Closed Injury
Intracranial hematoma:
Is a collection of blood within the skull, most commonly caused by rupture of a blood vessel within the brain or from trauma. There are four types:
- Epidural hematoma.
- Subdural hematoma.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage.
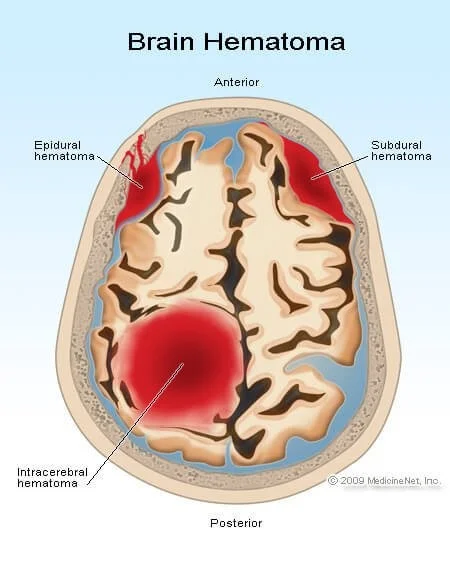
Epidural hematoma
Is a traumatic accumulation of blood between the inner table of the skull and the outer covering of the brain called (dura).
- Lacerated middle meningeal artery
- Fall, RTA, Strike on side of skull
- 90% have skull # (squamous portion of temporal bone)
Signs and symptoms:
- Headache (severe)
- Nausea/vomiting
- Seizures

Subdural Hematoma
Is a collection of blood below the inner layer of the dura but external to the brain and arachnoid membrane.
- Often around the tops and sides of the frontal and parietal lobes. Signs and symptoms:
- A history of recent head injury
- Pain
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Irritability
- Inability to speak or slurred speech

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: SAH
Is bleeding into the subarachnoid space the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain. Traumatic SAH: Blow to lateral neck with resulting damage to Vertebral Artery. Signs and symptoms:
- Thunderclap headache.
- Oculomotor nerve abnormalities.
- Neck stiffness.
- Increase in blood pressure.
- Cardiac arrhythmias

Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Is when blood suddenly bursts into brain tissue, causing damage to the brain.
Signs and symptoms:
- Patients with intraparenchymal bleeds have symptoms that correspond to the functions controlled by the area of the brain that is damaged by the bleed.
- Other symptoms include those that indicate a rise in intracranial pressure caused by a large mass putting pressure on the brain.
Concussion
Also known as mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) is typically defined as a head injury with a temporary loss of brain function.
Signs and symptoms:
| Physical | Cognitive and emotional |
|---|---|
| Headache is the most common mTBI symptom. | slow to respond to questions or directions or incoherent speech |
| Vomiting, nausea | Difficulty focusing attention |
| Lack of motor coordination | Loss of consciousness. |
| Problems with movement or sensation. | Disorientation. |
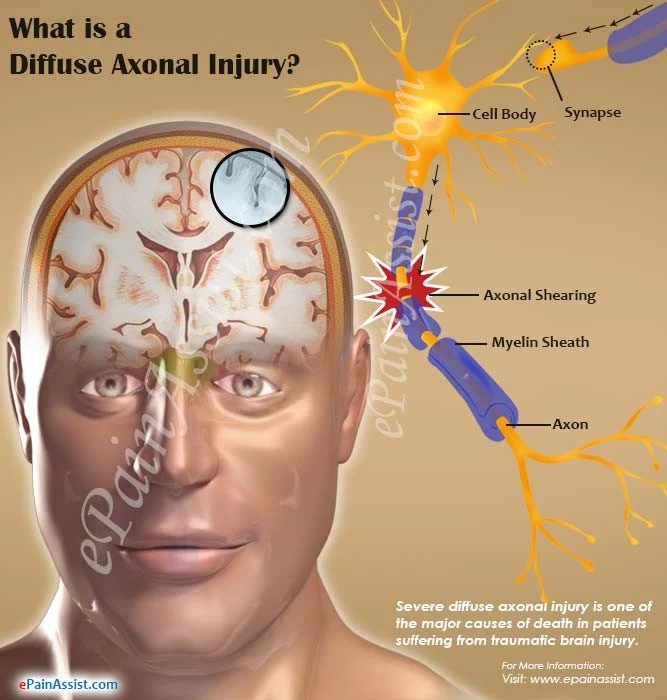
Diffuse Axonal Injury
Is form of traumatic brain injury.it happens when the brain rapidly shifts inside the skull as an injury is occurring. the long connecting fibers in the brain called axons are sheared as the brain rapidly accelerates and decelerates inside the hard bone of the skull. Z RR
Symptoms:
- Disorientation or confusion
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Trouble sleeping
- loss of balance or dizziness
Brain Contusion
SEVERE traumatic brain injury, like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple micro-hemorrhages, small blood vessel leaks into brain tissue.
Signs and symptoms: The symptoms of a cerebral contusion (bruising on the brain) depend on the severity of the injury, ranging from minor to severe.
Causes: Often caused by a blow to the head, contusions commonly occur in coup or contre-coup injuries.