The initial radiographs are normal as bone changes are not visible until 10–14 days after the onset of infection.
X-ray is the recommended initial imaging modality because it is inexpensive and can rule out differential diagnoses.
The earliest signs on plain radiographs are soft tissue swelling and bone destruction in the metaphysis, with a Periosteal reaction.
The 99mTc radionuclide bone scan and MRI show changes within a day or two of the disease
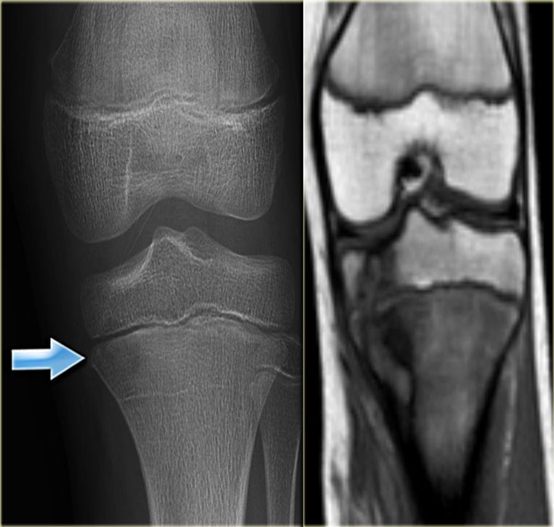
Compare X-ray and MRI in this case of acute osteomyelitis.
- It is difficult to be seen on plain x-ray.
- The extent of disease is well demonstrated by MRI
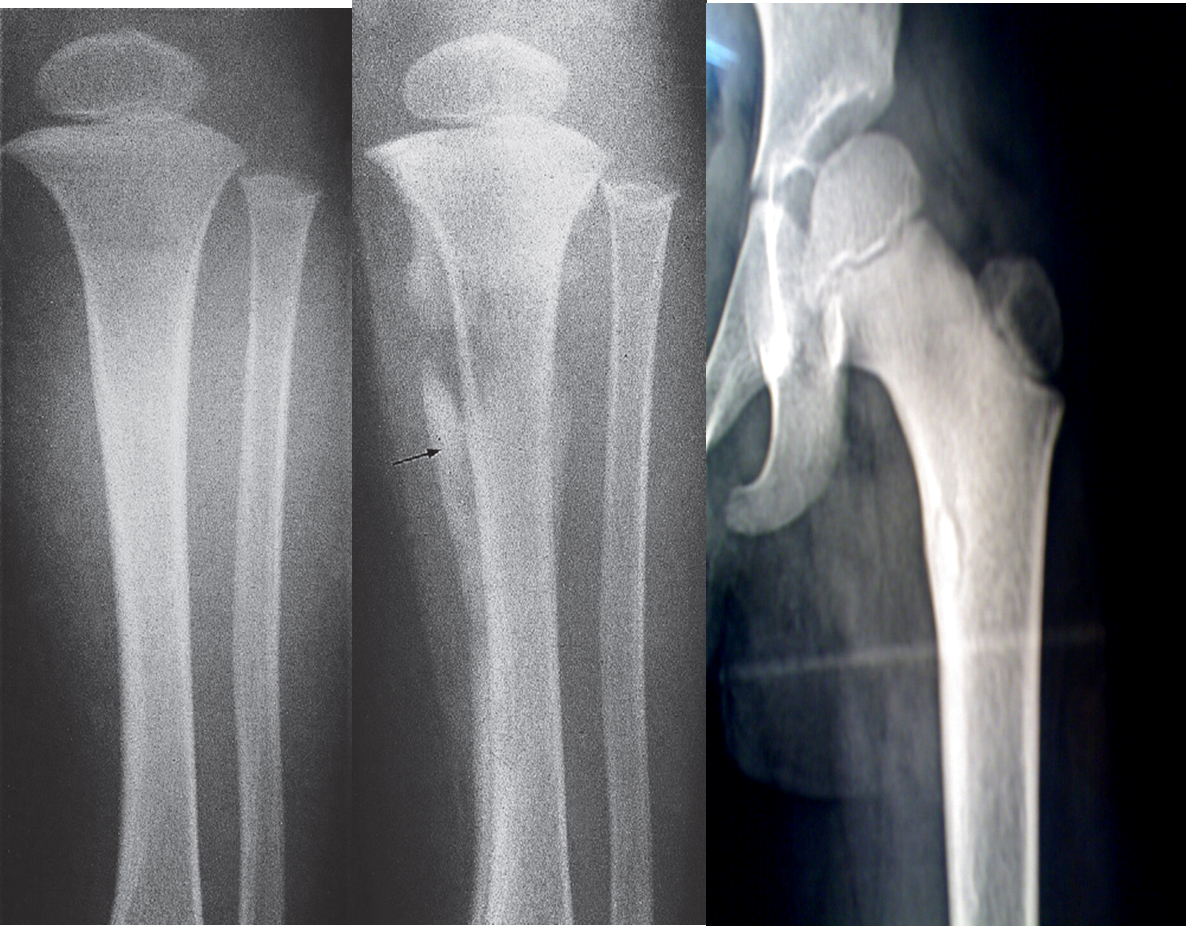 (A) An initial films reveals no abnormality
(A) An initial films reveals no abnormality
(B) A film taken 3 weeks later shows some destruction of the upper end of the tibia and an extensive periosteal reaction along the tibia, particularly the medial side (arrow).
