Sport Case Scenarios
Moath Alamir
Learning Objectives
- How to approach a clinical case systematically
- Taking history: Key questions and techniques
- Performing specific examination: Relevant physical tests
- Requesting specific investigations: Appropriate imaging and studies
- Reaching a diagnosis: Clinical reasoning process
- What specific treatment to recommend: Evidence-based management
Case Study 1: Acute ACL Injury
Patient Presentation
A 23-year-old male complains of pain in the right knee following a sports injury.
History
Acute Injury Details
- Mechanism of injury: Twisting injury during sports activity
- Key history point: Patient heard a “pop” in his knee
- Functional impact: Cannot bear weight on the knee and couldn’t continue to play
- Physical signs: Swelling, bruising, and subtle effusion in the knee
Chronic History
- History of giving way episodes
Activity Level
- Plays soccer very frequently (high-demand activity)
Examination
General Findings
- No swelling & no tenderness
- Range of motion is full
Special Tests
- Lachman Test: Positive ✅
- Anterior drawer test: Positive ✅
- Pivot shift test: Positive ✅
Imaging
Question: What is your finding? ACL tear
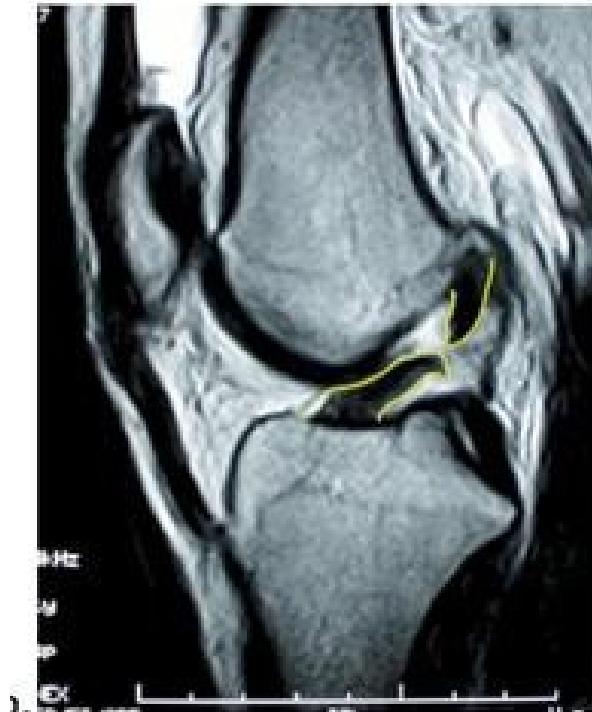
Treatment Plan
Conservative Management
- Physical therapy rehabilitation program
Surgical Intervention
- ACL reconstruction if:
- Failed physiotherapy and still symptomatic
- High level of activity lifestyle
- Patient desires return to pivoting sports
Case Study 2: Medial Meniscus Tear
Patient Presentation
A 31-year-old male complains of pain in the left knee for 4 weeks.
History
- Mechanism of injury: Twisting injury after stepping in a hole
- Pain characteristics: Painful with walking
- Functional limitation: Not able to fully flex knee
- Key symptoms: History of locking and clicking sensationsZ
Examination
Local Examination
- No swelling present
- Joint line tenderness on the medial aspect
- Range of motion: Limited flexion
Special Tests
- McMurray’s test: Positive ✅
- Lachman Test: Negative ❌
- Anterior drawer test: Negative ❌
- Pivot shift test: Negative ❌
Imaging
Question: What is your finding?
