, tachycardia, use of accessory muscles
- Asymmetrical chest wall movement
- Hyper resonance on percussion
- Absent or decreased breath sounds
- Distended neck veins
- Systemic hypotension
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- Tracheal deviation away from the affected side
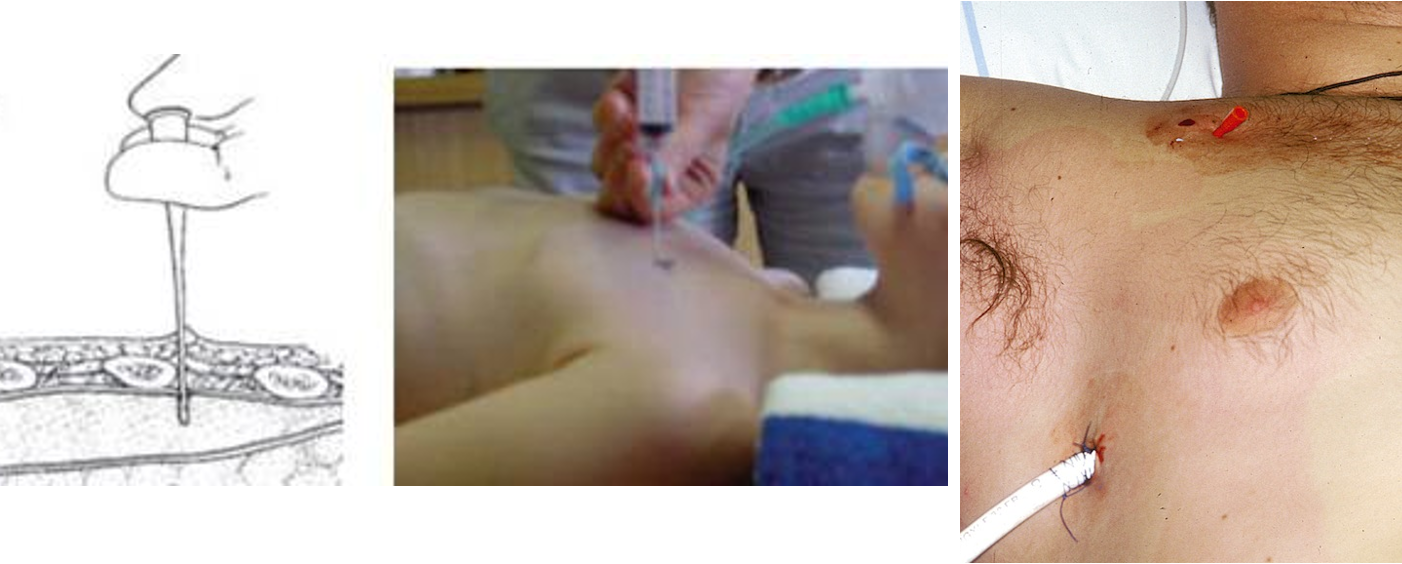
- Treatment: x-ray confirmation not required
- Wide bore needle in 2nd intercostal space, mid-clavicular line
- ideally Chest tube in 5th intercostal space, anterior axillary line
(Image: Tension pneumothorax Needle decompression Intercostal tube)