History
Framework
- Demographics (Name, Age, Gender, Nationality, Martial, Residency)
- Chief of complaint (Cause of hospitalization + days)
- HOPI (OPERATES NON PAIN | SOCRATES PAIN)
- B-Symptoms
- Systemic Review
- Past history (medical, surgical, medication, allergies, family, social)
- summary
- differential + justify differential
- investigations - appropriate
- treatment - suggestive
Introduction, explain, Permission, Assure privacy, chap.
Greetings im Mohammed 5th year medical student; could you tell me your name..“amm ahmad”. im here to take your full history, may i proceed? =-
call nurse, assure privacy.
1) Demographics
32 year old Egyptian engineer man married with two kids, lives in Riyadh
In biliary colic presentation in demographics are
- 35 years old male
-
40 age & Females most commonly
2) Chief of Complaint
why did you come to hospital; write same as “Abdominal pain ((not specific to Epigastric pain))
- Halitosis
- Abdominal Pain
- Steatorrhoea
- Vomiting & weight loss
- Other Git Symptoms - Constipation, Dysphagia, Acute Diarrhea etc..
- Heart Burn
- GI tract diseases
- Drugs and alcohol
- Functional
- Psychogenic
5 day abdominal pain
Biliary colic presentation example complain pain 5D in right upper quadrant - associated with jaundice
Jaundice Presentation 5D yellow eyes - usually follows through OPERATES METHOD
Ask when the patient first noticed, or someone that noticed since when… without character of pain or site more emphasis on PROGRESSION, TIMING, & EPISODE
3) HOPI
5 day progressive stabbing abdominal pain located on epigastric region radiating to the back increased with movement, subsides with rest prominent in the morning subsides later in the day… associated with vomiting & constipation, no diarrhea flatus or B symptoms, unremarkable systemic review
I- Site
Pain wide range - (quadrants)
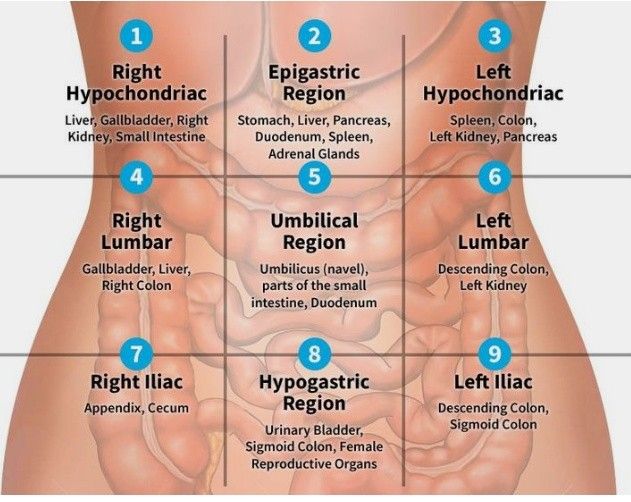
-
Right Hypochondriac
-
Right Lumbar
-
Right Iliac
- Appendicitis, Uriteric colic, pyelonephritis, cecum; IBD)
-
Epigastric
- Peancreatitis, GERD, Peptic Ulcer, Cancer, Deuodenal Ulcer, esophagitis, Left lobe of liver, Myocardial infacrtion)z
-
Umbilical region
-
Hypogastric region
-
Left Lumbar
-
Left iliac
- Divertucilitis
- Sigmoid -
- Ulcer
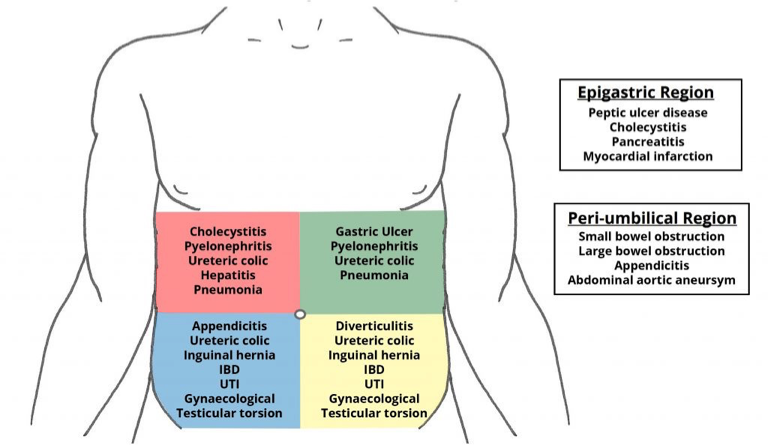
Important RUQ - rad to shoulder - Chole Epigastric - RAD Back - pancreatitis
| Region | Category | Differential Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| RUQ | Hepatobiliary | Biliary colic, Cholecystitis, Cholangitis, CBD obstruction (stone, tumor), Hepatitis, Budd-Chiari, Hepatic abscess/mass, Right subphrenic abscess |
| Gastrointestinal | Pancreatitis, Presentation of gastric, duodenal, or pancreatic pathology, Hepatic flexure pathology (CRC, subcostal incisional hernia) | |
| Genitourinary | Nephrolithiasis, Pyelonephritis, Renal: mass, ischemia, trauma | |
