Special Considerations
Beware! Non-Accidental Injuries
Consider Non-Accidental Injuries If:
- Delay in seeking medical attention
- Vague history
- Lacking the “real truth”
- Allegation of assault
- Varying history
- One parent contradicting the other / changing history
- Mechanism incompatible with injury
- Inappropriate parental attitude or behavior
- Lack of concern, over-concern, aggression
- Inappropriate parent-child interaction
- Inappropriate child response
- Features of failure to thrive or neglect
- Chronic illness, repeated hospital visits
- Multiple congenital problems, CP, low IQ
- Signs of prior injury or injuries of different age
- Physical location of injury / Characteristic injuries
- Femoral shaft fracture < 2 years (need strong force)
- Sternal fractures / multiple rib fractures
- Specific radiological features
Need social worker intervention
Physical Examination
- A silent child tells the story!
- Undress the child completely
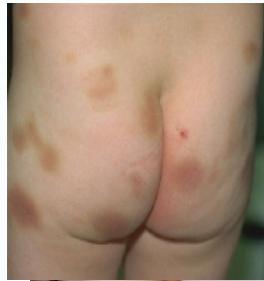
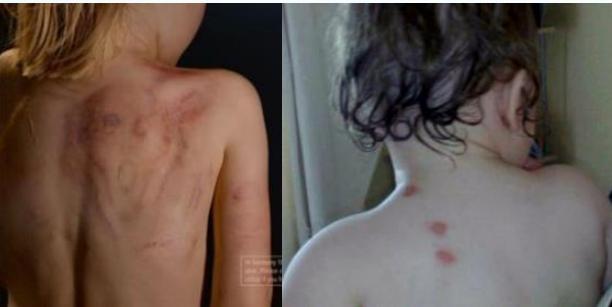
- Look for areas of bruising
- Bruises at different stages of healing
- Bruises take shape of inflicting instrument