(C) Bony sequestrum X-ray leg (left; AP view) of a child A fragment of bone has separated from adjacent bone and is surrounded by a lucent rim. chronic osteomyelitis.
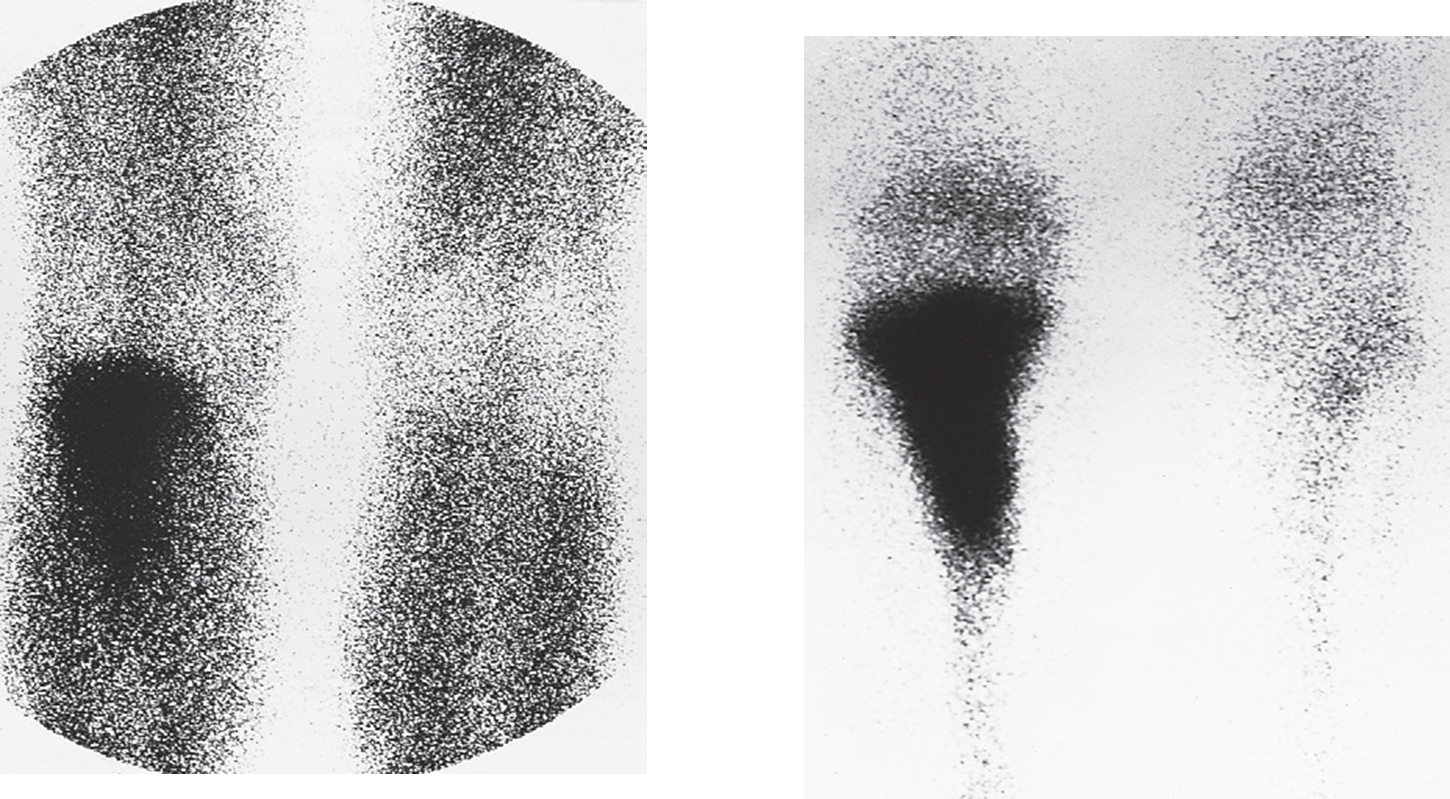 Osteomyelitis; radionuclide scans of knees.
(a) Scan taken 1 minute after injection of radionuclide showing increased uptake in the upper part of the leg.
(b) The delayed scan taken 3 hours later shows substantially increased uptake in the bone itself.
Acute osteomyelitis:
No abnormality on plain radiograph
Radionuclide study show high uptake
Osteomyelitis; radionuclide scans of knees.
(a) Scan taken 1 minute after injection of radionuclide showing increased uptake in the upper part of the leg.
(b) The delayed scan taken 3 hours later shows substantially increased uptake in the bone itself.
Acute osteomyelitis:
No abnormality on plain radiograph
Radionuclide study show high uptake
Spinal
PLAIN FILMS
- Narrowing and destruction of an intervertebral disk
