Methods of evaluation of spine & spinal cord
- Plain X-Ray
- Myelogram: injection of contrast medium in CSF followed by x-ray images. Rarely performed now-a-days
- Computed Tomography (CT Scan)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Discogram: injection of contrast medium in the disc followed by x-ray images .
- Spinal angiography: To evaluate arteries and veins.
- Ultrasound.
- Radionuclide Bone Scan: Intravenous injection of radioactive material which deposit in bones, followed by images by gamma camera.
- DEXA – Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry: (osteoporosis)
Anatomy
Presentations
- Trauma
- Infection
- Metabolic
- Neoplasm
- Spinal curvature
- Spinal dysraphism
- Spinal Congenital anomalies
- Collapse of Vertebral bodies
- Dense Vertebrae
- Disc Space Narrowing
- Degenerative disk disease
- Pedicle Abnormalities
- Osteomyelitis
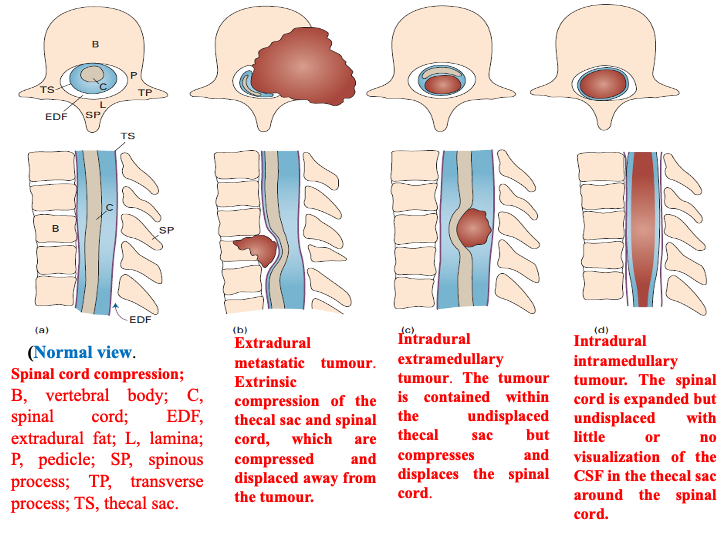
Spinal Cord Tumours
- Extra-dural; - Hemangioma
- Intra-dural extra-medullary; - Spinal Schwannomas Z & Meningioma Y
- Intra-medullary; - Multiple Sclerosis, Syringomyelia
- Spinal Metasteses
(cc TB)