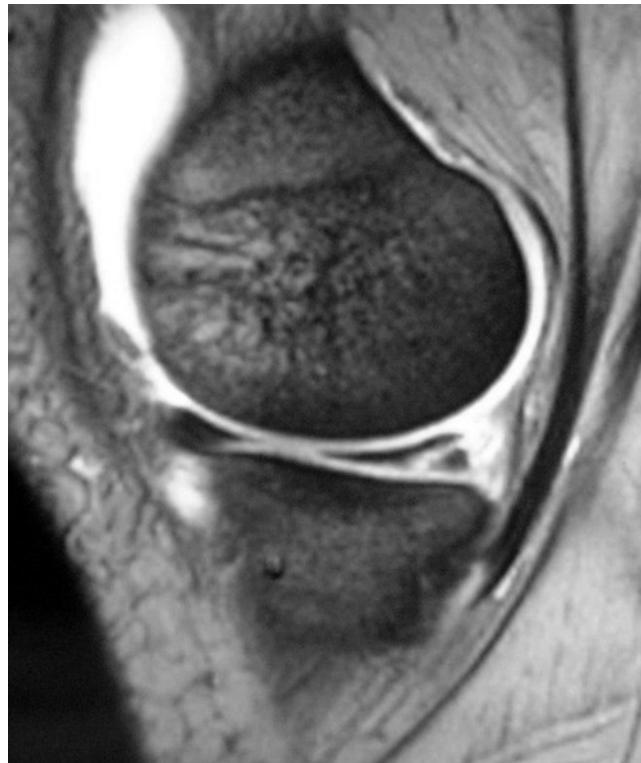
Treatment Plan
Conservative Management
- Physical therapy for strengthening exercises
Surgical Options
If conservative management fails:
- Diagnostic arthroscopy for definitive diagnosis
- Meniscal repair vs. Meniscectomy:
- Decision depends on:
- Type of tear
- Zone location of tear
- Patient age and activity level
- Decision depends on:
Additional Case Questions
Questions for discussion:
- What is the diagnosis?
- What is the sign called? pocket handle
- What is the treatment?
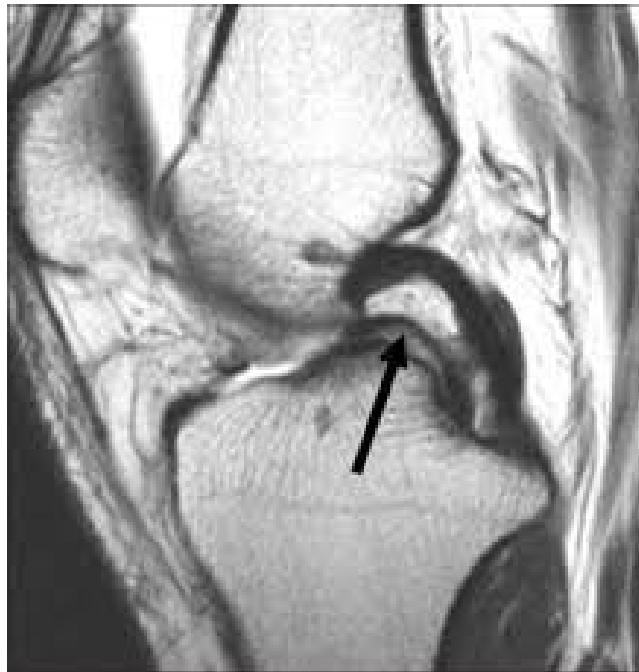
Case Study 3: Posterior Shoulder Dislocation
Patient Presentation
A 29-year-old male with known seizure disorder presented in the ER complaining of left shoulder pain for 2 weeks.
History
- Mechanism of injury: Preceded by seizure, patient non-compliant with medication
- Initial treatment: Treated only with sling in ER
- Current status: Still painful with significant functional limitation
- Duration: Cannot move shoulder after 2 weeks
Examination
- Asymmetry of shoulders noted
- Shoulder position: Locked in internal rotation
- Range of motion: Limited external rotation
Imaging

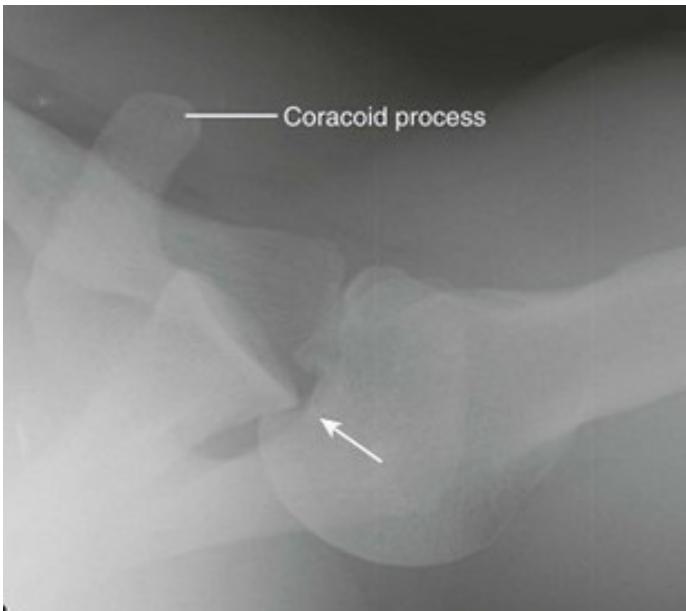
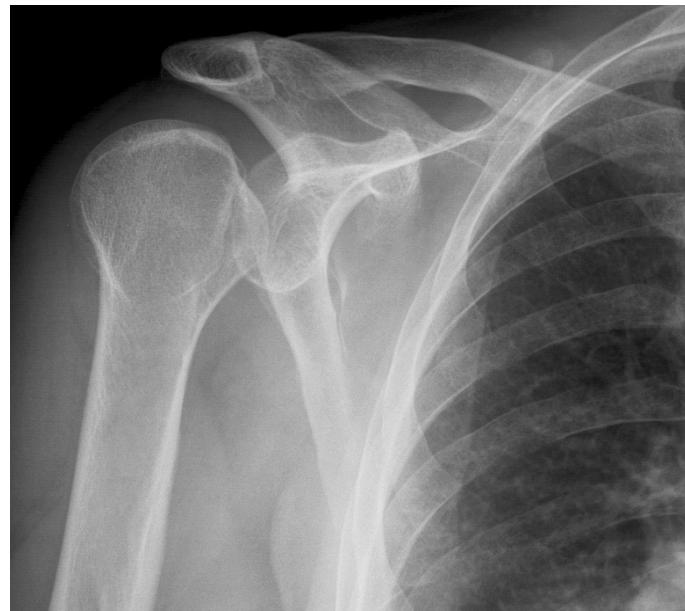
