Surgery
The classic presentation for appendicitis is the relatively slow onset of mid-abdominal pain that eventually localizes in the right lower quadrant with associated nausea and, later, vomiting. Myocardial infarction should always be considered in this age group, and a posterior, or diaphragmatic, infarct is well recognized to cause abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Acute pancreatitis can be caused by either a penetrating (posterior) duodenal ulcer or acute cholecystitis. If vomiting does not relieve the abdominal pain, pancreatitis should be considered.
IMAGING
Acute Appendicitis:
Common acute abdominal condition.
- Symptoms: Pain in the Rt iliac fossa ,Vomiting and fever
- Signs: Tenderness and rebound tenderness in the right iliac fossa
- LAB: Increase white blood count and raised ESR.
Options for first-line imaging in nonpregnant adults
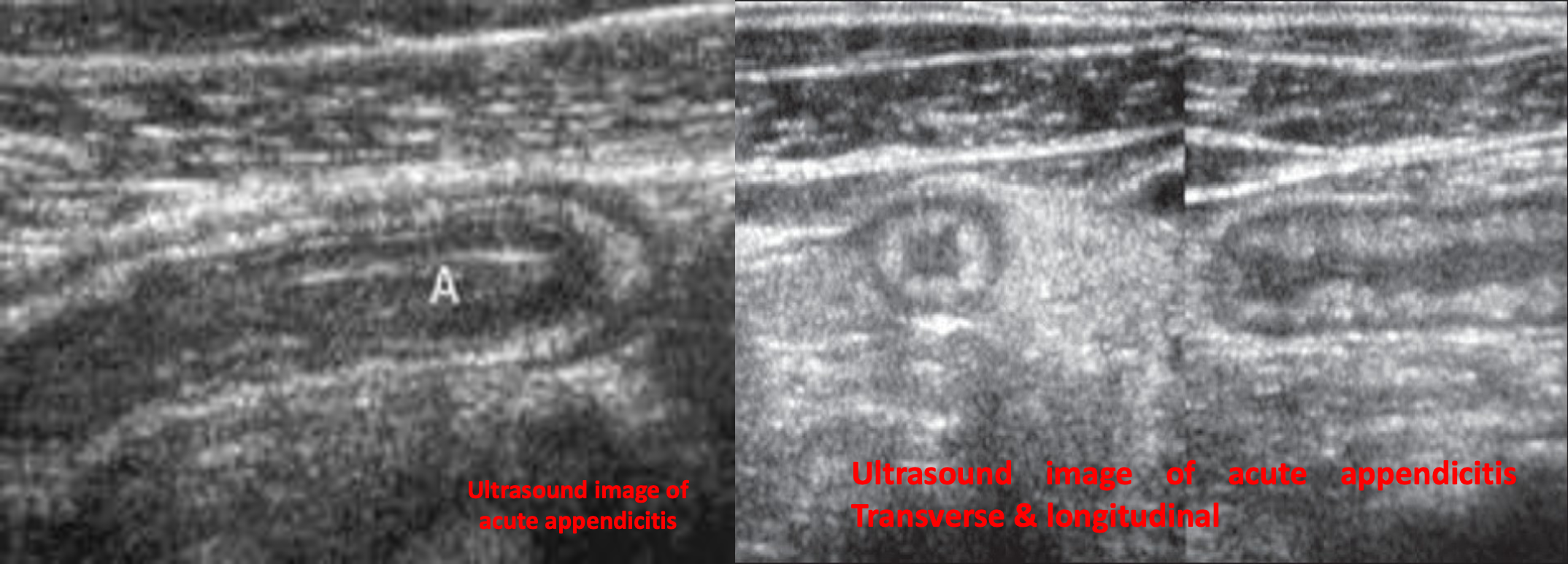
1- US : Supportive findings
Advantages: can limit the exposure to radiation and contrast. First-line imaging for pregnant adults and children: ultrasound abdomen
- Distended appendix (diameter > 6 mm)
- Noncompressible, aperistaltic, distended appendix
- Target sign: concentric rings of hypo- and hyperechogenicity in the axial/transverse section of the appendix
