Ankle Fractures
Epidemiology and Mechanism
- Incidence increased in elderly women
- Most are isolated malleolar fractures
- Mechanism of injury:
- Position of the foot at time of injury
- Magnitude, direction, and rate of loading

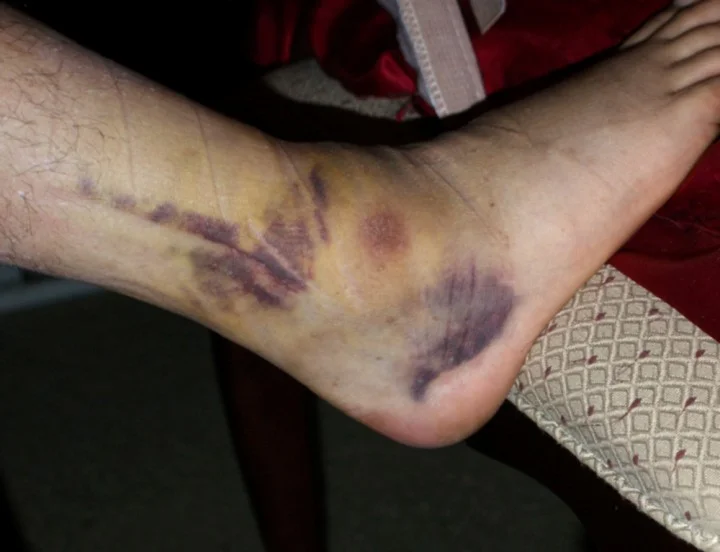
Evaluation
- Clinical
- A dislocated ankle should be reduced and splinted immediately (before radiographs) if clinically evident
- Radiographic
- AP, Lateral and
- Mortise views

Radiographic Views
- AP view
- Tibiofibula overlap of <10 mm is abnormal:
- Syndesmotic injury
- Tibiofibula & /Tibiofibula/ media clear space of >5 mm is abnormal:
- Syndesmotic injury
- Talar tilt
- Tibiofibula overlap of <10 mm is abnormal:


- Lateral view
- The dome of the talus should be centered under the tibia and congruous with the tibial plafond
- Posterior tibial malleolus fractures can be identified

- Mortise view
- Ap with foot in 15° of internal rotation
- A medial clear space
- Tibiofibular overlap
- Talar shift
Important to assess syndesmotic injury