Treatment Plan
Early Presentation (< 2 weeks)
- Closed reduction procedure
- Immobilization in sling
- Physical therapy for rehabilitation
Late Presentation (> 2 weeks)
- Surgical intervention required
Important Consideration
- Seizure control: Essential to prevent redislocation
- Optimize epilepsy management plan
Case Study 4: Recurrent Shoulder Instability
Patient Presentation
A 35-year-old male presented in clinic complaining of left shoulder pain and instability.
History
- Recurrent dislocation history
- Previous treatments: Multiple reductions and physiotherapy
- Treatment failure: Physiotherapy was ineffective
Examination
- Symmetrical shoulders on inspection
- Range of motion: Good and pain-free
- Apprehension test: Positive ✅ (indicates instability)
Imaging
Questions for analysis:
- What are the two findings in recurrent shoulder dislocation?
- What do you see on the images?
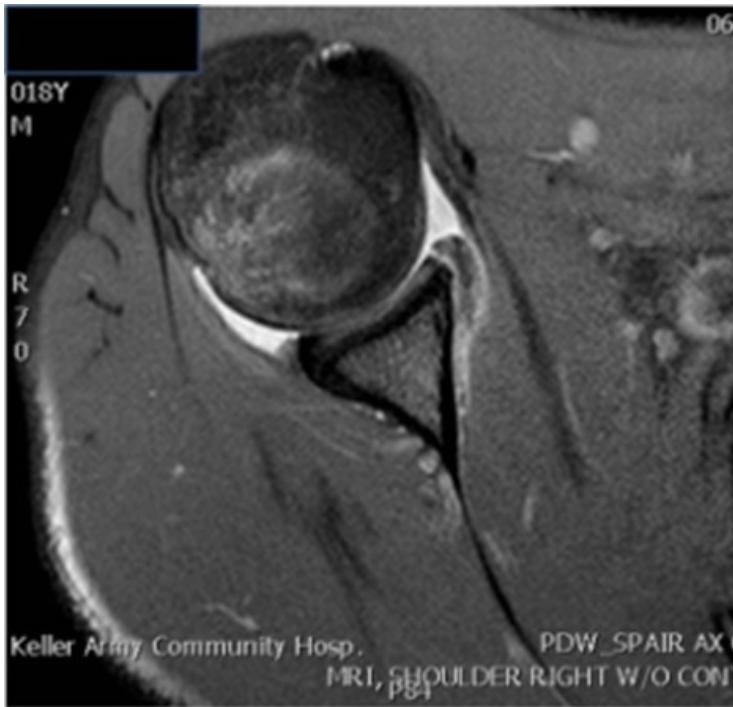
Treatment Plan
Surgical Management #±
- Bankart repair procedure
- Consider capsular shift if needed
- Post-operative rehabilitation protocol
Case Study 5: Rotator Cuff Tear
Patient Presentation
A 55-year-old lady presented in clinic complaining of right shoulder pain.
