RAPE
Medicolegal view
Rape defined as unlawful sexual intercourse by a man with a woman:
- Against her will; without her consent;
- With her consent, when;
- Her consent has been obtained by putting her or any other person in whom she is interested in fear of death or hurt
- With her consent, when the man knows that he is not her husband and that her consent is given because she believes that he is her lawful husband
- With her consent, when at the time of giving such consent, by reason of unsoundness of mind or intoxication
TYPES OF RAPE:
- Statutory Rape: It is a forcible sexual intercourse by a man with a woman, who is less than 16 years of age.
- Marital Rape. Also called as spousal rape. It is a forcible sexual intercourse by a man with his wife without her consent if the Wife is living separately from him under a decree of separation.
- Custodial Rape (Custody Rape). It is done by persons taking advantage of their custodial positions and has forceful sexual intercourse with woman in their custody.
- Gang Rape. Also called as group rape or pack rape. When rape is committed on a female by more than one person acting in furtherance of their common intention, it is called as gang rape.
- Date Rape. It is a forcible sexual intercourse by a boyfriend with girlfriend when they are on date (for stay or vacation). In such cases, the girl may allege that her boyfriend had given her some intoxicant and proceeded with the act
- Stranger Rape: It is the rape committed by a male on a female who had no previous contact
MEDICAL EXAMINATION OF RAPE VICTIM
Some mandatory points for examination:
- Examined within 24 hours after taking proper consent
- Always examined in presence of female
- Note the time of start and the time of end
- Always state reasons for all conclusions
- It is necessary to keep samples for examination of blood, stains, semen, swabs, sweat, hair, nails, DNA etc as required
Responsibilities of Doctors Examining Rape Victims:
- Doctors examining a victim of rape are shouldered with dual responsibilities,
- Firstly, they have to treat the patient and provide support and
- Secondly, they have to examine the victim and collect material evidences to facilitate and aid justice.
- A female nurse or attendant should be present while examining the victim.
- Whenever a female has to be examined, it should be done by (or under the supervision) of a lady doctor.
DUTIES OF REGISTERED MEDICAL PRACTITIONER TOWARDS STATE
- Consent
- Confidentiality
- Maintenance Of Records
- Collection And Preservation Of Samples
STEPS IN SPECIFIC CASES:
- IN RAPE CASE
- Inform the police
- After taking consent, medicolegal examination and treatment given
- Samples for examination of blood, stains, semen, swabs, sweat, hair, nails etc preserved, sealed, labeled and sent to police under proper receipt
- Send report as early as possible
THE MEDICAL EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF:
- Recording history
- Examination of clothes
- Physical examination
- Collection of material evidence.
CONSENT
- Written informed consent of a victim is a must.
- Without consent, the doctor cannot proceed with medical examination.
- A victim of and over 18 years of age can give consent.
- If she is a child under 18 years of age or of unsound mind, the consent of parent or guardian should be taken.
PREPARATION OF MEDICOLEGAL REPORT
- Medicolegal report (MLR) prepared immediately after the examination of a medicolegal case is done
- It is prepared in duplicate, preferably with a ball-point-pen, in clear and legible handwriting
- Cutting/ overwriting etc avoided as much as possible.
- Abbreviations of any sort avoided.
HISTORY:
- VICTIM
- CONDITION
- ASSAILANT
The History OF VICTIM
The history includes
- ?Whether the victim had attended menarche
- ?If yes, whether she was menstruating at the time of alleged incident
- .Her marital status and history
- .Obstetric history, if relevant
- .History of any venereal disease
The History OF CONDITION
History about the incident; , ,date ,the time,the location ;Nature of assault, whether penetration was
- vagina.
- anal.
- oral.
EXAMINATIONS OF CLOTHES:
Should be examined for tears or presence of any foreign materials like hair, secretions or blood.


Physical Examination:
- Request the victim to stand on a large clean, white sheet of paper and undress herself. The purpose is to collect any material evidence that falls on the paper.
I. General Examination:
II. Local Examination:
- PUBIC HAIRS
- THIGH
- LABIA
- HYMEN: It is said that tears of the hymen due to rupture with fingers are usually lateral, whilst rupture with the penis are usually posterior.
In children, hymen may not be ruptured but becomes red and congested because the hymen is deeply situated.
Hymen may not be ruptured if:
- If penetration was not full
- If the victim happens to be a female child as the hymen is deeply situated
- If the hymen is tough, fleshy, elastic (false virgin).
