Presentation
Parathyroid glands
There are four, oval-shaped endocrine glands embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
-
Two superior glands: located near the superior pole of the thyroid gland at the junction of cricoid and thyroid cartilages.
-
Two inferior glands: located in the area between the inferior poles of the thyroid lobes and the superior mediastinum.
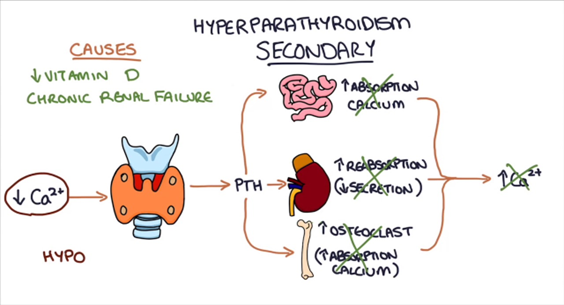
- Function: secretion of PTH in response to low calcium serum levels
- Arterial supply: Inferior thyroid arteries
- Venous drainage: Thyroid venous plexus
Different cells of the parathyroid glands:
- Chief cells: secretion of parathyroid hormone
- Oxyphil cells
- Adipocytes
Effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH):
Calcium:
- Increases blood calcium levels by directly stimulating osteoclasts to break down bone.
- Promotes calcium reabsorption by the kidneys
- Increases gastrointestinal calcium absorption by activating vitamin D
Phosphate
- Inhibits proximal tubular reabsorption of phosphorus