Fungal Infections CS-OSPE
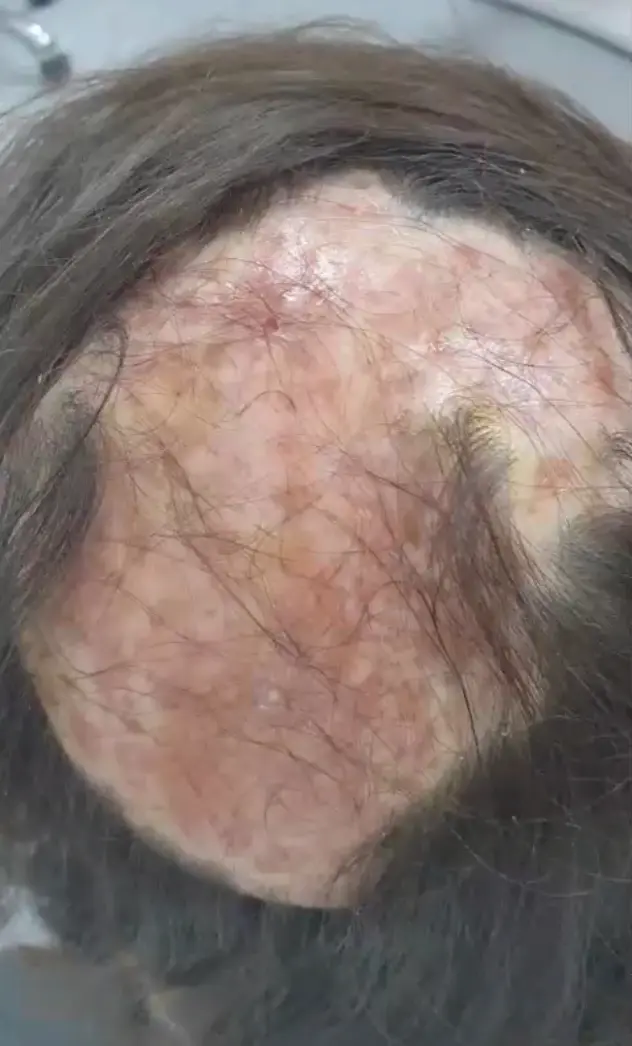
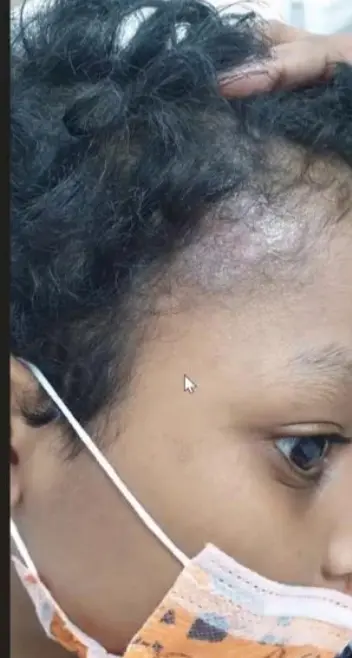
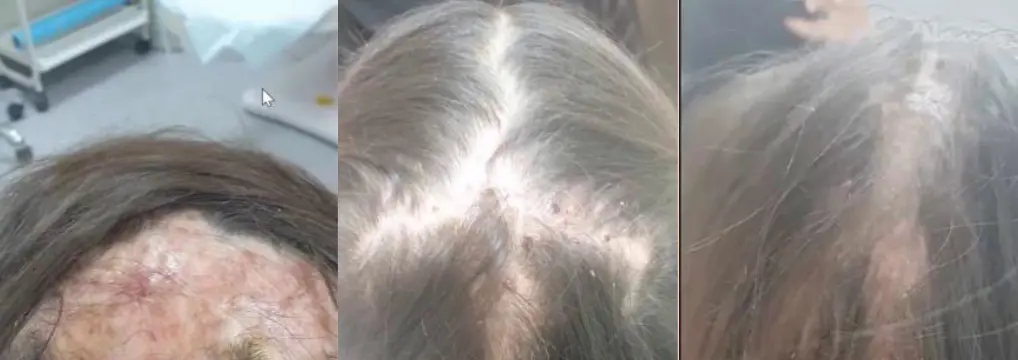 Tinea Capitis Valvus; Tinea capitis with severe bacterial infection and hairloss Z
Tinea Capitis Valvus; Tinea capitis with severe bacterial infection and hairloss Z
 Z
Z
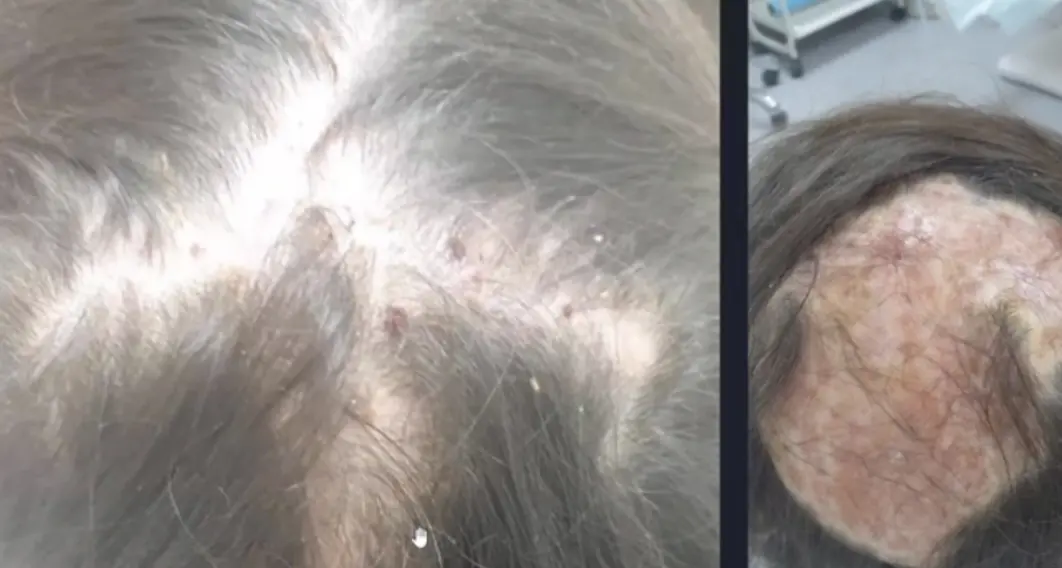
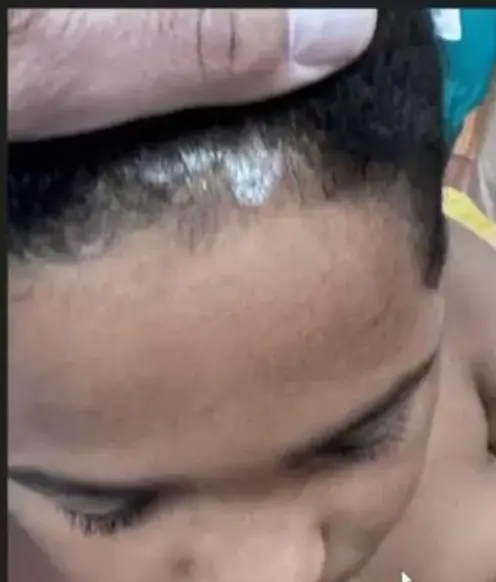
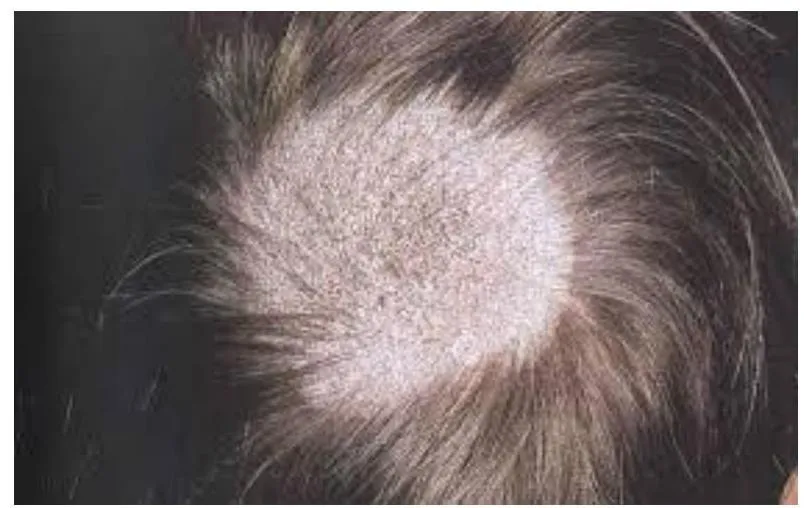
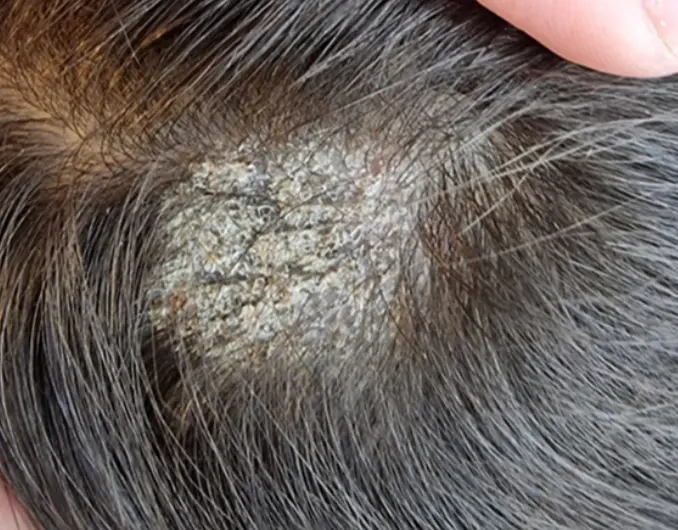
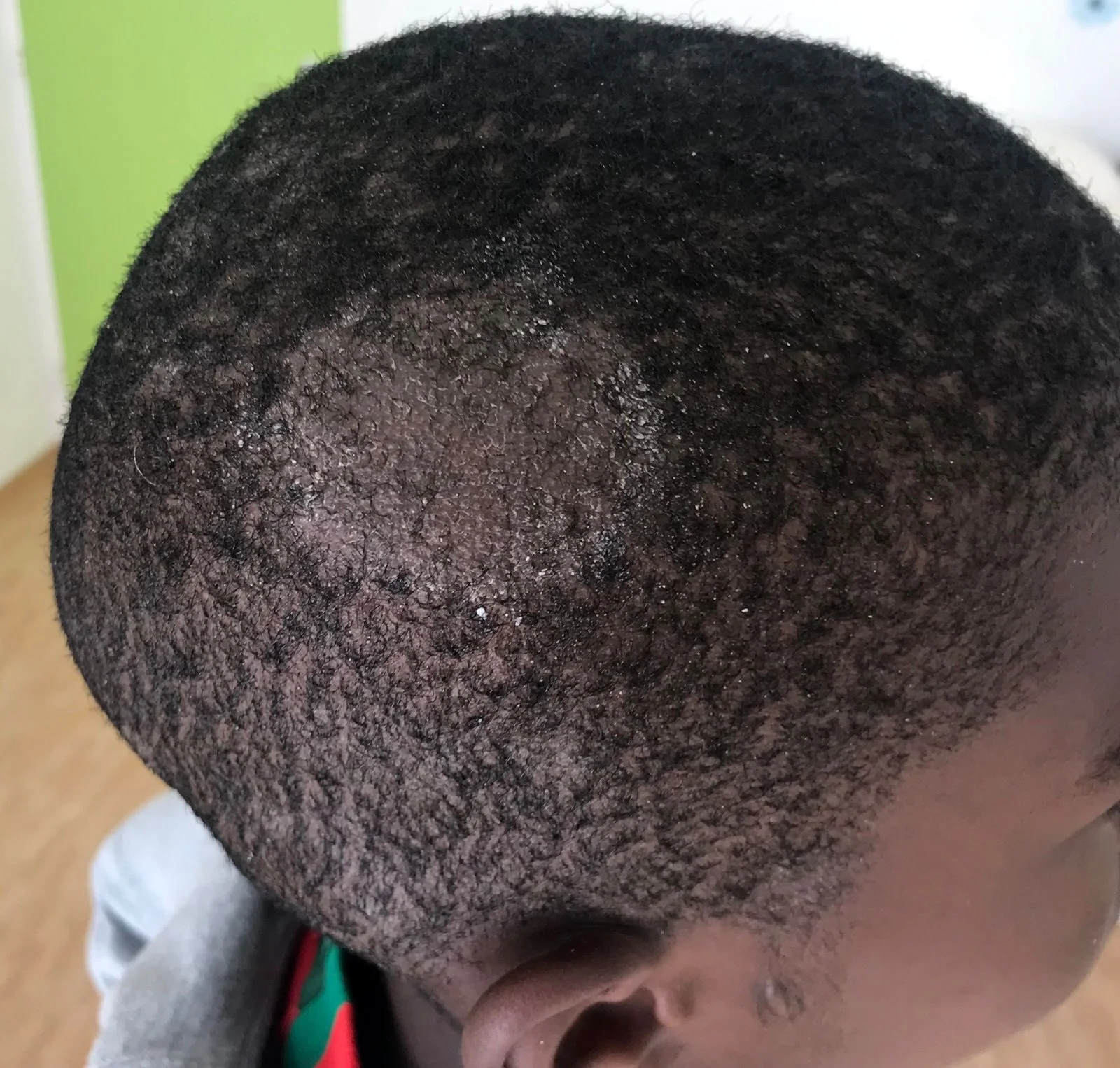
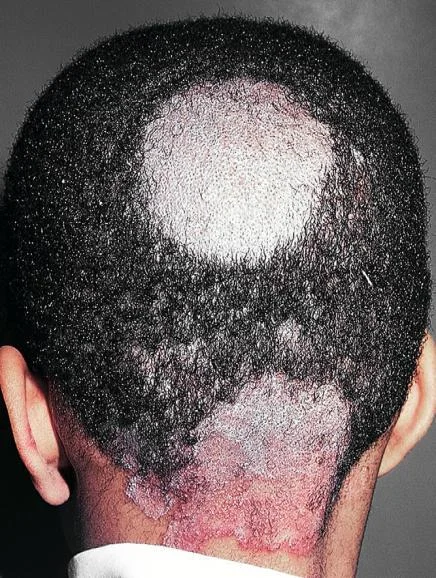
Tinea Capitis & Favus
Diagnosis:
- Tinea capitis
- Tinea capitis vulvus
- Favus (Tinea capitis with severe bacterial infection)
Differential Diagnosis:
-
Telogen effluvium, treated with Minoxidil 2%.
-
Scarring alopecia (e.g., from Lupus erythematosus or Lichen planopilaris), which leads to irreversible hair loss.
Clinical Presentation/Description:
- 1-year-old girl, scalp with a cat at home.