| Cardiopulmonary | RLL pneumonia, Effusion/empyema, CHF (causing hepatic congestion and R pleural effusion), MI, Pericarditis, Pleuritis | |
| Miscellaneous | Herpes zoster, Trauma, Costochondritis | |
| LUQ | Pancreatic | Pancreatitis (acute vs. chronic), Pancreatic pseudocyst, Pancreatic tumors |
| Gastrointestinal | Gastritis, PUD, Splenic flexure pathology (e.g. CRC, ischemia) | |
| Splenic | Splenic infarct/abscess, Splenomegaly, Splenic rupture, Splenic artery aneurysm | |
| Cardiopulmonary | (see RUQ and Epigastric) | |
| Genitourinary | (see RUQ) | |
| RLQ | Gastrointestinal | Appendicitis, Crohn’s disease, Tuberculosis of the ileocecal junction, Cecal tumor, Intussusception, Mesenteric lymphadenitis (Yersinia), Cecal diverticulitis, Cecal volvulus |
| Hernia | Femoral, inguinal obstruction, Amyand’s (and resulting cecal distention) | |
| Gynecological | See ‘suprapubic’ | |
| Genitourinary | See ‘suprapubic’ | |
| Extraperitoneal | Abdominal wall hematoma/abscess, Psoas abscess | |
| LLQ | Gastrointestinal | Diverticulitis, Diverticulosis, Colon/sigmoid/rectal cancer, Fecal impaction, Proctitis (ulcerative colitis, infectious; i.e. gonococcus or Chlamydia), Sigmoid volvulus |
| Hernia | ||
| Gynecological | See ‘suprapubic’ | |
| Genitourinary | See ‘suprapubic’ | |
| Extraperitoneal | Abdominal wall hematoma/abscess, Psoas abscess | |
| Epigastric | Cardiac | Aortic dissection/ruptured, AAA, MI, Pericarditis |
| Gastrointestinal | Gastritis, GERD/esophagitis, PUD, Pancreatitis, Mallory-Weiss tear | |
| Suprapubic | Gastrointestinal | (see RLQ/LLQ): Acute appendicitis, IBD |
| Gynecological | Ectopic pregnancy, PID, Endometriosis, Threatened/incomplete abortion, Hydrosalpinx/salpingitis, Ovarian torsion, Hemorrhagic fibroid, Tubo-ovarian abscess, Gynecological tumors | |
| Genitourinary | Cystitis (infectious, hemorrhagic), Hydroureter/urinary colic, Epididymitis, Testicular torsion, acute urinary retention | |
| Extraperitoneal | Rectus sheath hematoma | |
| Diffuse | Gastrointestinal | Peritonitis, Early appendicitis, perforated appendicitis, Mesenteric ischemia, Gastroenteritis/colitis, Constipation, Bowel obstruction, Pancreatitis, Inflammatory bowel disease, Irritable bowel syndrome, Ogilvie’s syndrome |
| Cardiovascular/Hematological | Aortic dissection/ruptured AAA, Sickle cell crisis | |
| Genitourinary/Gynecological | Perforated ectopic pregnancy, PID, Acute urinary retention | |
| Endocrinological | Carcinoid syndrome, Diabetic ketoacidosis, Addisonian crisis, Hypercalcemia | |
| Others | Lead poisoning, Tertiary syphilis |
II- Onset
Acute
- Peritonitis follower by perforation (dialysis)
- Appendicitis
- Truama
- Rupture Ectopic
- Ruptured Aortic Aneurysm
- Mesenteric Ischemia
- Bleeding ulcer
Chronic Inflammations
- Hepatitis
- IBD
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Biliary colic
Both
- Intestinal Obstruction
III- Character
Colicky, Constant dull aching pain Biliary colic if there’s impaction of stone
