SURGE
Thyroid carcinoma
Aetiology
-
papillary carcinoma - History of irradiation— Papillary (including mixed papillary & follicular) - 75% ++ LYMPH Thyroglossal cyst—papillary carcinoma. Hashimotos thyroiditis—lymphoma and papillary carcinoma.
-
follicular carcinoma - Hx of longstanding multinodular goiter - 16% ++ METASTASES
-
medullary carcinoma thyroid.- Family hx 20%? — 5%
-
Undifferentiated (Anaplastic Carcinoma) - 3%
-
Miscellaneous ( lymphoma, fibrosarcoma, squamous cell ca, teratoma, & metastatic ca)— 1%
Management of Papillary & Follicular Carcinoma
- Low risk group:
- Age <45
- Primary *lesions <1cm *
- No evidence of intra/ extra-glandular spread.
Treatment: Lobectomy + isthemectomy
- All other high risk: Total thyroidectomy.
- Modified neck dissection for lymphatic spread.
- Surgery followed by RAI ablation therapy
- Patient placed on L-thyroxine suppressive therapy
- Regular F/U: Thyroglobulin, US, whole body scan.
IMG
Thyroid ultrasound:
- to assess for sonographic signs of thyroid malignancy
- Irregular margins
- Taller-than-wide shape
- Microcalcifications within nodules
- Extrathyroidal growth
Thyroid scintigraphy
Indications
- Thyroid nodule(s) with ↓ TSH levels
- Multinodular thyroids (to identify nodules that require FNAC)
Supportive findings: decreased or no radiotracer uptake (i.e., hypofunctioning or nonfunctioning nodules, referred to as cold nodules)
Solid, hypoechoic nodules with irregular margins, microcalcifications, taller-than-wide shape, extrathyroidal growth, and/or cervical lymphadenopathy should raise suspicion for malignancy and require further evaluation with FNAC.
Highly suspicious malignancies
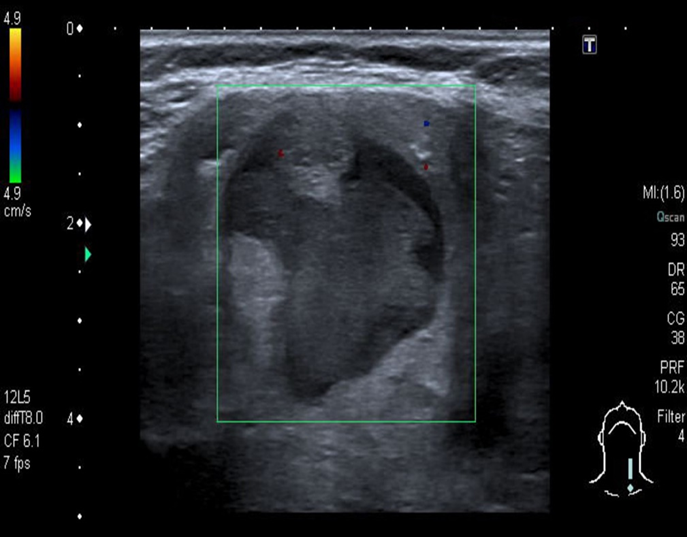
A-Solid thyroid nodule with microcalcifications
Ultrasound thyroid (longitudinal plane) A solid nodule in the upper pole has ill-defined margins and contains multiple microcalcifications.
The presence of microcalcifications increases suspicion for malignancy
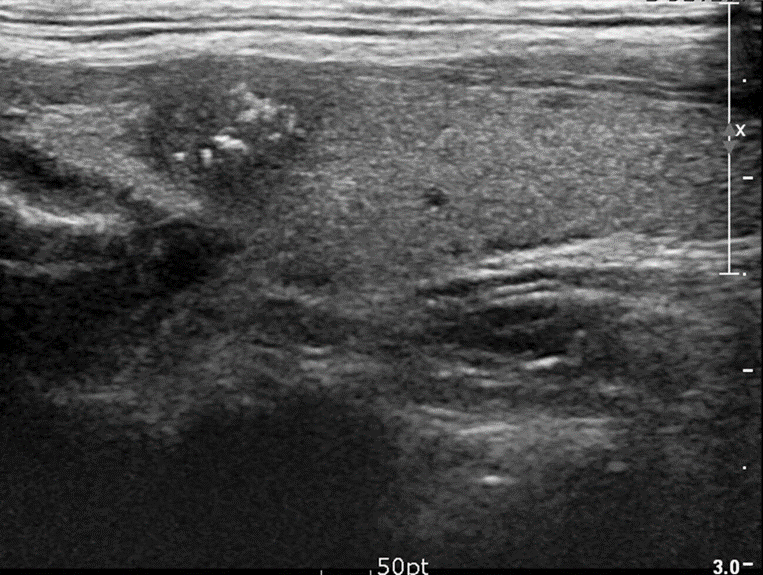
B-Mixed echogenicity thyroid nodule
Ultrasound thyroid (left lobe; longitudinal plane)
A rounded mixed-echogenicity nodule with irregular (lobulated) margins contains hypoechoic and hyperechoic components.