- Child, erythematous lesion within hairline.
- Young patient + hair loss.
- A kid + animal contact.
- Favus presents with hair loss.
Treatment (Tt):
- Griseofulvin (oral systemic antifungal) Z
- Systemic antifungal (always required, especially for young patients and hair loss).
- You can give topicals but always systemic with it.
- For Favus: Systemic antibiotic + systemic antifungal.
- Terbinafine is an antifungal indicated for Tinea capitis and severe dermatophytosis.
- Oral antifungal (general answer).
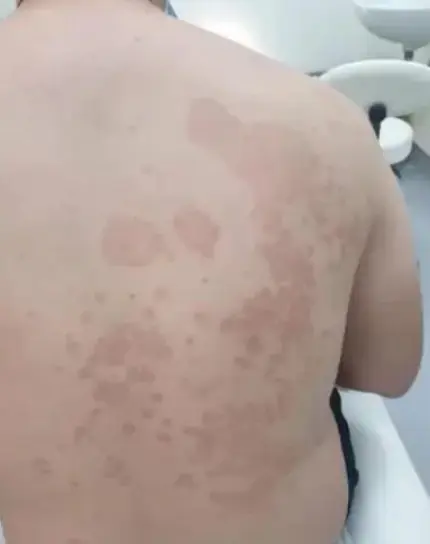
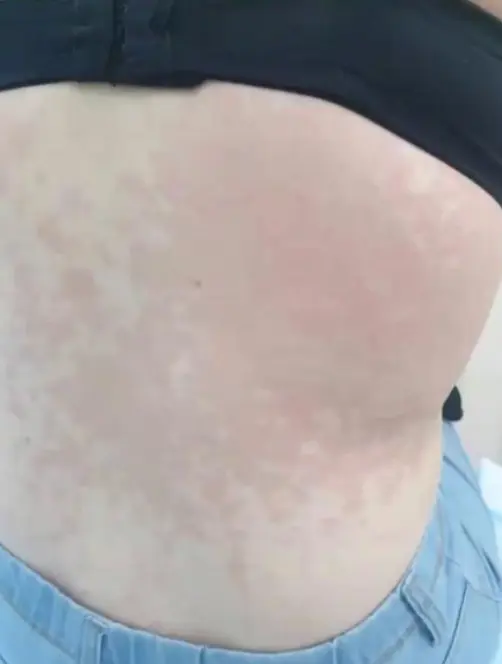
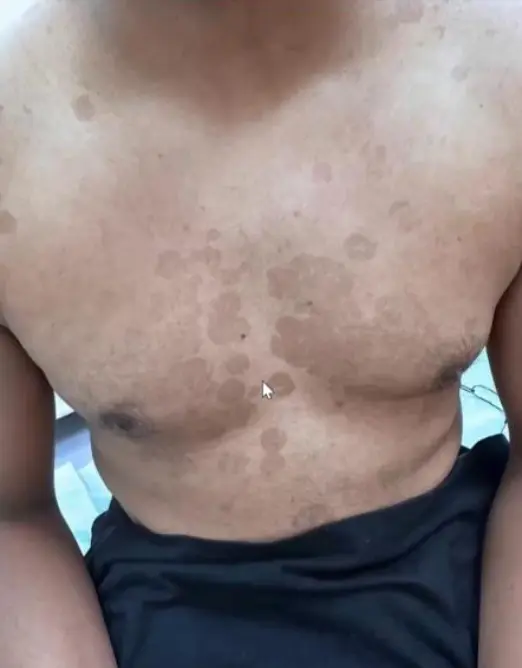
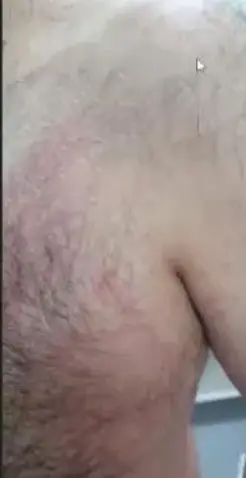
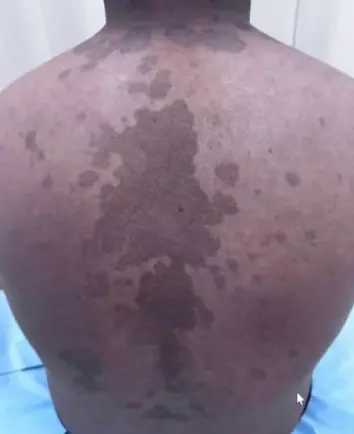
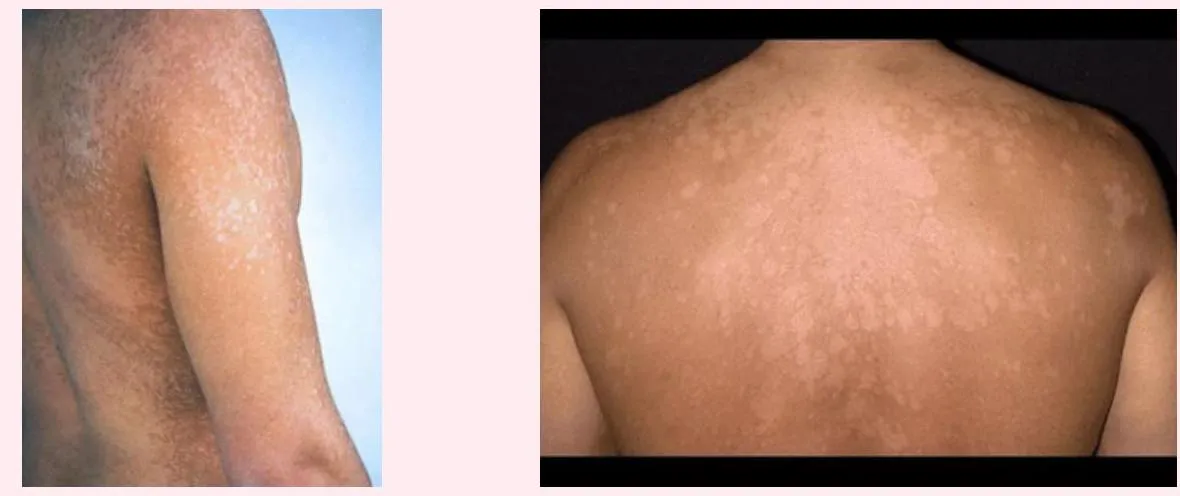
Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor) Z
Diagnosis:
- Tinea Versicolor
- Pityriasis Versicolor
Clinical Presentation/Description:
- A 22-year-old man presents with persistent rash on his upper back and shoulders that he first noticed several months ago. He reports that the patches worsen with humidity, no family history of melanin skin diseases, the hair on it is not grey.
- Multiple hypopigmented, well-defined macules and patches with fine scaling on the upper back.
- Asymptomatic, Well demarcated brown patches with branny over the trunk and upper extremities.
- Multiple pink to tan-colored, round, flat lesions with sharp, irregular borders and varying sizes on his upper chest, back, and flexures of the arms.
- A 32 Y/O patient who visited the dermatology clinic for a fine scaly slightly pruritic rash for six months which worsen in summer and with humidity and sweating. No loss of hair colour within the lesions. Woods light golden yellow, past medical history unremarkable.
- Scattered hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation patch, macule, on the trunk and right upper arm, well demarcated.
- Hypo/hyper-pigmented macule, patch, well demarcated on the trunk and upper arm.
Cause:
- Malassezia furfur (Pityrosporum)
Also causes:
- Seborrheic dermatitis
Differential Diagnosis:
- Vitiligo (it is not the diagnosis because there is no change in hair colour)
- Pityriasis rosea
- Tinea corporis
- Plaque psoriasis
- Guttate Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
Investigation (Clinical investigation in the office to confirm the diagnosis):
- Skin scraping + KOH preparation
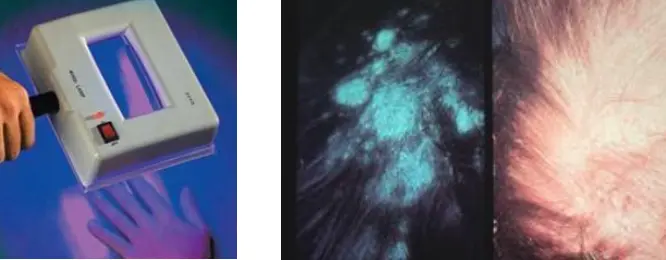
- Wood’s lamp (characterized by golden yellow fluorescence)
What will you see in KOH?
- Spores and pseudohyphae
- Spaghetti and meatballs appearance (spores + pseudohyphae)
Sign of Improvement:
- Post inflammatory Hypopigmentation
Management:
- Full history
- Examination
- Education
- Topical Antifungal (e.g., Imidazoles, Ketoconazole) Z
- Systemic Antifungal (if in the face or extensive, e.g., oral Fluconazole) Z
- The disease is not contagious as it is due to Malassezia furfur, which are skin commensals.