Ankle views
- AP, Lateral, and Ankle mortise views

Classification and Treatment
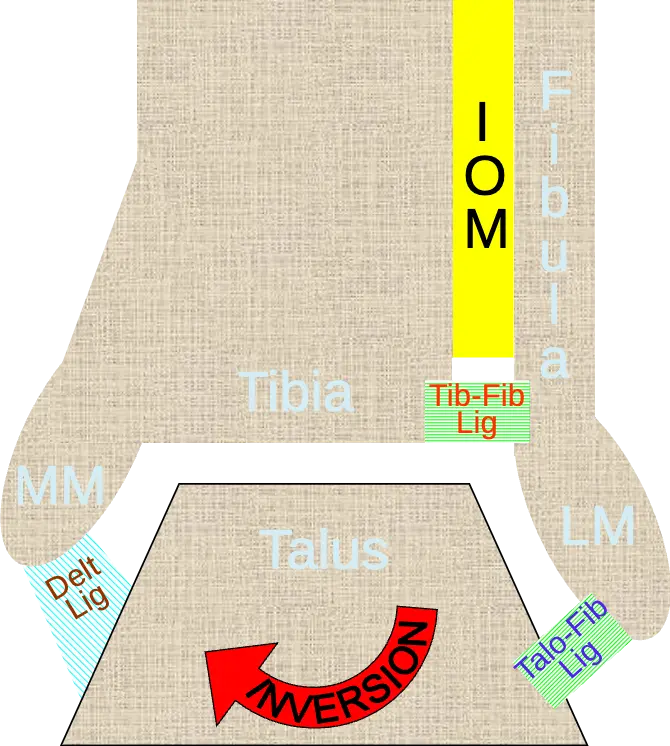
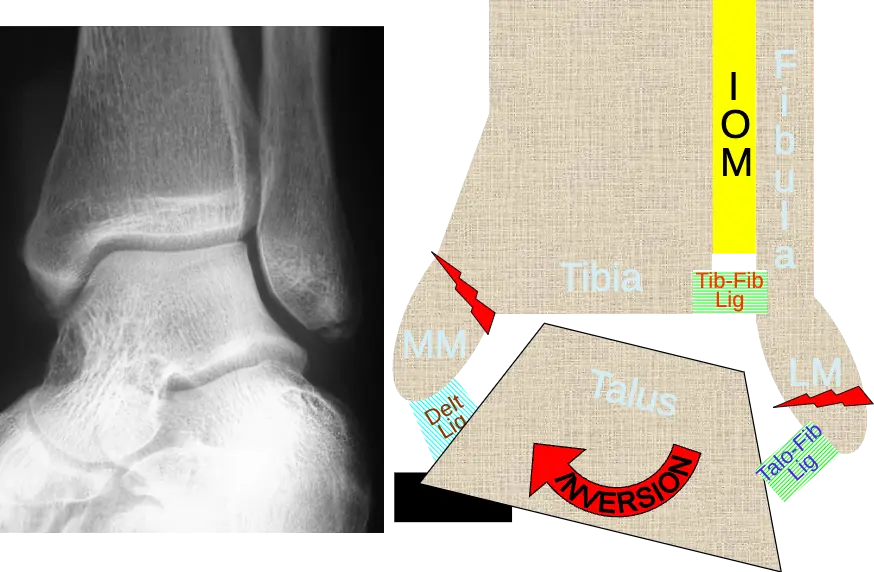
- Denis -Weber classification
- Based on fibular fracture:
- A. Infra-syndesmotic
- B. Trans-syndesmotic
- C. Supra-syndesmotic:
- usually syndesmosis is torn
- Based on fibular fracture:

Mechanism of injury









- Treatment
- Undisplaced:
- Below knee cast (NWB)
- Indications for ORIF
- All fracture-dislocations
- All type C fractures
- Tri-malleolar fractures
- Talar shift or tilt
- Failure to achieve or/maintain closed reduction
- Undisplaced:

Decision-making and stability


Operative

Complications
- Post traumatic arthritis
- Stiffness
- Skin necrosis
- Malunion / Nonunion
- Wound infection
- Complex regional pain syndrome
Fractured Talus


Complications: AVN

Calcaneal Fractures
Mechanism and Associated Injuries
- Fall from height
- Associated injuries – must always exclude
- Fracture neck femur
- Compression of spine
Imaging
- X-rays: Lat, & Axial view
- CT scan: shows details


Treatment
- Treatment:
- Conservative
- Extra-articular fractures
- Undisplaced fractures
- Severely comminuted
- No expertise
- Operative
- Intra-articular fractures
- Conservative

Metatarsal Fractures
Epidemiology and Types
- Common
- Sport injury / others
- 5th is the commonest
- followed by 1st & 2nd
- Types:
- Acute trauma / Stress
- Closed / Open
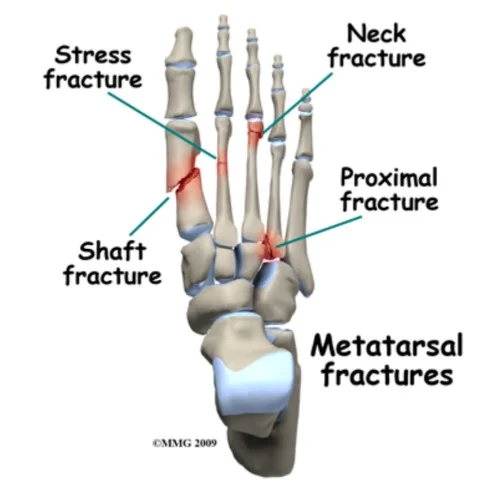
5th Metatarsal Fractures
- Types: Avulsion – Base – Shaft - Neck

Treatment
- Treatment
- Usually conservative
- May need surgery if unstable and multiple
