Patient Preparation
Fasting 4- 6 hours
Patient position
Supine head first
Technique
Scanogram
-
The technician select the area of interest, select the slice thickness.
-
The routine CT examination involves making 20–30 axial sections and slice thickness for the brain is 10 mm.
-
Slice thickness for pituitary may 5 mm or less. Pre +/- post contrast images are acquired.
CT Terminology
Non enhanced scan (CT without contrast)
- Hypodense= Less dense
- Hyperdense= More dense
- Isodense= of equal density
Intra-axial lesions can involve the white and grey matter structures of the brain parenchyma.
Extra-axial lesions may involve the meninges, extracerebral spaces and skull vault.
- Specific diagnoses are suggested by combining the clinical features with information about multiplicity, size, position and density of the lesion.
The key signs of an abnormality on a CT scan are:
- Abnormal tissue density
- Mass effect
- Enlargement of the ventricles.
CT Terminology
Contrast enhanced CT ( CT with contrast)
- Non enhanced lesion: Lesion which did not show any contrast uptake
- Enhanced lesion: Lesion with contrast uptake
- Homogenous
- Heterogeneous
- Ring (marginal)
- Serpiginous
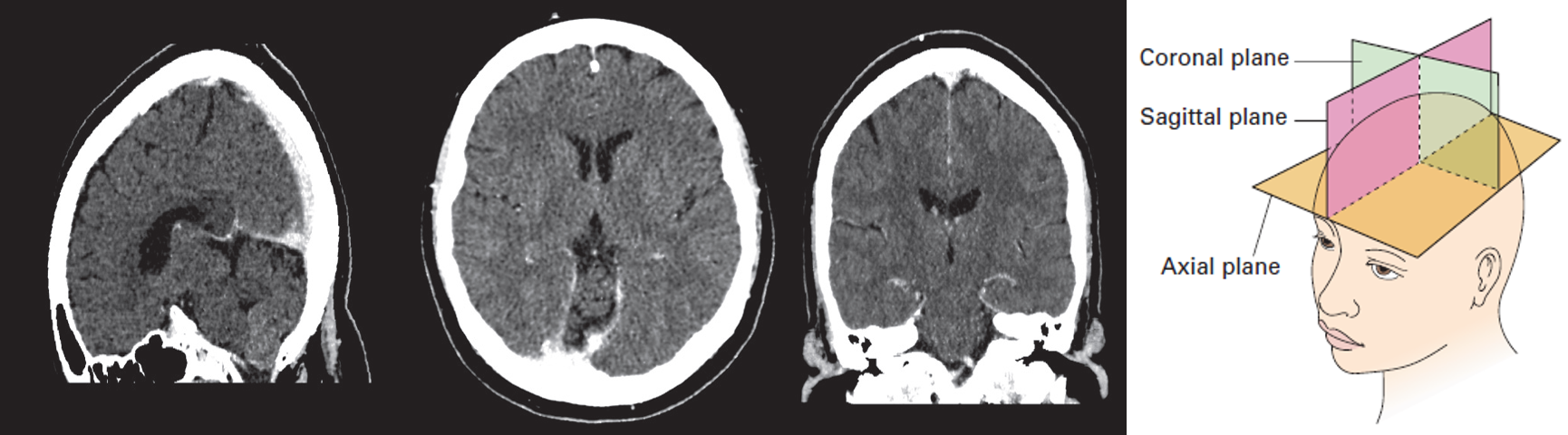
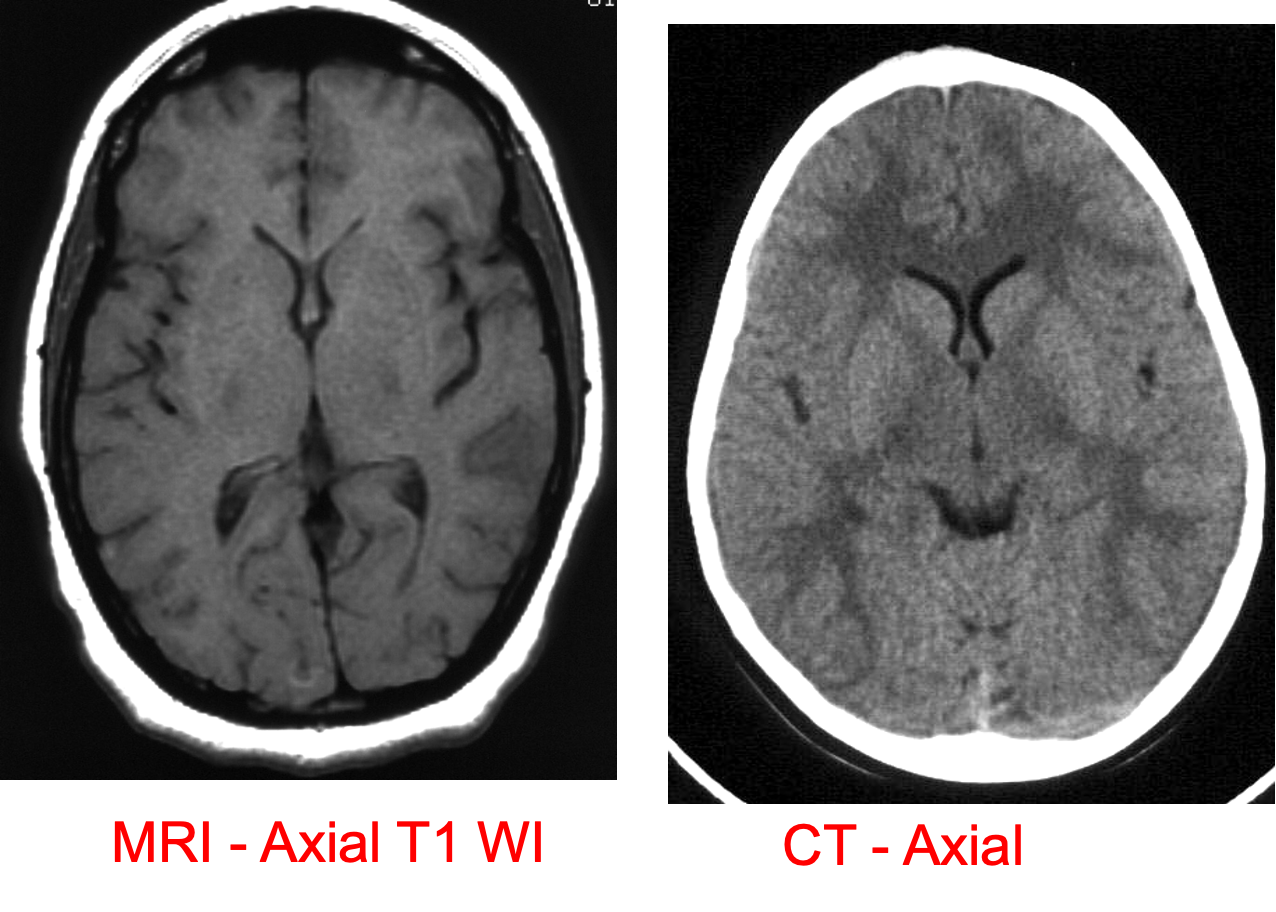
Diagram of the axial, coronal and sagittal planes Corresponding CT images of normal brain
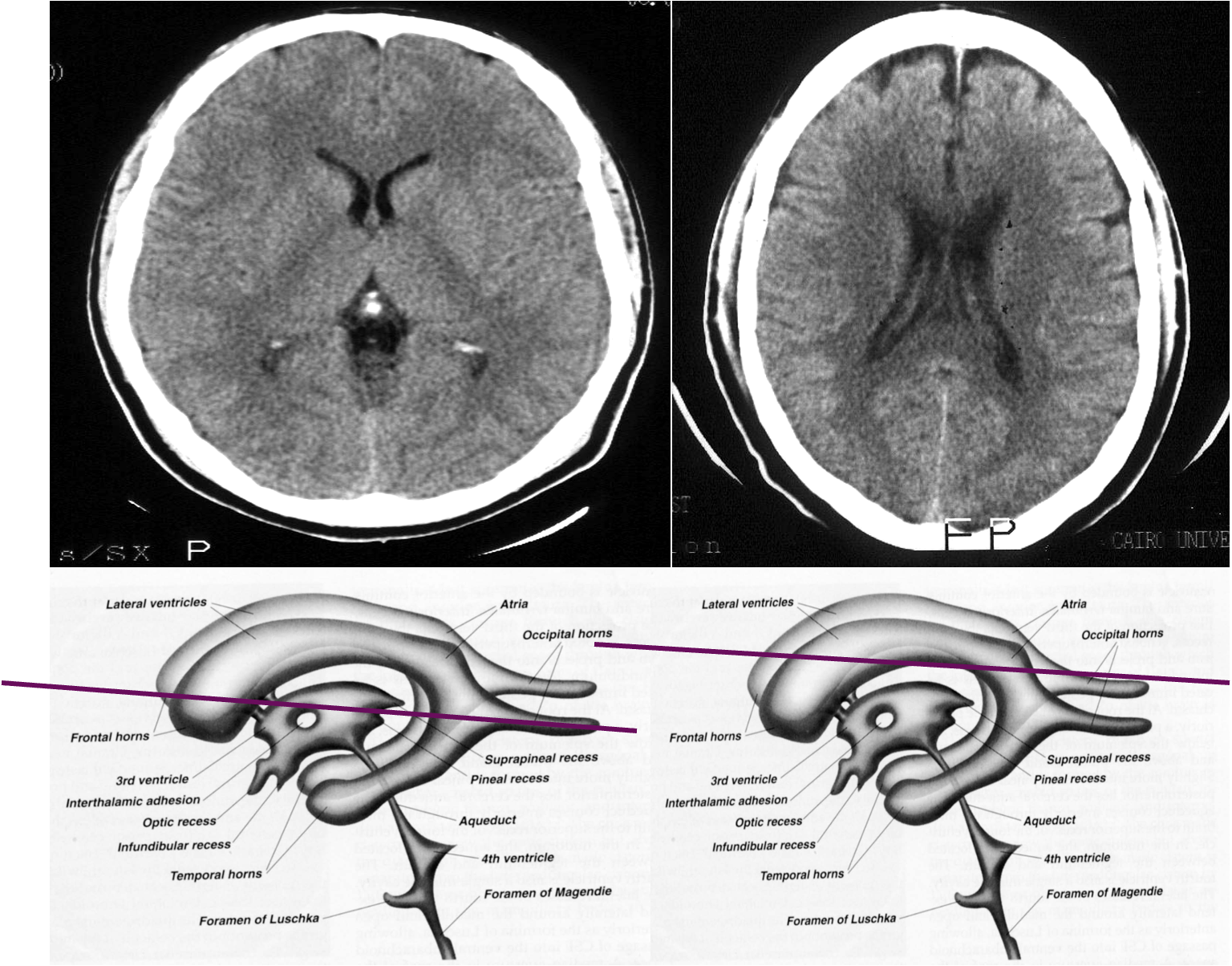
Ventricular anatomy
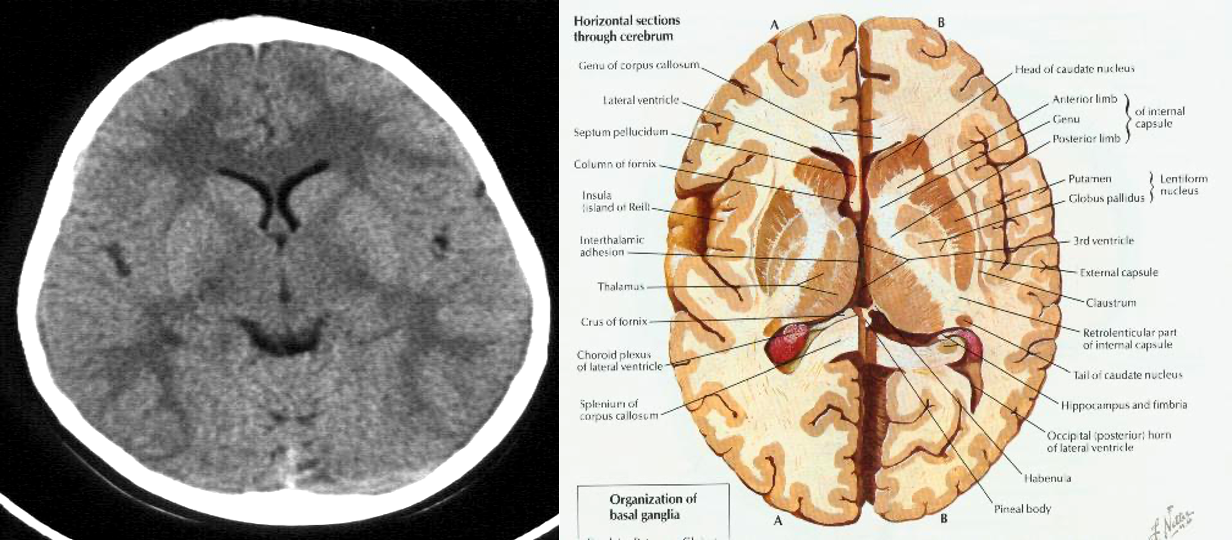
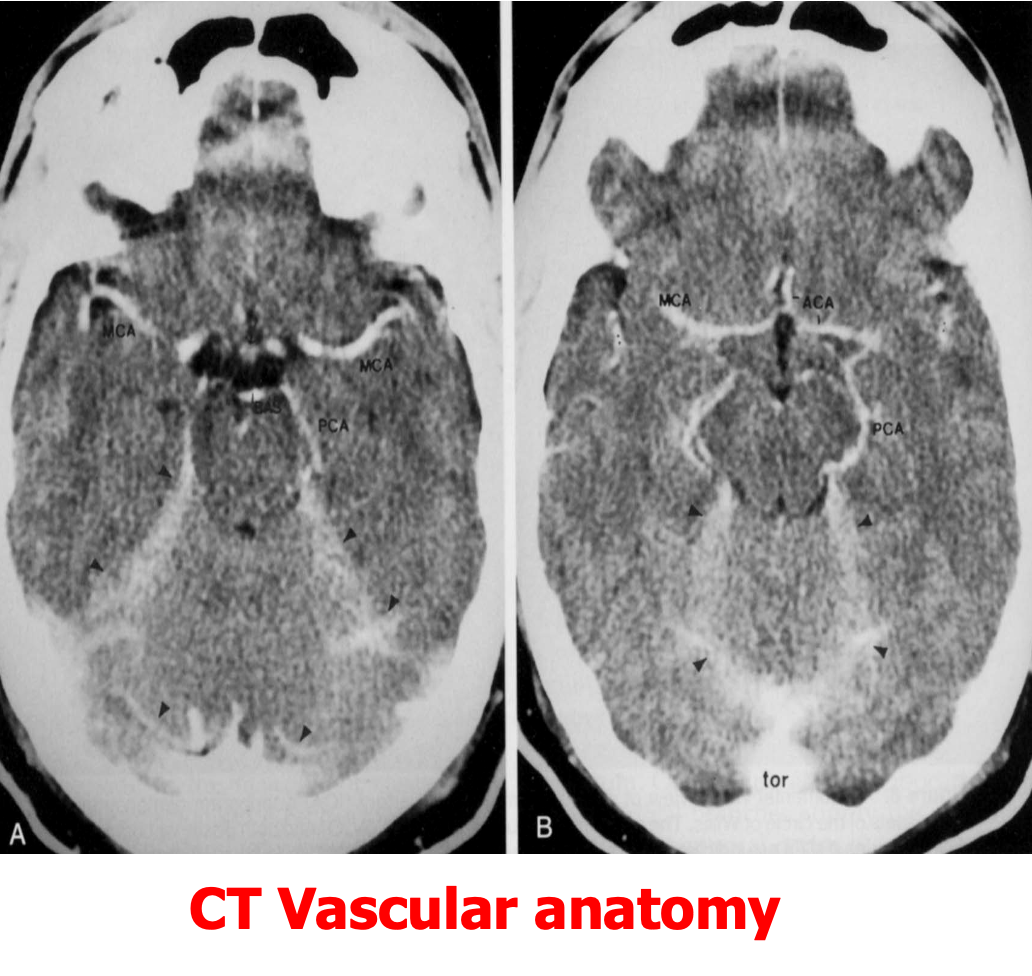
CT show the anatomy of skull in transverse section
Brain Emergency
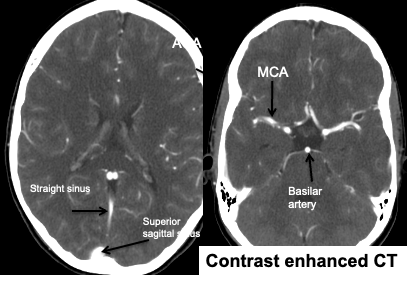
Contrast enhanced CT:
IV injection of contrast medium is often given because the abnormality not seen in pre contrast scans, may be rendered visible following contrast enhancement.
Consequence of breakdown of blood brain barrier allowing contrast to enter the lesion particularly in neoplasm, infection, inflammation and certain stage of ischemia.
Also it is helpful in demonstrating blood vessels