- Defoliated female
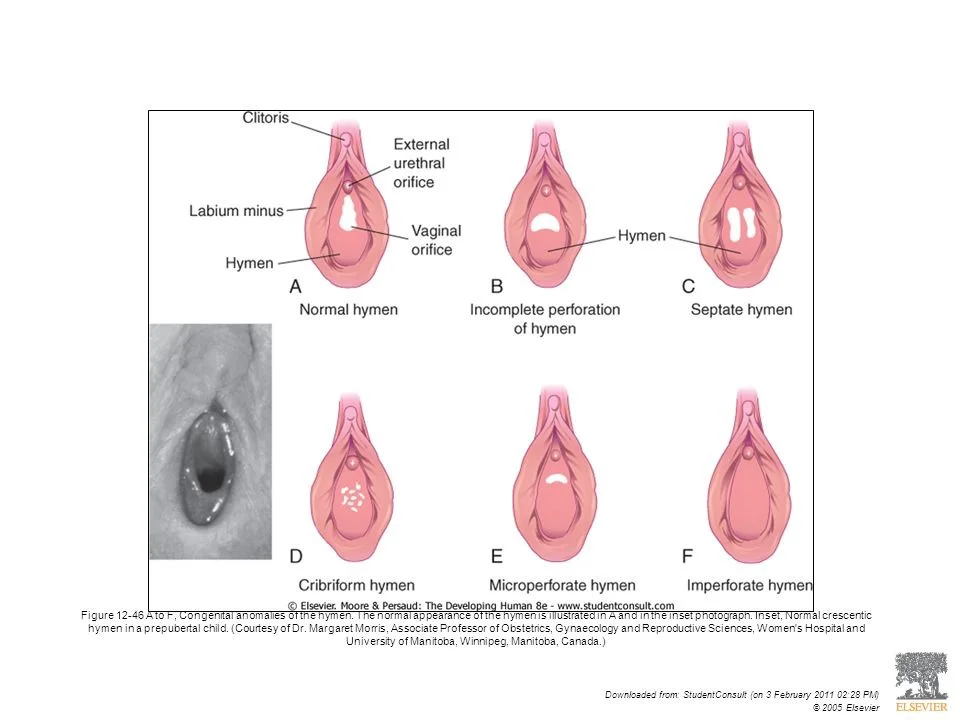
Types of Hymen
The image illustrates various types of hymens, which are labeled and described below:
- A. Normal hymen
- Clitoris
- Labium minus
- Hymen
- External urethral orifice
- Vaginal orifice
- B. Incomplete perforation of hymen
- C. Septate hymen
- D. Cribriform hymen
- E. Microperforate hymen
- F. Imperforate hymen
Physical Examination Cont:
- Vagina Look for any vaginal bleeding Look at vaginal mucosa for presence of any;
- Injury,
- foreign body. Rugae of vaginal wall – distinct or not distinct.
- Vaginal canal and fornix for collection of
- any fluid/semen.
The examination should include deep vaginal examination, as occasionally, high vaginal tears occur, especially in violent assaults on children.
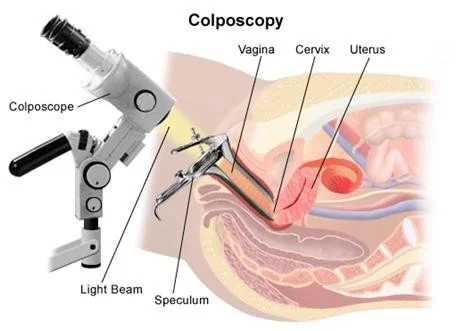
Colposcopy - provides magnification in a range of 5 to 30 times and greater illumination and thus helps in detection of minor trauma. Many authorities recommend the use of colposcopy examination in sexual assault victims.
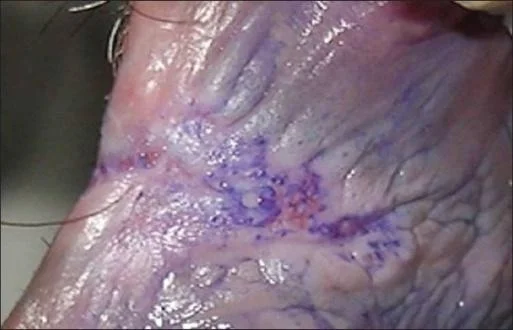
Toluidine blue - Toluidine blue stains nuclei and is used on the posterior fourchette to identify lacerations of the keratinized squamous epithelium that are not apparent on gross visualization.
Physical Examination Cont:
ANUS - look for any:
- Discharge.