**Sharp/Stabbing/
Constrictive
Burning
- GERD
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
Throbbing
- Acute severe inflammation (infections)
- Abcess
Dull / Aching
- Acute cholecystitis (Inflammatory process)
constant Dull aching pain - radiation to shoulder due RT dome diaphragm supplied by phrenic nerve
Colicky Pain (Tubular structures - smooth muscle contractures)
- Stones (gallbladder, kidney, intestinal…)
- Uterine contractions
Biliary Colic type of pain - it comes in goes
- Renal colic
- biliary colic
- urinary colic
Heaviness?
IV- Radiation
- Pancreatitis - RAD to the back
- Spleen - Left shoulder
- Renal colic: to groin
- Cholecystitis - RAD Right shoulder (phrenic nerve)
- Appendicitis - Peri-umbilicus shifting to the right illiac fossa
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm: to back or flank
- Perforated ulcer: to RLQ (right paracolic gutter)
- Hip pain: to groin
V- Associated Symptoms
General abdominal pain Fever, melena, hematemesis colon/biliary cancers - and others depending on differential…
In biliary colic Itching, Fever, maliase , nausea, vomiting, urine, stool
(obstructive jaundice in case pale stool) (Urine dark due liver is normal water soluble goes serum body fluids) (Pre-hepatic insoluble bilirubin - Normal urine & Stool Dark) (steatarohea due ??)
jaundice if someone noticed it do you have itching or dark urine
In Jaundice
- Itching
- dark urine
- dark stools
- weight loss
- fever / malaise
- bruising
Vomiting
- Non- bilious: Early stage, late- pyloric obstruction
- Bilious: bowel obstruction
- Faeculent: late stage of bowel obstruction
- Blood: Duodenal ulcer, oesophageal varices, tumor
- Vomiting relieves pain- gastric ulcer
- Vomiting food taken few days ago: pyloric stenosis
Bowel Habits Constipation:
- habitual, recent (neoplasm)
- Absolute constipation (obstipation):
- Intestinal obstruction
Diarrhoea:
- Duration (acute, chronic)
- Number of stool
- Any blood or mucous (IBD)
Color of stool:
- Bright red (anal, rectum),
- maroon (colon) black-
- melena (upper GI)
VI- Timing/Episodes
General
- More after waking up, waking up in middle of night, more in the afternoon?
- timing, Duration, episodes of free disease.
In biliary colic usually after eating meal
VII- Factors
- relieving factor, sitting position? leaning forward? (acute pancreatitis), eating? (DU)
- Exacberating factors not eating? after fatty meal?, eating? Peptic ulcer GERD - R Milk peritonitis - any movement pain - stand still IBD IBS - Stress factor
In biliary colic Eating especially in Fatty food will increase pain - due bilestone contraction Leading forward? Not eating? Analgesics?
VIII- Severity
1-10 Grading with Limitations - cant walk, work, or think
4) B Symptoms
Fever, Night sweats, Weightloss, loss of apetite
5) Systemic Review
can be after HOPI or past Hx If the chief complaint is related to gastrointestinal system(GI)- continue with the GIT inquiry.