- Paravertebral soft tissue mass
- Endplate sclerosis (during healing phase)
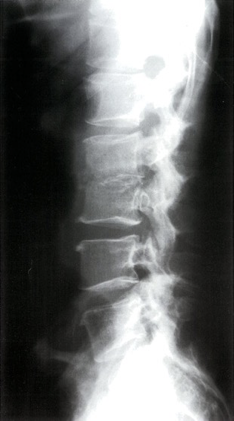
Spondylodiscitis (discitis-osteomyelitis)
X-ray lumbar spine (lateral view)
The inferior endplate of L2 and superior endplate of L3 are osteopenic and the cortices appear fragmented. The intervening L2–3 disc space is narrowed.
MRI
- Bone marrow edema in infected vertebrae, discs and paraspinal soft tissues
- Dark on T1 and bright on T2 images
- Enhancement of inflamed tissues after contrast
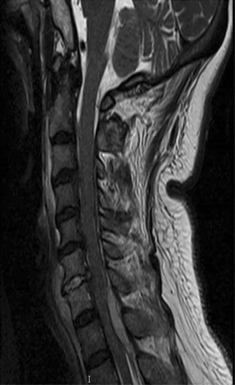
Spinal epidural abscess, osteomyelitis, and discitis MRI cervical spine (T2-weighted; sagittal plane) High signal intensity collections are seen in the posterior epidural space. The largest collection causes anterior displacement and compression of the spinal cord from C7-T2. The appearance is consistent with epidural abscess. High signal intensity consistent with osteomyelitis and discitis involves the C6 and C7