- Injury
- Hemorrhage.
SAMPLES TO BE COLLECTED from VICTIM
-
Clothes.
-
Foreign evidentiary material - like hair, fiber, button etc.
-
Fingernail scrapings
-
Scrapings from suspected stain marks from body surface.
-
Scalp hairs - for comparison with scalp hairs found over body/clothes of alleged accused
-
Swab from teeth bite mark
-
Combing of pubic hairs
-
Hair clipping of victim.
-
Vaginal swab/smears, cervical smears.
-
Washings of posterior fornix of vagina for:
- Detection of spermatozoa.
- Presence of mycobacterium smegmatis (smegma bacilli)
- Presence of sexually transmitted disease
- Blood for;
- Serology
- Pregnancy test
- presence of drug/intoxicant
- DNA profiling
- For venereal disease.
- Urine for
- Pregnancy test
- Detection of alcohol.
- Condom if found at the scene of crime - laboratory examination of condom may reveal presence of blood/vaginal epithelial cells on one side and semen on the other. Pubic hairs may also be present. DNA profiling of semen may be of help.
- Spermatozoa - motile sperm found in endocervix up to seven days after intercourse
- Semen not likely to be found in the mouth after a few hours
- Sperm not recovered if the assailant is azospermic or vasectomized
- Acid phosphatase found up to 12 hours after intercourse in 50% vaginal swabs. Also found after a vasectomy
- Anal intercourse - semen may be found up to 3 days later
Summary of Sample to be taken
- Clothing.
- Sheet of paper.
- Head hair (cut/combed).
- Pubic hair (cut/combed).
- Saliva.
- Mouth swab.
- Venous blood (EDTA/preserved).
- Penile swab.
- Anal swabs.
- Vaginal swabs.
- Fingernail scrapings.
- Skin samples (UV light).
TREATMENT
- Physical injuries
- Psychic trauma.
- Hepatitis B vaccine.
- Chlamydia Prophylaxis Azithromycin 1g.
- Prevent pregnancy:
- Contraceptive pills
- IUD.
Physical Examination of Accused:
The medical examination consists of:
- Recording history
- Examination of clothes
- Physical examination
- Collection of material evidence
CONSENT CLOTHES General Physical Examination
Systemic medical examination should be done. Examination of the Penis
- swelling,
- tenderness and
- injury especially to the rim of the glans and the frenulum.
- Examine the shaft of penis for presence of vaginal epithelial cells and/or for presence of bloodstains. Glycogen-rich vaginal epithelial cells may be detected from the penis in sexual assault.
- Potency.
The Smegma:
Is thick, cheesy whitish secretion with disagreeable odor comprising desquamated epithelium and smegma bacilli (Mycobacterium smegmatis).
It takes about 24 hours to collect the smegma on corona glandis. The smegma is wiped out during the act of sexual intercourse.
Therefore, the presence of smegma indicates non-participation of a male in the recent sexual intercourse act. However, caution should be exercised because the smegma may be removed by a person during daily baths as part of maintaining local hygiene.
Wipe the shaft of penis with moist filter paper and exposed to vapors of Lugol’s iodine.
Development of brown color indicates the presence of glycogen-rich vaginal epithelial cells. Similarly, microscopic examination may also show vaginal epithelial cells.
COMPLICATION OR DANGERS OF RAPE
-
Hemorrhage and shock due to injuries sustained to genitals or perineum
-
Death may occur due to:
- Assault to obtain consent or put her in fear.
- By suffocation - to prevent shouting
- Strangulation - to hide the crime.
- Suicide - due to depression or frustration of being raped
- Intoxicants - overdose or adulteration.
-
Mental agony, which disrupts the victim’s physical, social, mental and sexual life.
-
Rape trauma syndrome: The syndrome includes behavioral, somatic or psychosocial reaction to the act of forceful sexual intercourse. It is regarded as post-traumatic stress disorder. The syndrome has been defined in two stages.
Complications OR DANGERS OF RAPE Cont.
Immediate - the phase of disorganization characterized by feeling of guilt and humiliation.
Delayed - or phase of reorganization characterized by protracted response in form of recurrent and intrusive recollection of stressful event either in flashbacks or in dreams.
MEDICOLEGAL ASPECTS
- Rape is a legal term and not a medical diagnosis. Whether the rape has taken place or not is a legal conclusion drawn by judicial officer and not by medical doctor.
- Mere penetration by penis up to vulva is sufficient to constitute the sexual intercourse necessary to the offense of rape.