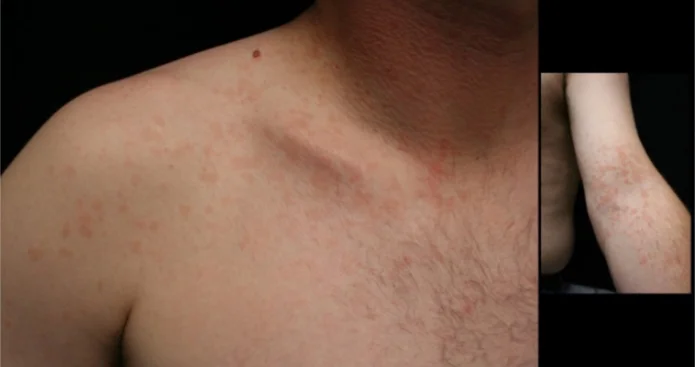
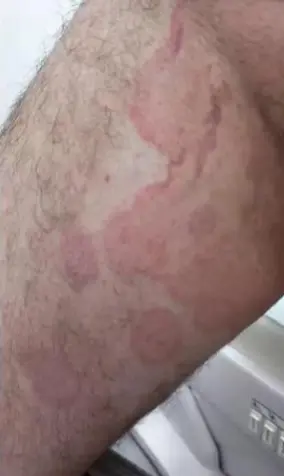 Tinea Corporis/Cruris
Tinea Corporis/Cruris
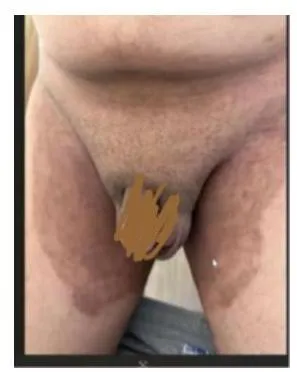
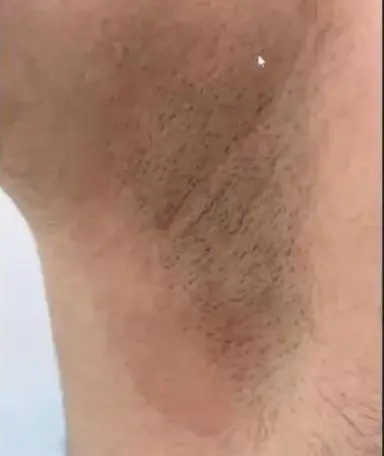 Tinea Cruris Z
Tinea Cruris Z
Tinea Cruris
Diagnosis:
- Tinea cruris
- Tinea Corporis/Cruris
Treatment (Tt):
- Topical antifungals
- Ketoconazole (Best treatment)
- Hygiene
Investigation:
- KOH

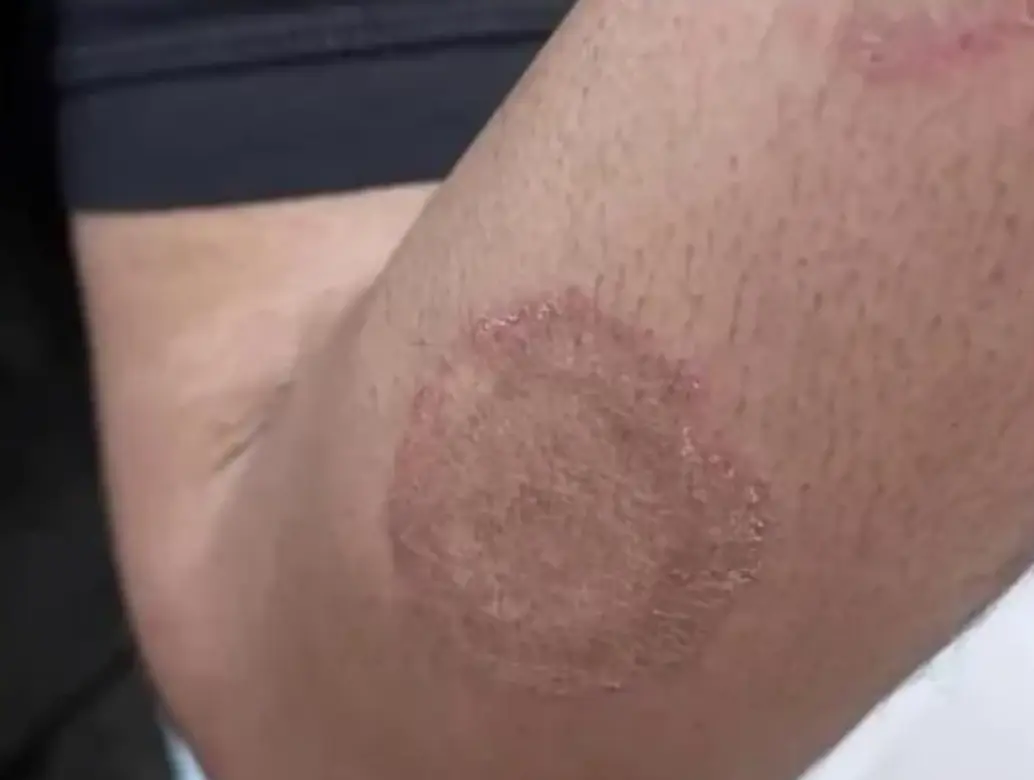
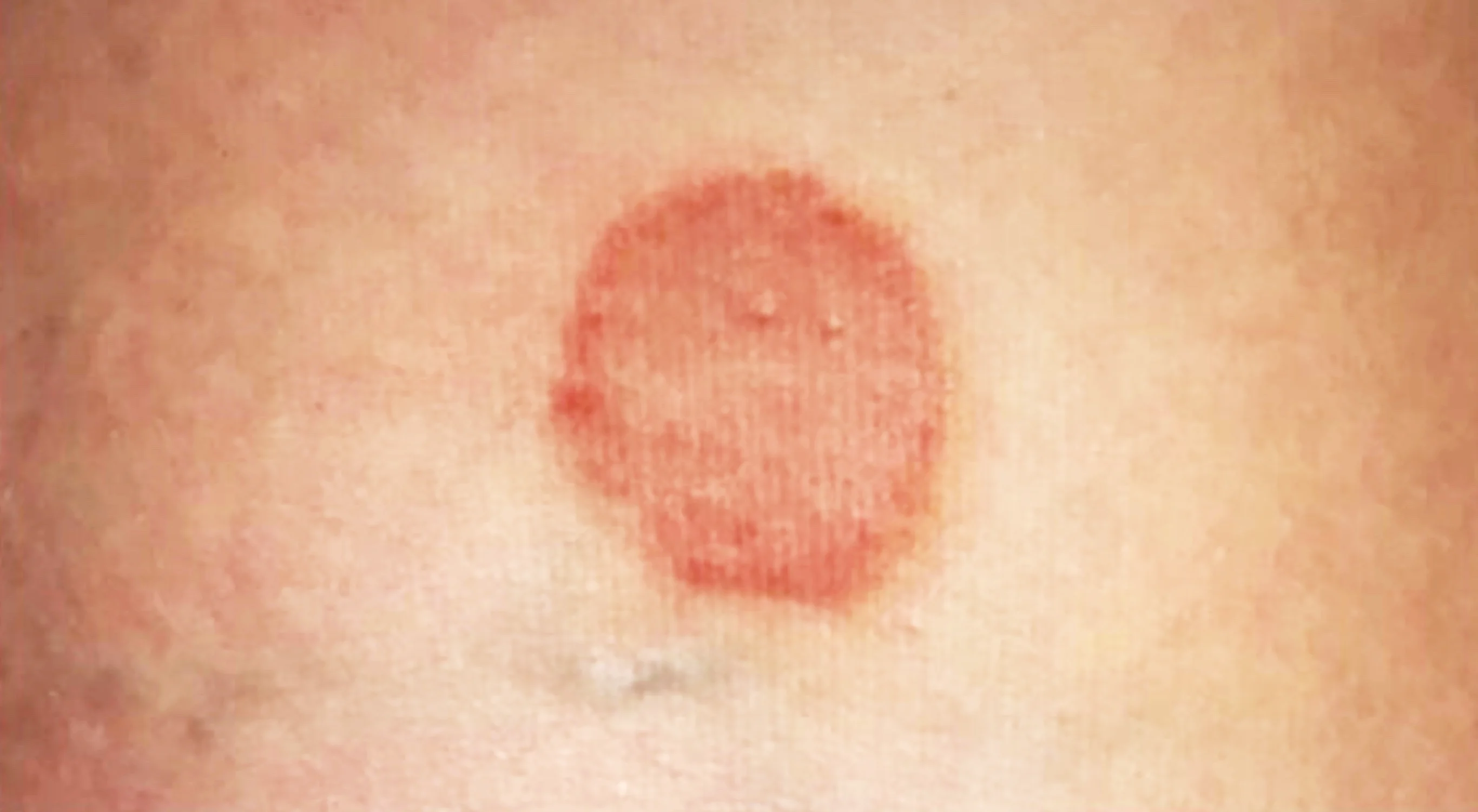
Tinea Corporis
Diagnosis:
- Tinea Corporis
- Tinea Corporis/Cruris (shared image)
Clinical Presentation/Description:
- Red circles don’t itch.
- Well demarcated erythematous plaque, elevated margins and clear center.
- Multiple Scaly plaques with elevated margin, annular patches.
- A 7 Y/O boy with these skin lesions on shoulder and abdomen. He gives a history of contact with cats.