History
- No history of trauma (insidious onset)
- Pain pattern: Night pain is a prominent feature
- Functional decline: Cannot raise hand above head, symptoms worsening over time
- Bilateral involvement: Other shoulder is less severe
- Treatment history: Physiotherapy failed to improve symptoms
Examination
- Symmetrical shoulders on inspection
- Muscle atrophy: Notable atrophy of shoulder muscles
- Tenderness: Localized tenderness at greater tuberosity (GT)
- Range of motion: Limited abduction
- Strength testing: Weak abduction & external rotation
- Special tests:
- Neer’s test: Positive ✅
- Hawkin’s test: Positive ✅
Imaging
Question: What do you see on these images?
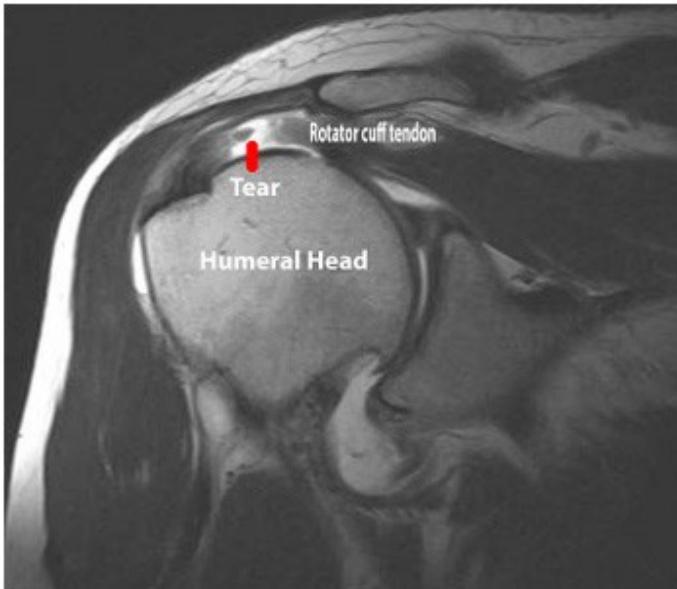
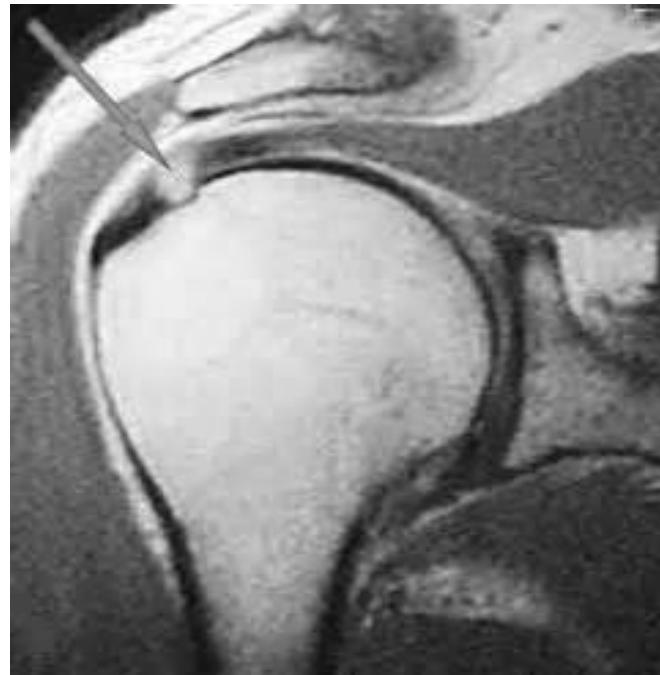
Treatment Plan
Indications for Surgery
Since physiotherapy failed and patient has complete tear of rotator cuff muscles:
Surgical Management
- Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair is recommended
- Post-operative rehabilitation protocol
- Expected recovery timeline and outcomes
Summary
These sport medicine cases demonstrate the importance of:
- Systematic history taking and identification of key symptoms
- Thorough physical examination with appropriate special tests
- Proper imaging interpretation for accurate diagnosis
- Evidence-based treatment planning tailored to patient needs
- Consideration of activity level and patient goals in management decisions