GYN
Table of Contents
- Evaluation of the Baby Throughout Pregnancy
- Fetal Antenatal Assessment & Fetal Wellbeing
- Fetal Anomaly/Abnormality
- Fetal Growth
- Fetal Wellbeing
- Fetal Maturity
- Mother’s Complaint & Decrease in Fetal Movement
- Conclusion
Fetal Antenatal Assessment
Evaluation of the Baby Throughout Pregnancy
Importance:
- To detect the appropriate time to deliver the baby with no harm and mode of delivery.
- To decide the delivery mode.
- To pick up complications early and to limit and prevent them.
- To determine if the baby needs special care during labor, delivery, or after delivery.
- To evaluate the baby’s growth.
- To rule out congenital anomalies.
- To make sure the baby is healthy.
Fetal Antenatal Assessment & Fetal Wellbeing
Assessment Evaluate the baby’s structure, growth, wellbeing, and maturity; check for any anomalies.
Fetal Wellbeing Growing and its condition (evaluate and assess the baby from a health status perspective only).
- Fetal Antenatal Assessment involves:
- Fetal Anomaly/Abnormality
- Fetal Growth
- Fetal Wellbeing
- Fetal Maturity
US (Ultrasound) plays a major role:
- 1st Trimester: Dating at 11th week, check for nuchal translucency to rule out any trisomy.
- 2nd Trimester: Anatomy scan.
- 3rd Trimester: Growth scan to rule out IUGR (Intrauterine Growth Restriction), assess fetal wellbeing (if there’s a decrease in fetal movement or liquor), and determine fetal maturity (baby’s weight).
Fetal Anomaly/Abnormality
First step in assessment.
- By History:
- Any previous babies with anomalies?
- Any family history of anomalies?
-
Chemical Tests: Screening for Trisomy
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): A major serum protein in the fetus, maximum at 13 weeks. Elevated in cases of spinal tube defects (e.g., spina bifida, hydrocephalus).
- Maternal AFP is elevated in:
- Anencephaly.
- Open spina bifida.
- Exomphalos.
- Gastroschisis.
- Placental abnormalities.
- Threatened abortion.
- Intrauterine fetal death.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Must be done between 16 and 20 weeks; after this, it’s not reliable.
- Maternal AFP is elevated in:
- Serum test has 99% sensitivity: Cell-free DNA = Non-Invasive Prenatal Test.
- Take a blood sample from the mother at week 10 to see fetal RBCs and rule out trisomy and check gender.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): A major serum protein in the fetus, maximum at 13 weeks. Elevated in cases of spinal tube defects (e.g., spina bifida, hydrocephalus).
-
BHCG (Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin).
-
US (Ultrasound): Now can pick up early signs:
- Down syndrome suggestions can be detected between 11 to 14 weeks.
- Cardiac anomalies can be shown and picked up by 24 weeks.
- Prenatal Diagnosis Procedures (all under US guidance):
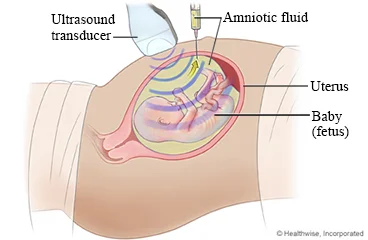
- ✔ Amniocentesis:
- Amniotic fluid sample.
- Check for anomalies; chromosomal, genetic.
- ✔ Chorionic Villus Sampling:
- Placental tissue sample.
- ✔ Cordocentesis:
- Fetal blood sample.
- Prenatal diagnosis.
Fetal Anomaly/Abnormality Detection Methods
1. Amniocentesis
- Amniotic fluid sample for congenital anomaly in early pregnancy.
- Therapeutic at any GA (Gestational Age).
Indication:
- Fetal karyotyping (chromosomal abnormalities).
- Assessment and follow-up of bilirubin (RH isoimmunization).
- Therapeutics (polyhydramnios).
- Assessment/ of lung maturity.
Result: 1 to 2 weeks.
Complication:
- RH isoimmunization.
- Miscarriage.
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- PROM (Premature Rupture of Membranes).