Characteristic Feature:
- Raised or elevated margin called (active border or margin)
Causes:
- Trichophyton and Microsporum species
Differential Diagnosis:
- Pityriasis rosea
- Lichen planus
- Drug eruption
Investigations:
- Skin scrapping with KOH
- (Translucent branching, septate hyphae)… {+VE}
- Scraping test
- Skin biopsy
- Wood’s lamp positive (green)
Management:
- Full history
- Examination
- Education
- Antifungal a. If lesion in chest and back (extensive): systemic antifungal b. If lesions (single- 4): topical antifungal (e.g., Imidazole cream)
 #Z
#Z
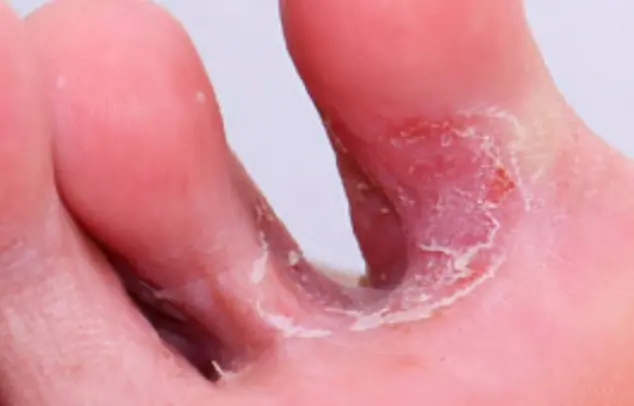
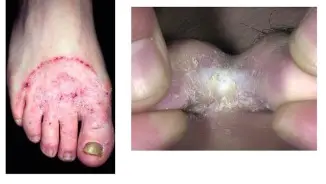
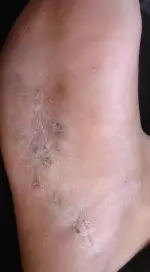
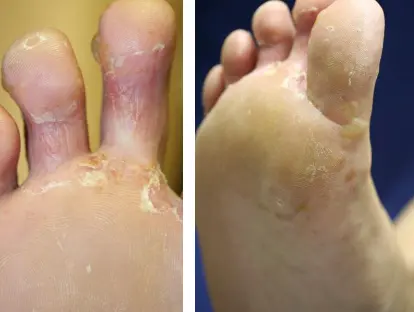
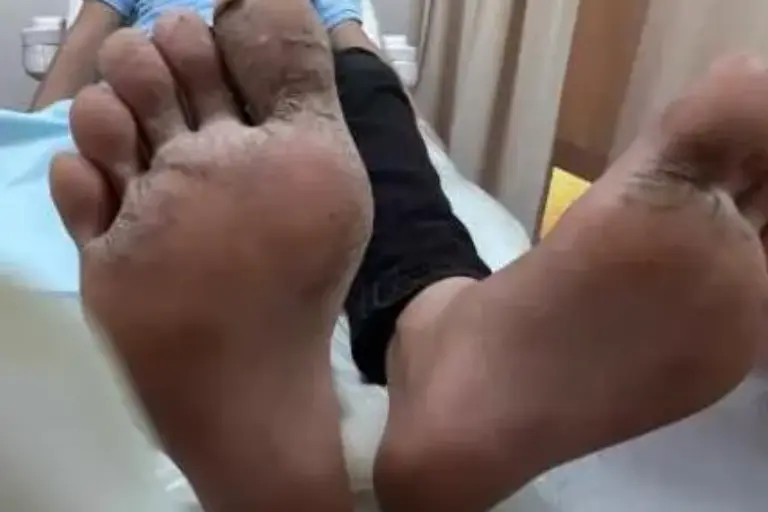
Tinea Pedis
-
Key finding: +KOH test.