Respiratory system:
- Cough, sputum, hemoptysis, wheeze, dyspnea, chest pain
Cardiovascular system:
- Angina (cardiac pain), dyspnea ( rest/ exercise),
- Palpitations, ankle swelling, claudication
Obstetric & Gynecology
- LMP
- Vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pregnancies
Nervous system
- Headache
- Fits
- Depression
- Facial/limb weakness
METABOLIC/ENDOCRINE
- Muscular pain
- Bone & Joint pain
- Swelling of joints
- Limitation of movements
- Weakness
- Bruising/ bleeding (nutrients deficiencies)
- Sweating (thyrotoxicosis)
- Thirst (diabetes)
- Pruritus (skin infection, jaundice, uremia, Hodgkin’s)
- Alcohol
- Weight loss- ?dieting, amount and duration
6) Past Hx
Past medical / Surgical / Family
-
similar episode as before similar problem - (you can mention with HPI)
-
Chronic diseases + Family Hx / similar conditions Pancreatitis, bleeding peptic ulcer or inflammatory bowel disease, stones. RA, HTN, DM, Malignancy, cause of death in family
-
Past Admission + transfusion + Surgeries + past immunization Important to ask about previous abdominal surgery and if there were any complications during or after surgery
-
Pregnancy / Lactation
Medications / Allergies
-
Medication (name/dose/side effects)
- Antibiotics cause diarrhea
-
Allergy
Social im going to ask some specific question to reach to diagnosis, may i?
- Occupation,
- Travel,
- kids,
- smoking,
- alcohol,
- drugs,
- sexual activity
Other Hx presentations of past Hx
In biliary colic
Past Medical: recurrence, DM, HTN
Past Surgical; cholecystectomy, previous stone removal
Drug abuse: Alcohol, Travel (malaria),
…
In Jaundice CLD, Hematological, IBD, GB diseases Paracetamol, steroids, Anti TB Social: alcohol / smoking
7) Summary
77 yo sudanese male complaining of abdominal pain for 9 days which was severe compressing radiating to back associated with cough, with no hx of palpitation, syncopal attack - with hx of cabg.
8) Differential, Impression, most likely diagnosis
- Pancreatitis
- Gastric Ulcer
- biliary colic
- …
Then justify - most likely diagnosis follow through with directive investigations
9) Investigations
The investigations in all cases of the acute abdomen share the same generic outline:
Labs
- Routine bloods – FBC, U&Es, LFT, CRP, amylase
- Calcium in suspected Pancreatitis.
- Blood cultures – infection
- Lactate, Troponin
- Urine dipstick – infection/hematuria ± MC&S.
- Urine Analysis
- B-HCG pregnancy test - for all women of reproductive age.
- ABG – useful in bleeding or septic patients, especially for the pH, pO2, pCO2, and lactate for signs of tissue hypo perfusion, as well as a rapid hemoglobin.
- Note: Any amylase / lipase 3x greater than the upper limit is diagnostic of Pancreatitis. if lower than 3x it may indicate perforated bowel, ectopic pregnancy, or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Imaging
ECG In the emergency setting, every patient with abdominal pain should have an ECG to exclude myocardial infarction. Other imaging modalities that may be initially requested include:
Ultrasound:
- Kidneys, ureters and bladder (‘KUB’) – for suspected renal tract pathology
- Biliary tree and liver – for suspected gallstone disease
- Ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus – for suspected tubo-ovarian pathology
Radiological:
- An erect chest X-ray (eCXR) – for evidence of bowel perforation.
