Cervical Cancer
Overview
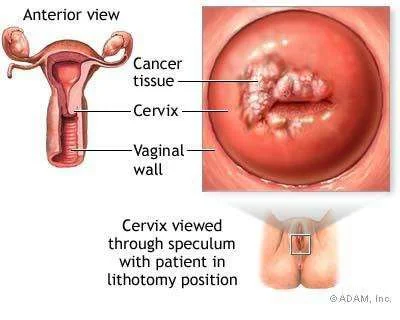
Cervical cancer is cancer of the uterine cervix.
Cervix viewed through speculum with patient in lithotomy position

Epidemiology
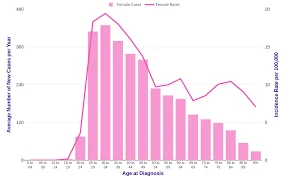
- Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women.
- In 2018, an estimated 570,000 women were diagnosed with cervical cancer worldwide
- about 311,000 women died from the disease.
- Effective primary (HPV vaccination) and secondary prevention approaches (screening for, and treating precancerous lesions) will prevent most cervical cancer cases.
Pathophysiology
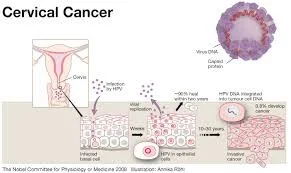
- Cervical cancer starts with abnormal changes in the cellular lining of the cervix.
- Typically these changes occur in the squamous-columnar junction of the cervix.
- Here, columnar epithelial cells meet the protective flat squamous epithelial cells from the outer cervix and vagina in what is termed the transformation zone.
- The continuous replacement of columnar epithelial cells by squamous epithelial cells in this area makes these cells vulnerable to take up foreign or abnormal genetic material
Cervical Cancer Aetiology
- Cervical cancer is a sexually transmitted disease. HPV is the primary cause of cervical cancer. Some strains of HPV have a predilection to the genital tract and transmission is usually through sexual contact.
