Prepregnancy Counselling
To clarify quantify . minimize
risk of pregnancy from any pre-existing medical condition or lifestyle pattern of either partners that affect reproductive outcome.
Prepregnancy Visit
- Optimize maternal health.
- Identify and treat or optimize any pre-existing disease.
Who Will Do Prepregnancy Counselling?
MDT (Multi-Disciplinary Team) consisting of:
- Obstetrician.
- Nurse.
- Midwife.
- Anesthetist.
- Others according to needs.
Plan
I. Revise
- Patient history.
- Lifestyle.
- Medications. Vit A … ↝ lead to congenital Anomaly
II. Optimize Optimize the previous points.
III. Do Examination
IV. Investigation Basic investigations according to need.
V. Medication We give “Folic Acid” 400 microgram/day only ↝ give Folic acid. high doses in some studies showed association with Autism
- In high doses:
- Hx of Congenital Anomaly ‘spinal Bifida’
- Diabetic delivery
- Epilepsy “liver drugs” “Folic Acid consuming drugs” / methotrexate “chelating - consuming”
- Rheumatic disease
- Malabsorption
- Hx of Congenital Anomaly ‘spinal Bifida’
Guidelines for Treating Women with Respect and Dignity
- Treat women with kindness and dignity.
- Respect her cultural and religious beliefs.
- Services should be accessible & continuous.
- Appropriate, verbal and written information on which women can base their choices & decisions.
Who Will Provide Care
- Community-based team of:
- Midwives
- And family practitioners (such as GPs)
- A hospital consultant team.
- Or a combination of the two.
- Hospital-based obstetric team:
- For complex pregnancies.
- They are said to have consultant care.
Primary components
- early registration and first checkup within first trimester (12 wk)
- Minimum 4 antenatal check ups; at least one ANC by M.O (Preferably 3rd ANC)
- Vaccination
Essential components
- History taking
- physical examination (Weight, BP, Pallor, Respiratory rate, Edema)
- Abdominal examination
- Laboratory investigation
- (Hb % Urine for sugar and proteins)
Desirable components
- Blood‑group & Rh typing
- Screenings: HIV, hepatitis, blood‑sugar
Counselling – key points
- Discuss delivery & birth preparedness
- Recognise danger signs & symptoms during pregnancy, labour, and the post‑natal period
- Outline a plan for complicated management
- Emphasise diet, rest, and family‑planning
New‑born care
- Initiation of exclusive breast‑feeding (EBF)
- Guidelines for supplementary feeding when needed
- Schedule of immunisations
How to Diagnose Pregnancy
From:
- History. Amenorrhea, N/V
- Examinations. Distended abdomen
- Investigations. BhCG in urine but blood accurate
History
- Amenorrhea.
- Symptoms & signs of pregnancy. as a first presentation, N/V
- Quickening. 16-20wk usually In 4 months “In lactating or women with irregular menses”
Examinations
Signs of pregnancy in face, neck & breast. Abdominal examination:
- inspection.
- palpation of Fetal parts & fundal height:
- At symphysis pubis 12 weeks
- At umbilicus 22 weeks.
- At xiphisternum 36 weeks.
- Auscultation FHS.
Investigations
A. Lab Investigations
- Urinary pregnancy test.
- most accurate
- Serum bHCG test.
- Quantitative bHCG.
- when to do?
- in Miscarriage susceptibility + ectopic pregnancy
- “normally” should double every 48h
- but ‘in this case’ will be less !!!
- or Molar pregnancy
- L will be more than the double
B. Images
- Ultrasound (AUS & TVUS).
Pregnancy Symptoms
Pregnancy is a time of great uncertainty and stress and physical changes experienced by the woman.
- Common symptoms include:
- Nausea.
- Heartburn.
- Constipation.
- Abdominal Discomfort.
- Shortness of breath.
- Dizziness.
- Swelling.
- Backache.
- Headaches.

Generally these reflect physiological adaptation to pregnanc ;… . CC File
Pregnancy Trimesters
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters:
- First trimester: 0-13 weeks
- Second trimester: 14-26 weeks
- Third trimester: 27-40 weeks
Why Divide Pregnancy into Trimesters?
- For the purpose of good follow-up as any trimester has its own features and changes.
Visits Schedule
-
Two times in the first trimester
-
Two times in the 2nd trimester
-
Monthly in the 3rd trimester till 36 weeks, then every two weeks till delivery.
Pregnancy Trimester & Visit Schedule Integrated Pregnancy Trimester & Care Table
| Trimester | Weeks (gestation) | Visit Frequency / Timing | Core Care Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 0 – 13 | 2 visits (including the booking visit) | • Detailed maternal history • Physical examination • Routine investigations (blood work, urine, etc.) • Dating scan; age of baby • Folic‑acid supplementation • Identify risk factors → referral to obstetric consultant or other specialists as needed (medical/psychosocial support) |
| Second | 14 – 26 | 2 visits (mid‑pregnancy) | • Anomaly scan (done at 18‑20wks) – fetal anatomy assessment • Iron Supplementation - • Vaccination • Ask about quicknening • Routine investigations each visit: – Full Blood Count (FBC) – Urinary analysis (UG) • Thyroid screening if prior history (each trimester) • Gestational diabetes (DM) screening – performed at each visit when indicated - Z |
| Third (early) | 27 – 36 | Monthly visits | (Follow up) • Maternal clinical assessment • Routine investigations (e.g., hemoglobin, glucose, urine) • Routine obstetric examinations • Ultrasound to reassess fetal growth & well‑being • Discuss mode of delivery & develop a written delivery plan |
| Third (late) | 37 – 40 | Every 2 weeks until delivery | • Continued maternal clinical assessment • Same routine investigations as early third trimester • Focused ultrasound if indicated • Finalize delivery plan & mode of delivery • Breast‑feeding education and postpartum preparation |

First Trimester
- First interactions booking visit:
-
Detailed history.
-
Examine the woman.
-
Routine investigations.
-
- If risk factors are identified specialized services:
-
This may mean referral to a hospital consultant obstetrician** or other specialist services as appropriate.
-
Medical or psychosocial issues offered.
-
Dating scan
-
Give folic acid.
-
-

Examinations in Booking Visit
- Height and weight should be measured at the booking visit.
- Body mass index (BMI) calculated and assessed.
- General pregnancy dietary advice (balanced meals).
- Blood pressure assessment.

Booking Tests
-
Full blood count (FBC)
- To identify women with anemia,
- to allow early initiation of treatment.
- Also to identify low platelets. (low platelet in the 1st trimester warrants further investigation).
-
Blood group & Rh status.

Antenatal Screening
- Gestational diabetes screening.
- Thalassemia Sickle cell screening.
- Infections screening:
- Rubella
- Syphilis
- Hepatitis B & C HIV
- Ultrasound for first trimester dating.
- Vitamin D deficiency


Second Trimester Care
Very Important
- Anomaly scan Between 20 and 22 weeks’ gestation it is recommended that fetal anatomy be assessed.
Every visit z
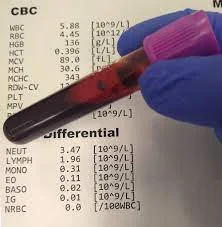
- Routine investigations:
- FBC Full blood Count
- UG.
If indicated: → each trimester
- Thyroid screening. Each trimester if there’s a history
- DM screening. Each visit

Third Trimester
- Assess the mother clinically.
- Routine investigations.
- Routine examinations.
- US to assess the baby.
- Discuss mode of delivery.
- Written plan for delivery.
- Breastfeeding education.

