Lichen Planus CS-OSPE
Lichen planus (LP)
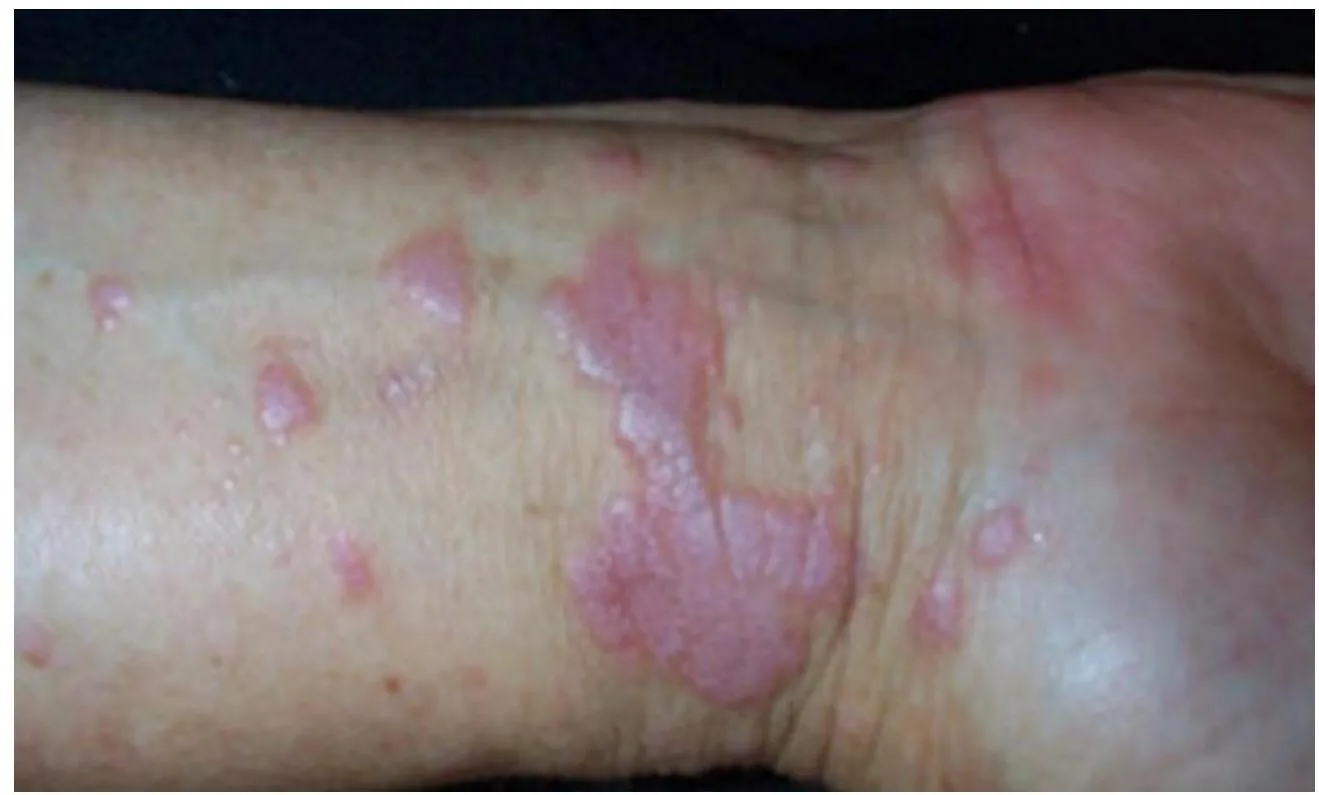
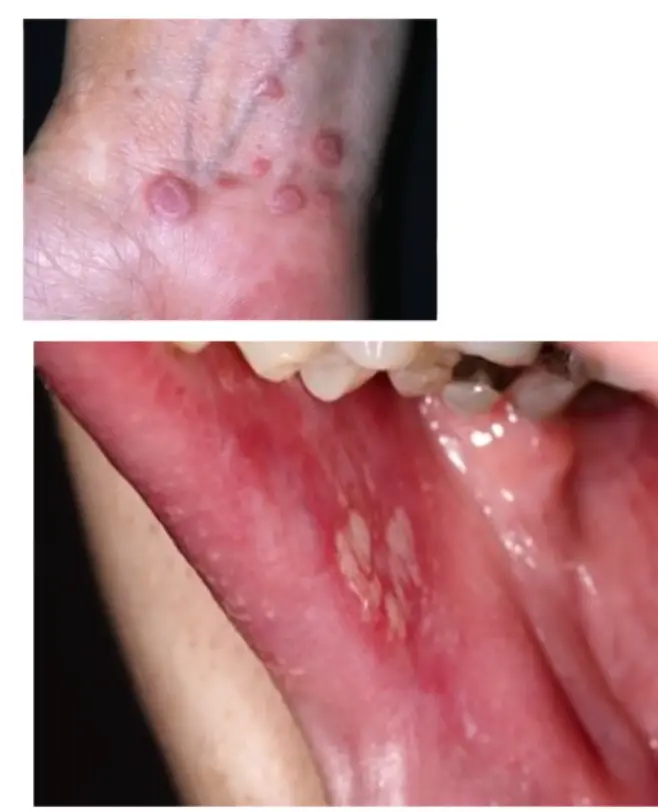
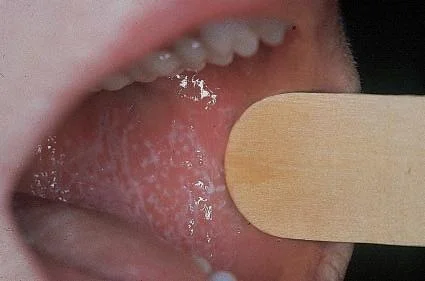
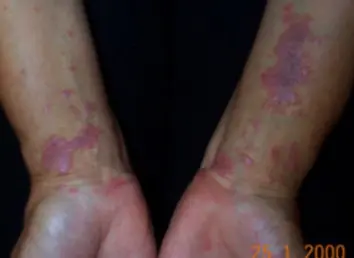
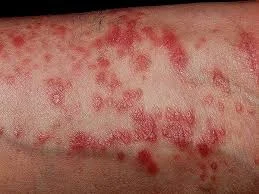
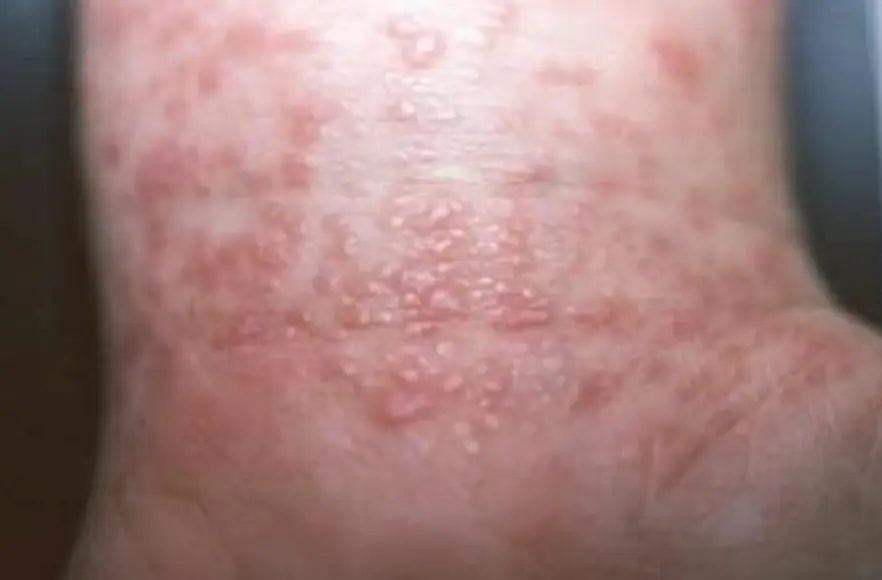
Typical itchy/pruritic papules, demarcated by skin lines on the extremities especially the volar aspects, particularly wrists. Patients may be 20-35 years old. Oral cavity may show whitish changes. History of drug intake like chloroquine may be present.
