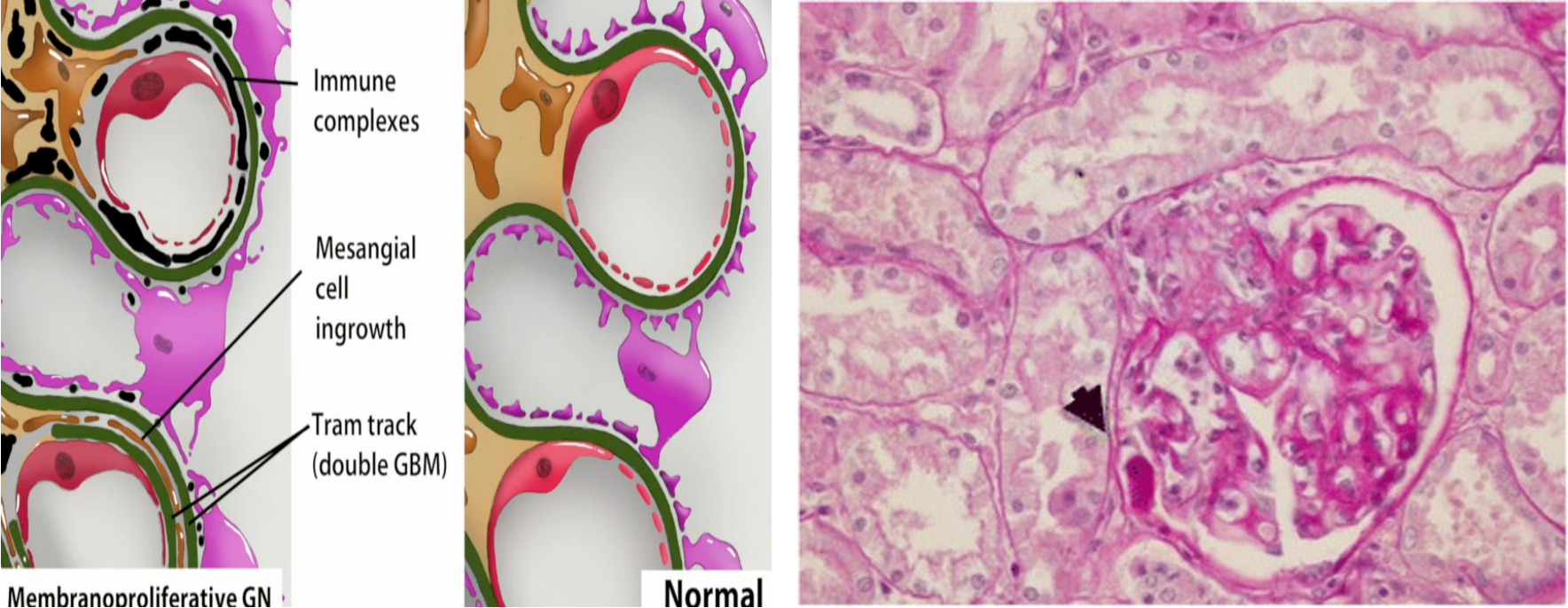
Membranoproliferative GN + nephrotic/nephritic
-
Primarily causes nephrotic syndrome (sometimes nephritic)
-
Type 1: Caused by Hepatitis C & B, cryoglobulinemia, and infective endocarditis, malarie, Antigen/antibody complex deposits in the basement membrane and sub-endothelium. Mesangial cells split the membrane, creating a characteristic tram-track appearance in renal biopsy.
/
- Type 2: AKA Dense deposit disease. Antibodies stabilize C3 convertase, leading to complement pathway activation and C3 consumption. These antibodies are known as nephritic factors. Complements deposit in the basement membrane. Renal biopsy shows a tram-track appearance.
Management of Symptoms of GN
- Proteinuria: ACEIs
- Acanthocytes/RBCs casts/hematuria: Corticosteroids & immunosuppressants
- Volume overload: Frusemide
- Hypertension: ACEIs
- Oliguria: Diuretics / dialysis
- Azotemia: If uremia
- Sterile pyuria: Decreases with decreased inflammation
Important note: The treatment approach for nephritic syndrome will depend on the underlying cause.