-
What is the diagnosis?
- Tinea pedis.
-
What is the clinical presentation?
- Elevated, raised active border and clear in center.
- Scaly.
- Erythematous.
-
What is the pathology?
- Dermatophytes.
-
What is the recommended treatment?
- Topical antifungal medications, including:
- Clotrimazole.
- Ketoconazole (available as Nizoral: tablets, shampoo, and cream).
- Miconazole.
- Topical antifungal medications, including:
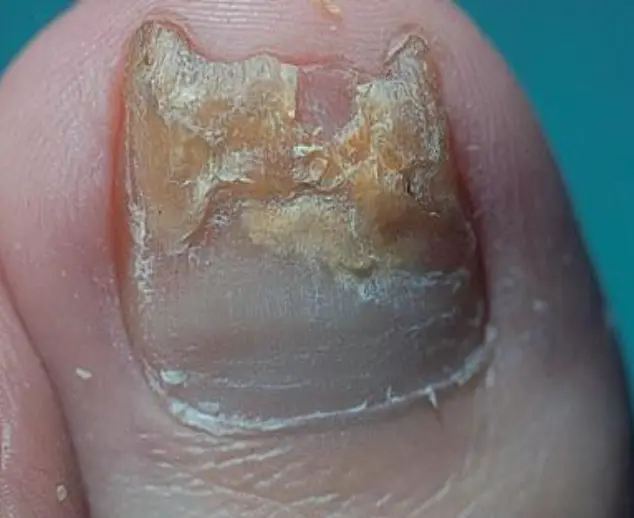
Tinea unguium
- Key diagnostic finding: +KOH test.
What is the diagnosis?
- Tinea unguium
What are the clinical presentations?
- Elevated raised active border and clear in center.
- Scaly.
- Erythematous.
What is the pathology?
- Dermatophytes.
What is the treatment?
- Systemic antifungal:
- Terbinafine.
- Fluconazole.
Antifungal Medications
best dermatophyte terbinafine
Terbinafine Indication:
- Tinea capitis
- Severe dermatophytosis
Ketoconazole:
- What is the action of this drug?
- Fungostatic
- Write 2 Uses:
-
- Genital Candidiasis
-
- Tinea versicolor, Tinea corporis
-
- Write 2 Microorganisms use for:
-
- Dermatophyte
-
- Candida
-
- Discuss the side effect of the drug and drug interaction?
- Low or no side effect and no drug interaction
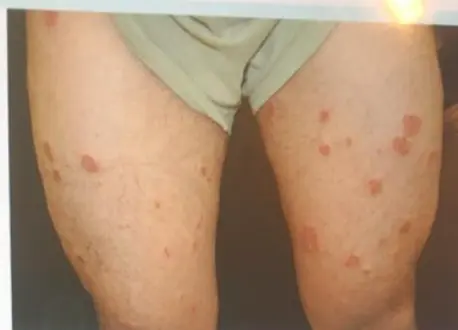
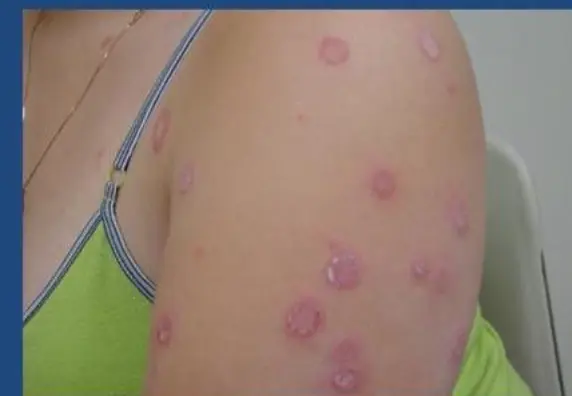
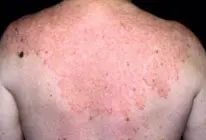
Nummular (Discoid) Dermatitis / Tinea Corporis (DD)
A 35 – year single unemployed man presented to the dermatology unit because of itchy erythematous patches, he tried Vaseline ointment which induced partial relief. His suffering had been started 3 years ago when he developed a similar condition three times on different body sites, that respond well to some topical treatment at one of them, he couldn’t remember it now, but this time it is more severe and numerous.
1. Write two differential diagnoses?
- a- nummular (discoid) dermatitis, b- tinea corporis
2. Mention a bedside investigation you have to do for all similar lesions?
- KOH test for fungal infection to find “hyphae and pseudohyphae”
3. If the test is positive, what you expect to see?
- +ve KOH test ⇒ T.corporis
4. Referring to the history and attached picture, what is the most likely diagnosis?
- nummular (discoid) dermatitis
5. From the history find out the supporting information aids your diagnosis or explains your exclusion for the other differential diagnosis?
- Explanation;
- A. +ve KOH test ⇒ T.corporis -ve KOH test ⇒ nummular (discoid) dermatitis
- B. From the case history figuration = long duration
- Pityriasis Rosacea = ❌
- nummular (discoid) dermatitis = ✅ for 3 years and more
6. What is the treatment for this particular patient?
- Clabetasol Ointment (potent steroid)
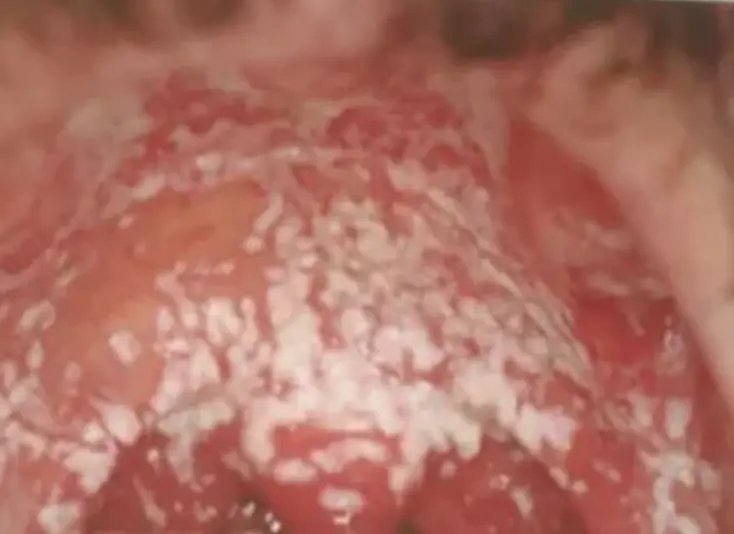
Oral Thrush (Candida Albicans)
This is a roof of the oral cavity of HIV infected patient.