What is the diagnosis? Lichen planus (LP)
Describe the lesion / What is the primary lesion? / What are the clinical presentations?
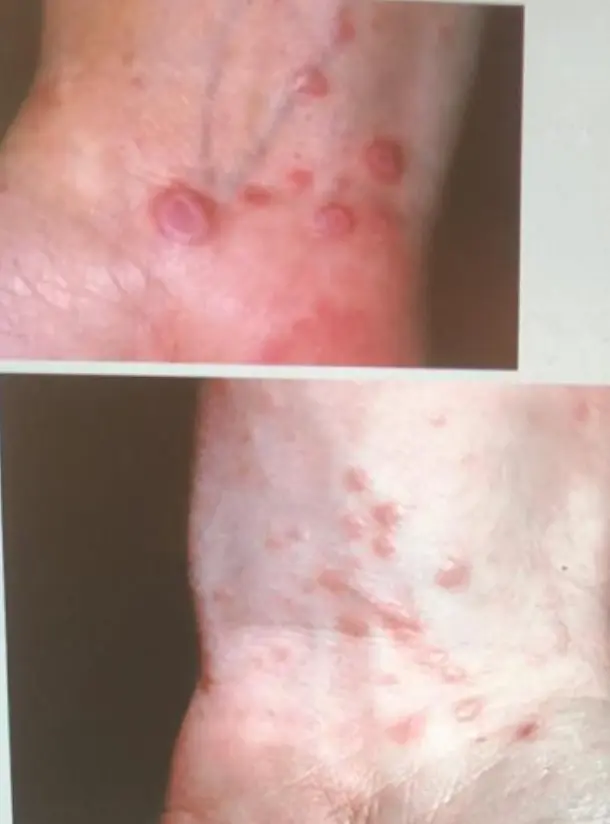
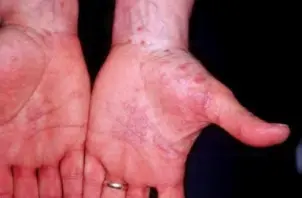
- Flat-top, itchy/pruritic papules, scattered.
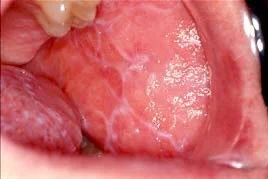
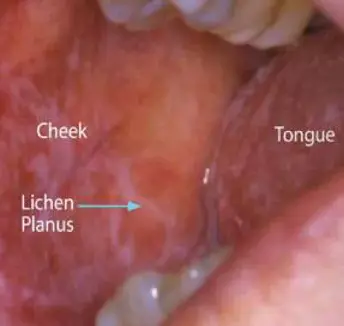
- White streaky pattern on the surface of the papules (Wickham’s striae), which can also appear as white lacy plaques/network in the buccal mucosa/oral cavity.
- Pigeon nails / nail pitting???
- It occurs on joint flexures especially the wrists, genitals, inner thighs, and scalp.
- Koebner’s phenomenon is also present.
- Neighboring papules may join together to form plaques that resemble lichen growing on trees.
- Sign of improvement: Hyperpigmentation.
Note on Pigmentation Please note that in Lichen planus (LP) and Pityriasis rosea improvement or resolving of the lesion shows hyperpigmentation but in Pityriasis versicolor shows hypopigmentation.
What is the type of pruritus in this lesion? Pruritoceptive
What is the differential diagnosis?
- Contact dermatitis
- Lichenoid drug reactions
- Discoid lupus erythematous
- Oral candidiasis / Oral Thrush
- Gold and heavy metal reaction.
- Scabies
Mention possible associated diseases? Hepatitis C, B, Autoimmune disorders such as alopecia areata and ulcerative colitis.
Complications of the disease?