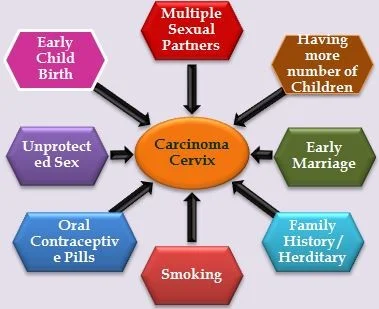
Cervical Cancer Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Giving birth to more than 7 children
- having first child before 17yrs
- Number of sexual partners
- Early age of intercourse
- weak immune system
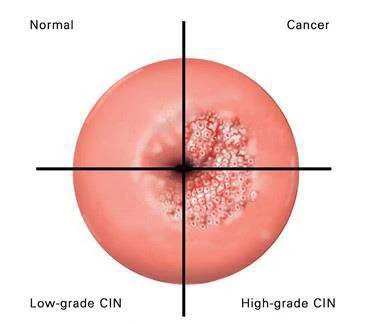
The stages of cancer progression
The pre-cancerous stage before the cells turn cancerous is called Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
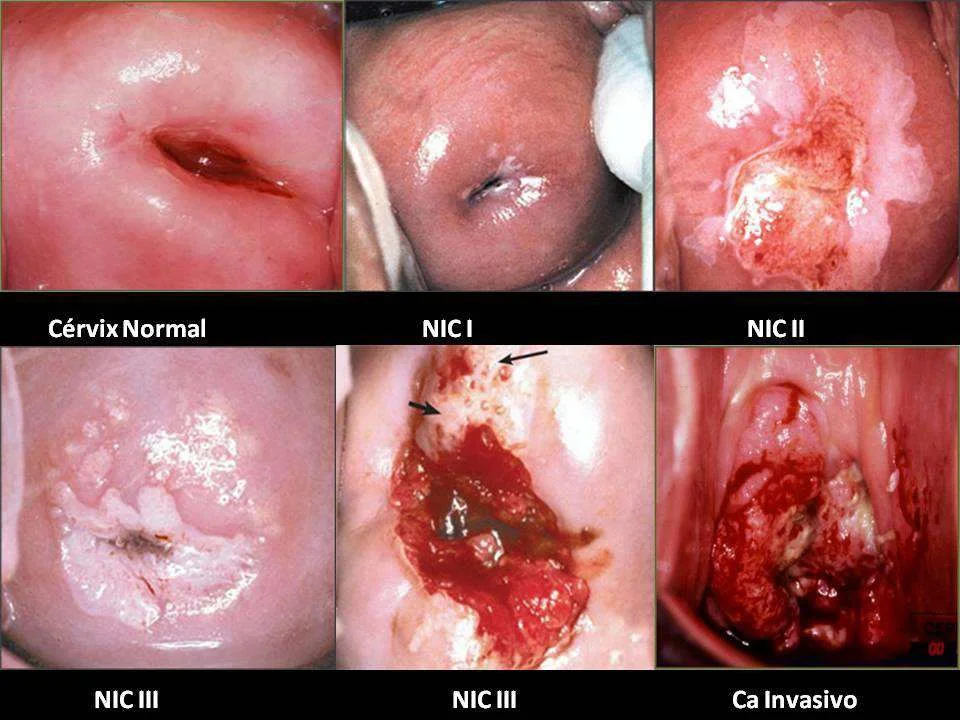
Cervical Pathology Images
Clinical Manifestations
- May be silent until advanced disease develops
- Symptoms of Invasion:
Assessment
- History
- Physical examination
- Investigation:
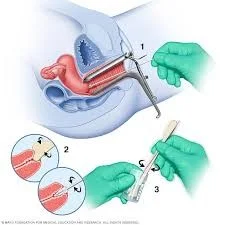
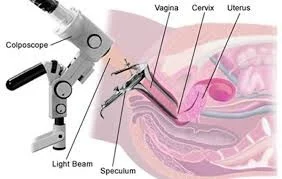
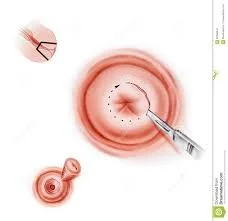
Treatment
- Treatment of Early Disease
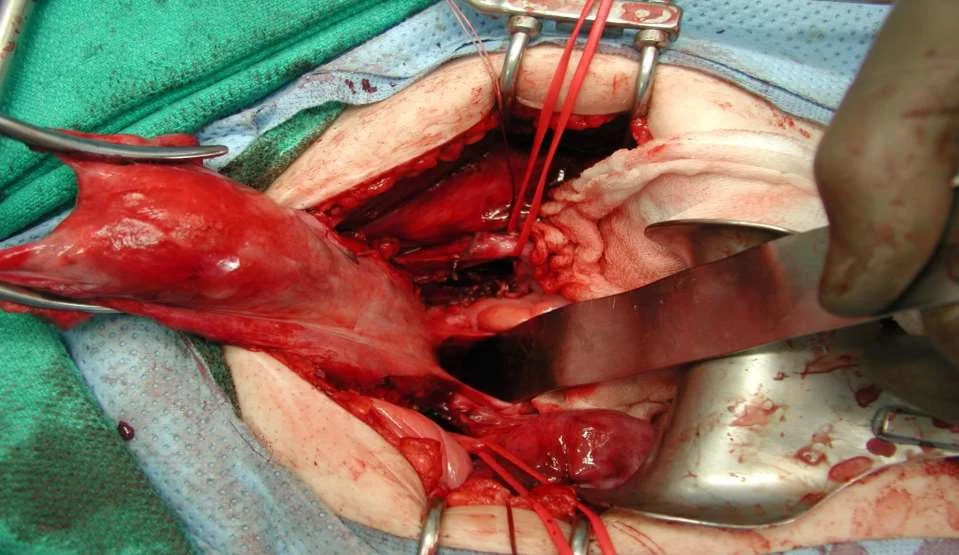
- simple hysterectomy Z
- microinvasive cancer Radical hysterectomy -removal of the uterus with its associated connective tissues, the upper vagina, and pelvic lymph nodes..
- Chemoradiation therapy
- Advanced Staging
- Chemoradiation
Five types of standard treatment are used:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
Radical Hysterectomy - removal of the uterus