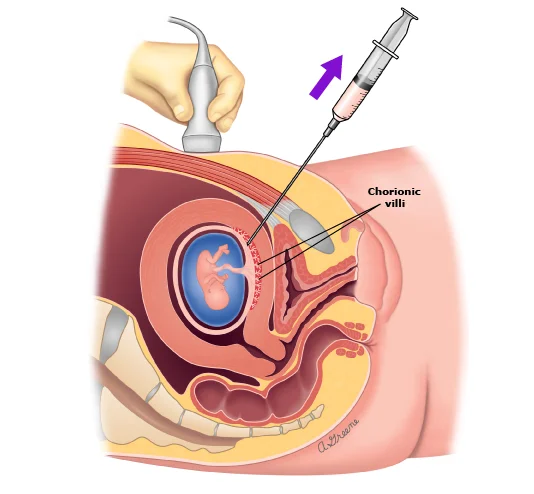
2. Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Placental tissue sample, done in the 1st trimester.
Indication: Chromosomal abnormalities detection.
Result: 1 to 2 days because it involves direct cells.
Complication:
- RH isoimmunization.
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- PROM.
- Limb defect (Characteristic). QA
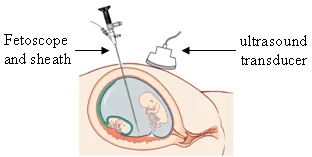
3. Feto-scope (Not Used Anymore)
- Fetal blood sampling, used before to detect anomalies.
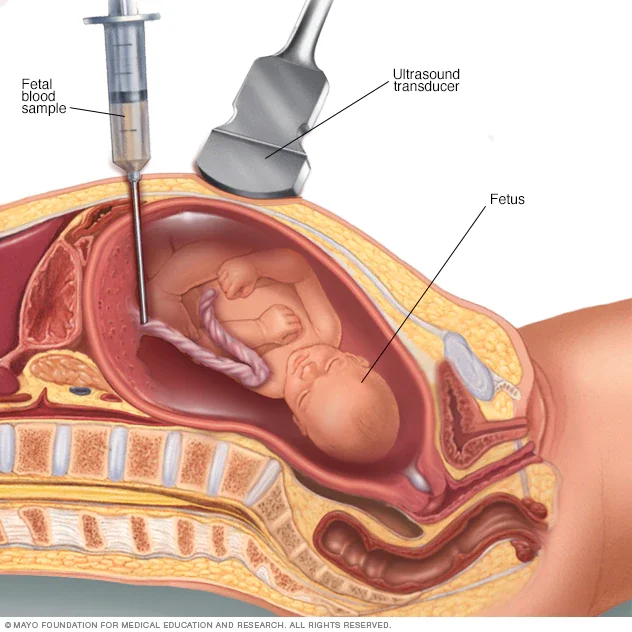
4. Cordocentesis
- Fetal blood sample from the umbilical cord.
Indication:
- Diagnostic: For chromosomal abnormalities.
- Therapeutic: Intrauterine blood transfusion. (Hydrops Fetalis - transfusion through the cord)
Result: 1 to 2 days.
Complication:
- RH isoimmunization.
- Miscarriage.
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- PROM.
Fetal Growth
If there are maternal or fetal risk High-Risk Patients:
- Previous IUGR.
- Previous IUFD (Intrauterine Fetal Death).
- Diabetic.
- Multiple pregnancies.
- Hypertensive.
- Preeclampsia.
Methods to Assess Fetal Growth:
- Confirming GA (Gestational Age).
- By: History, Early U/S, Examination: Fundal height.
- Biochemical Tests:
- Maternal blood sample.
- Placental hormones and enzymes; Estradiol, Human placental lactogen (Not used anymore).
Fetal Wellbeing
Tools to Assess Fetal Wellbeing:
History of Fetal Movement.
- Normal fetal movement is 10 per day.
- Multipara feels it earlier than primipara. In late months of pregnancy maybe the movement be less than before.
A. US (Ultrasound):
- Fetal growth.
- Biophysical Profile:
- Fetal movement.
- Amniotic Fluid Index.
- Fetal Tone.