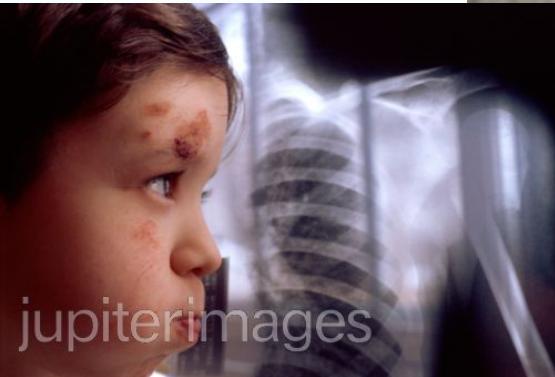
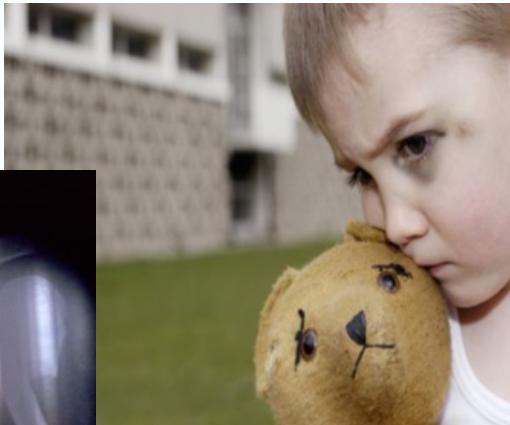
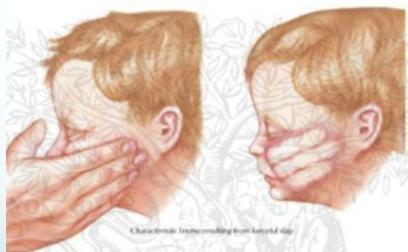

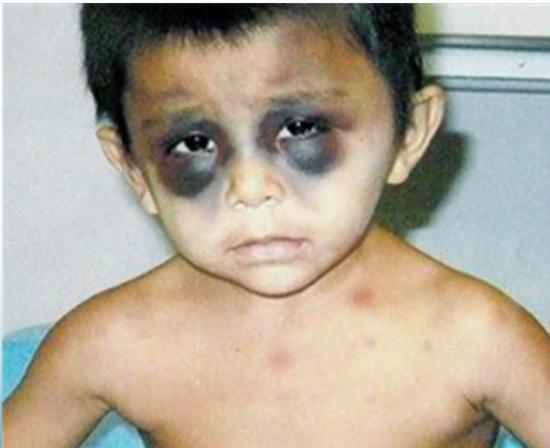
- Head examination - examine for skull trauma, palpate fontanelles if open, consider funduscopic exam for retinal hemorrhage
Specific Non-Accidental Fracture Patterns
- Femur shaft fracture
- <1 year of age (70%)
- Transverse fracture
- Humeral shaft fracture
- <3 years of age
- Sternal fractures
- Specific patterns:
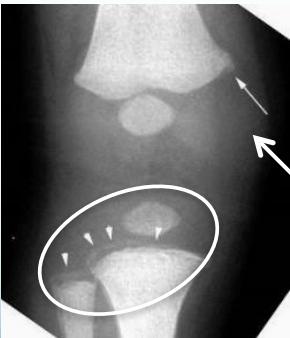
- Corner fractures (traction & rotation)
- Bucket-handle fractures (traction & rotation)
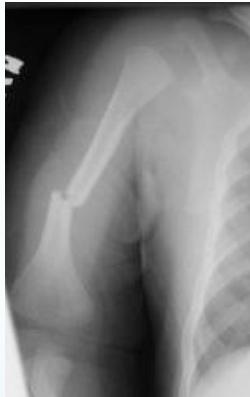
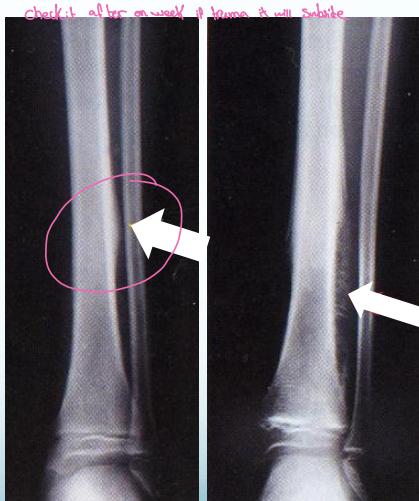
Corner Fractures:
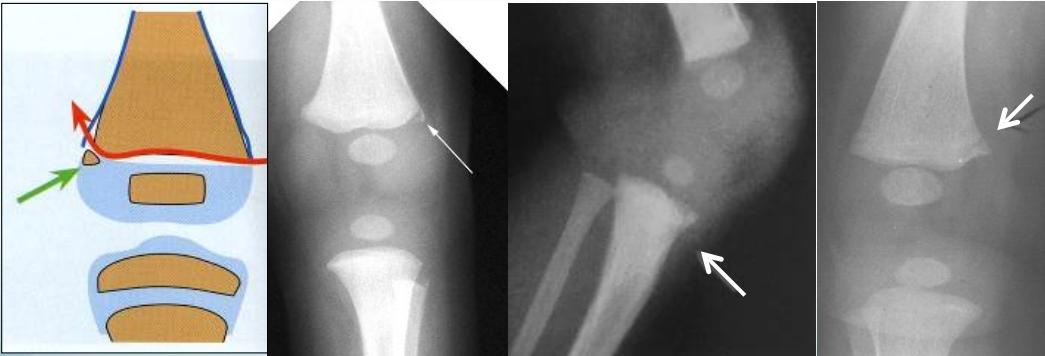
Bucket Handle Fractures:

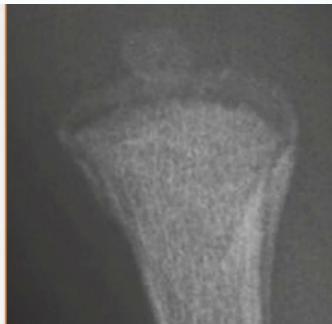
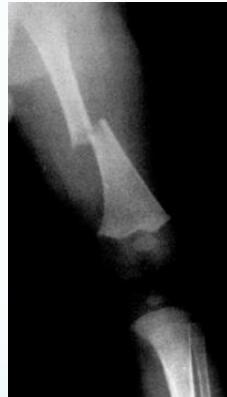
Beware! Malignant Tumors
- Can present as injury
- History of trauma is usual
Case Example:
- 12-year-old girl
- History of trauma
- Mild tenderness
- Periosteal reaction
- Initially diagnosed as injury
- 2 months later, still tender
- Final diagnosis: Ewing’s sarcoma