- Nail and hair loss (scarring alopecia) may be permanent.
- Ulcerative form in the mouth/oral cavity may lead to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
- Ulceration over bony prominences may be disabling.
What are the types/variants of this disease?
- Annular – area of central clearing.
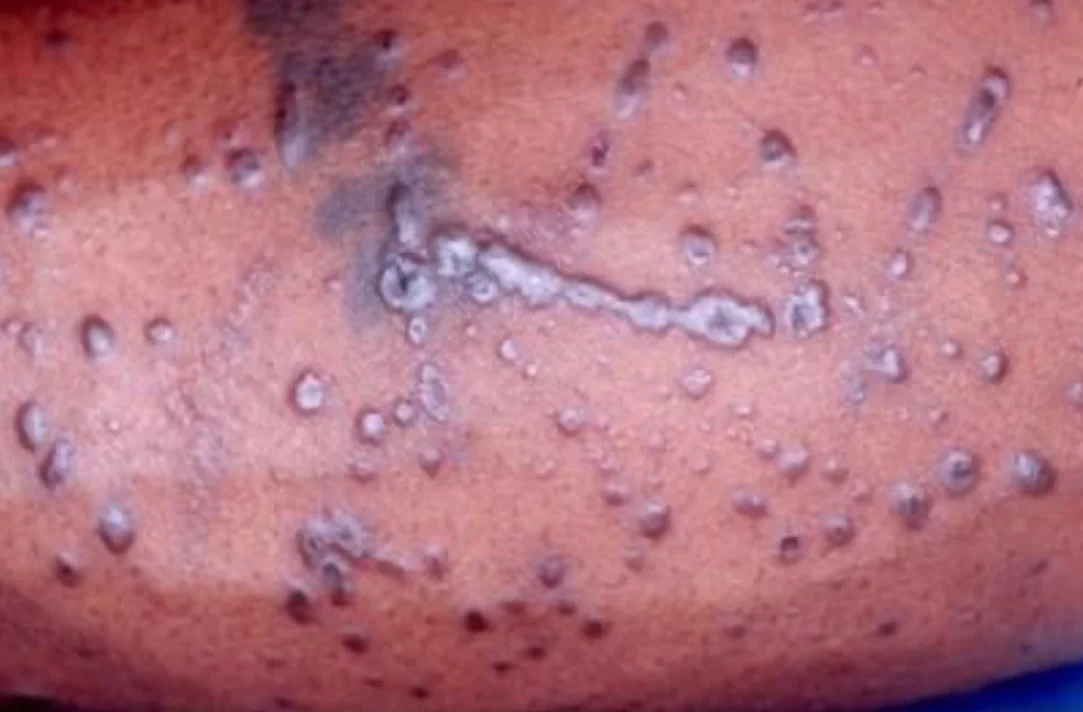
- Ulcerative – on soles and mucous membrane.
- Atrophic – in mucous membrane.
- Bullous
- Follicular
- Hypertrophic – around the ankles.
Drugs that may cause it?
- Streptomycin
- Chloroquine
- Methyldopa
- Phenothiazine
How to manage this patient / Treatment?
- Is a self-limiting skin lesion that lasts 1 month to 1 year, resolving and leaving flatter, darker, and discrete brown macules.
- Full history
- Examination:
- Body sites to be examined include wrists, oral mucosa, scalp, inner thighs, and genital area.
- Lab tests / Biopsy:
- Technique: Punch biopsy (It is more deep and suitable for inflammatory skin conditions).
- Histopathological findings: Lymphocytes attack the epidermis. Hypergranulosis, Saw-tooth appearance of the rete ridges, Band-like lymphocytic infiltrate at the dermo-epidermal junction.
- Education
- Stop offending agent.
- Anti-histamines (for sedation).
- Potent topical corticosteroids / Topical high-potency steroid (to relieve symptoms & flatten plaques).
- Emollient.
- UV radiation (reduce pruritus, help clear the lesions).
- Systemic corticosteroids (e.g., prednisolone).