- Breathing.
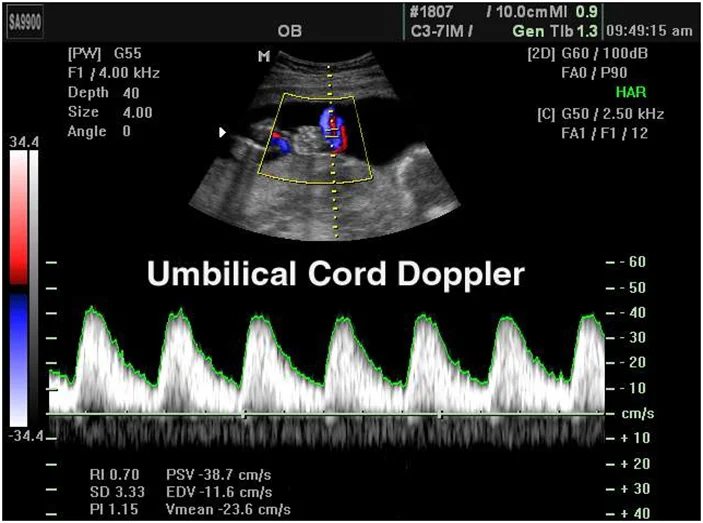
- Doppler Flow:
- Middle Cerebral Artery.
- Umbilical Cord.
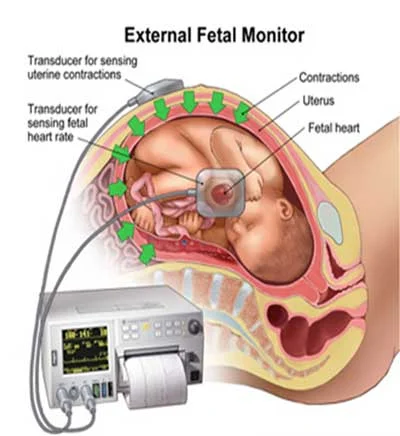
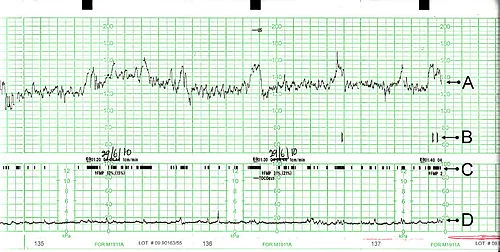
- B. CTG (Cardiotocography): Monitor fetal heart.
- C. Biochemical Tests:
- Placental hormones and enzymes; Estradiol, Human placental lactogen (Not commonly used).
Fetal Maturity
- Confirm Gestational Age.
- Amniocentesis; Surfactant.
- X-Ray → (ossification) not used now.
Mother’s Complaint & Decrease in Fetal Movement
- Biophysical Test (Better) vs. Biochemical Test.
- Direct vs. Indirect methods.
- Fetal kick count used as screening.
- CTG (non-invasive).
In ER: Do modified Biophysical Profile.
- Components:
- AFI → Liquor.
- CTG.
- Both should be normal to say the fetus has a normal modified biophysical profile.