- Possible appendiceal fecalith: focal hyperechogenicity with posterior acoustic shadowing
2- CT abdomen with IV contrast
CT abdomen is the most accurate initial imaging modality for appendicitis. Advantages: higher accuracy and reliability, allows operative planning, better evaluation of differential diagnoses (e.g., for patients > 60 years old)
Supportive findings
- Distended appendix (diameter > 6 mm)
- Edematous appendix with periappendiceal fat stranding
- Possible appendiceal fecalith: focal hyperdensity within appendiceal lumen
- Evidence of complications
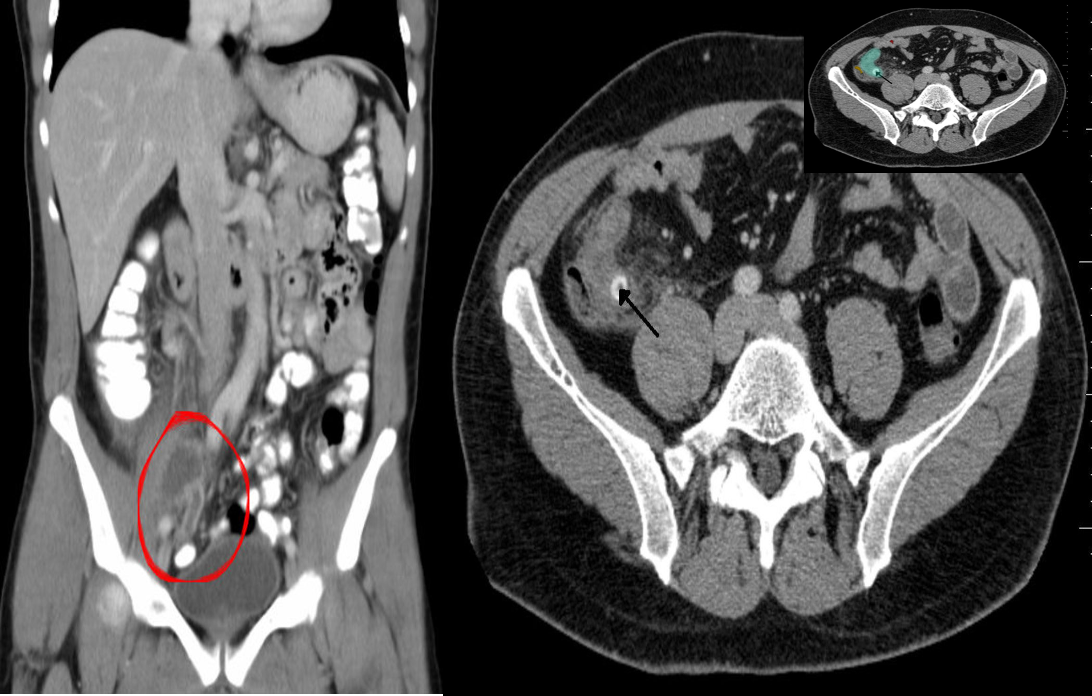 (A) Appendiceal abscess
Abdomen CT (IV and oral contrast; coronal section)
The appendix is markedly distended, with a well-defined hyper-dense rim is visible at the cecal end of the appendix (peri-appendiceal abscess)
(A) Appendiceal abscess
Abdomen CT (IV and oral contrast; coronal section)
The appendix is markedly distended, with a well-defined hyper-dense rim is visible at the cecal end of the appendix (peri-appendiceal abscess)
(B) Perforated appendicitis due to fecalith CT abdomen (IV contrast; axial section) There is distension of the appendix (green overlay). A well-defined, round, hyperdense lesion (black arrow), characteristic of an appendiceal fecalith. A small pocket of extraluminal air (red overlay)