1. What is the diagnosis of this condition?
- oral thrush
2. Mention another two possible dermatological diseases that could be associated with the condition?
- candidiasis el tongue
- Angular cheilitis
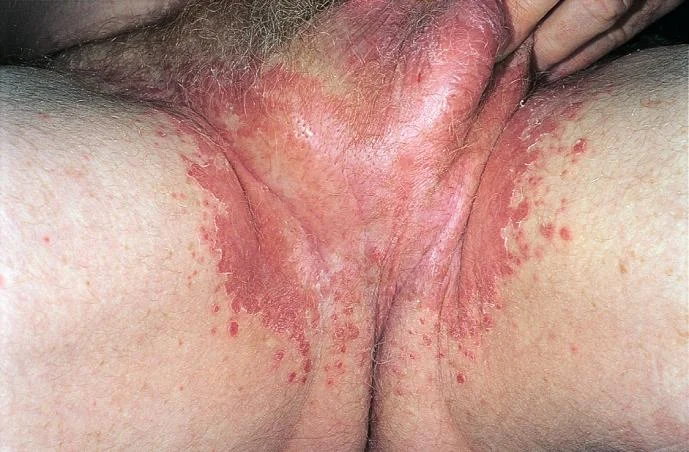
Candida of the Groin (Candida Albicans)
What is the diagnosis?
- Candida of the groin
What is the treatment?
- Good hygiene
- Topical antifungal (e.g., Ketoconazole)
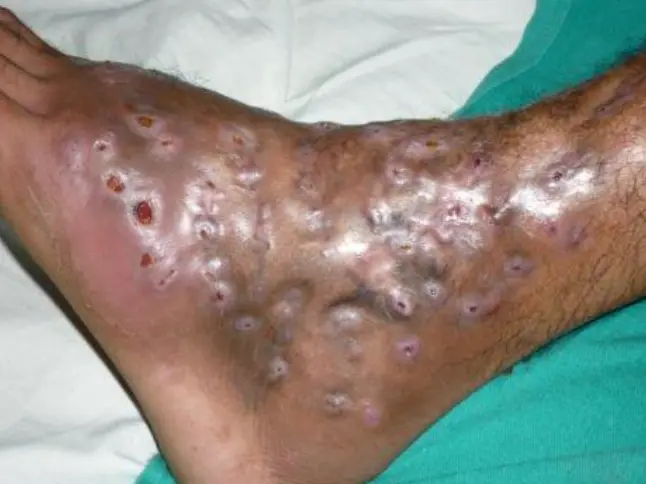
Mycetoma
-
Diagnosis:
- Mycetoma (Madura foot).
-
Clinical Presentation:
- Multiple opening sinus with discharge.
- Tiny granules.
-
Pathology:
- Eumycetoma.
-
Treatment:
- Surgery.
- Systemic anti-fungal.
- Systemic antibiotics.
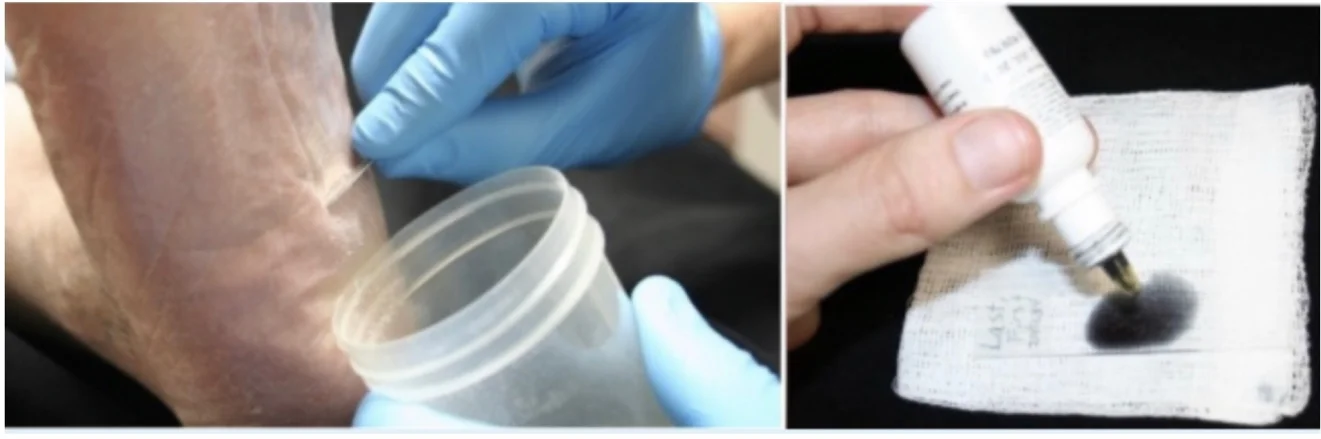
Scraping Skin Test
A 24-year-old woman presented with scaly lesion.
1. What is name of the test?
- Scraping skin test. KOH
b. If it is positive what you expect to see?
- Hyphae, Pseudohyphae
2. What is the added substance?
- Potassium hydroxide
3. Two different diseases that you could diagnose through this test?
- Tinea capitis
- Tinea versicolor

Wood’s Lamp Diagnosis
1. What is the name of this instrument?
- Wood’s lamp
2. What is the disease it could be diagnosed by using this instrument?
- Tinea versicolor, characterized by golden yellow fluorescence