FM
B.2: Fetal Assessment
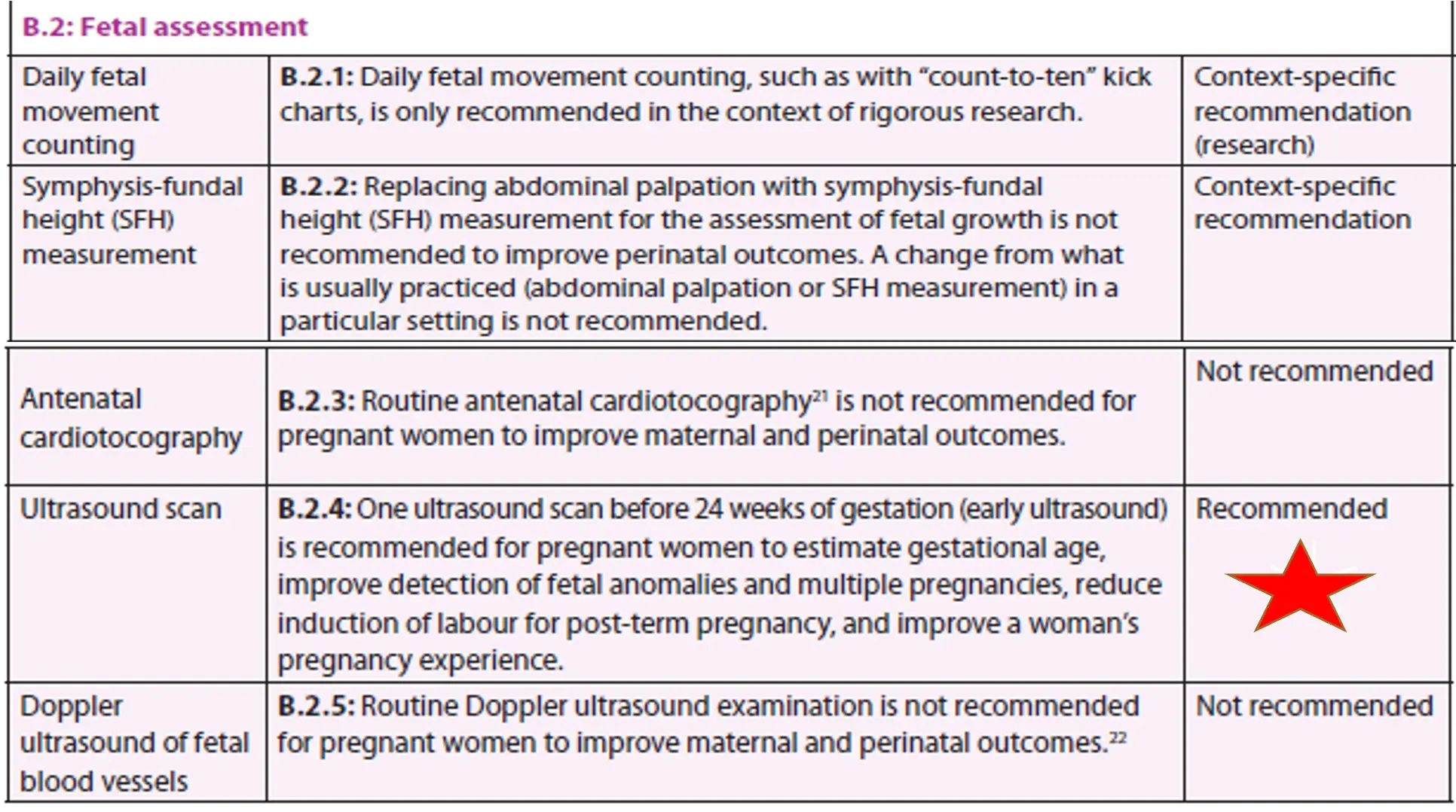
Daily Fetal Movement Counting
- B.2.1: Daily fetal movement counting, such as with “count-to-ten” kick charts, is only recommended in the context of rigorous research.
- Context-specific recommendation (research)
Symphysis-Fundal Height (SFH) Measurement
- B.2.2: Replacing abdominal palpation with symphysis-fundal height (SFH) measurement for the assessment of fetal growth is not recommended to improve perinatal outcomes. A change from what is usually practiced (abdominal palpation or SFH measurement) in a particular setting is not recommended.
- Context-specific recommendation
Antenatal Cardiotocography
- B.2.3: Routine antenatal cardiotocography is not recommended for pregnant women to improve maternal and perinatal outcomes.
- Not recommended
Ultrasound Scan
- B.2.4: One ultrasound scan before 24 weeks of gestation (early ultrasound) is recommended for pregnant women to estimate gestational age, improve detection of fetal anomalies and multiple pregnancies, reduce induction of labour for post-term pregnancy, and improve a woman’s pregnancy experience.
- Recommended Z
Doppler Ultrasound of Fetal Blood Vessels
- B.2.5: Routine Doppler ultrasound examination is not recommended for pregnant women to improve maternal and perinatal outcomes.
- Not recommended