- CT imaging, depending on the suspected underlying diagnosis
KEY TESTS FOR OR SURGICAL PREPARATION
- CBC, electrolytes, creatinine, glucose
- INR/PTT
- CXR (if history of cardiac or pulmonary disease) bowel perforation
- ECG if clinically indicated by history or if >69 years and no risk factors - MI
in biliary colic
Blood tests: (complete blood count, liver function tests and serum amylase) will be normal
Imaging: Ultrasound abdomen will show the gallstones with acoustic shadowing.
in Jaundice
-
CBC (leukocytosis; obstruction, RBCs)
-
LFT (ALT AST ALP GGT Amylase…)
-
Coagulation profile (increased prothrombin in obstruction - deficient liver vit K)
-
Lipid Profile
-
Viral profile (hepatitis/Hiv)
-
U/S - size CBD (gallstone, carcinoma), acoustic shadow, thickness wall, distended, collapse, tumor in pancreas
-
ERCP - endoscopy, deuodenum, ampulla vater, dye is injected - to see any strictures or stone - stone can be retrieved - retrograde
-
MRCP - Diagnostic - intra/extra hepatic biliary tract imaging
-
CT - cancer, staging, malignancy
-
PTC - TANSEEM; used in severe cases of bilirubin to decompression - ?? -
10) Treatment Plan
General Acute Abdomen Depends on diagnosis and findings
in biliary colic cholecystectomy
In Jaundice Depends on the cause
- Choledicocholethiasis - ERCP if fails open surgery
- Carcinomas - chemotherapy, surgery depending on stage/operable diseases
- Head Pancreas carcinoma - Whipple’s surgery
Q&A Jaundice
Prehepatic: hemolysis, Malaria
- normal hepatic function - high indirect bilirubin
- urine & stool normal
Hepatic: Liver cirrhosis, Viral Hepatitis,
- Fever + malaise, Organomegaly
- ALT & AST ratio is higher
- Total bilirubin raised
- ALP is normal?
Post-Hepatic: Obstruction (Stones, head pancreas, carcinomas, strictures, inflammatory conditions; cholangitis, ((((((perampilliary tumour around the ampulla of vater - oppening both cbd????) ))) ((2cm pearmapillary tumour - maybe cancerinoma of ampulla of pancreas or bile duct or deuodenmum??)))))
Internal Obstruction… External obstruction - carcinoma head pancreas, LN’s in portal triad
- Jaundice, pleuritis, (Itching??)
- ALP, GGT high
types of stone and its location list?
stool & urine color depending on hepatics
Other Notes
gallbladder palpable - carcinoma ? Corviesar law? - distendended gallbladder suggested carcinoma
not palpable - in stone due to reccurent stones resulting in fibrosis
Charcot Triad (jaundice, Tenderness, RUQ, Fever)
Pentad (Triad + confusion + Hypotention)
typical presentation head pancreas - painless progressive jaundice

Examination
-
WIPER
- Wash hands
- Introduce
- Right side of bed
- Explain Procedure
- Permission for examination
- Position & Exposure
-
Preliminary examination
- General Appearance (man, comfortable, comatose, connected device)
- General examination (Vitals, hand/arm/axilla, hair, face, neck, chest, abd,leg)
-
Focused Examination + (correct technique)
- Specific System Exam - IPPA
- Inspection
- Palpation
- Percussion
- Auscultation
- Lesion/Swelling/Ulcer if present - SSSS TTEDC
- Specific System Exam - IPPA
-
Describe correct physical findings
1) WIPER
Exposure | position | privacy | Ask for vitals
- W ash hands (before and after)
- I ntroduce yourself to the patient and seek his or her consent
- P osition the patient correctly.
- E xpose the patient as needed (e.g. ‘Please take off your shirt for me now, if that is all right’)
- R ight side of the bed
Position & Exposure Abdominal (liver) exam: Supine - Mid nipple to mid thigh - cover genitalia
Intro
Greet, Introduce (5th year med), assure privacy (curtain, nurse), explain procedure, position (mention good position - supine semisitting) & exposure (from midchest to midthigh - cover genatelia)
In the end thank the patient document.
2) General Appearance
- Conscious and alert
- features
- connected devices
elderly male with good build lying comfortable to be - connected to cannula - not connected oxygen. (note general exam findings)
adult sudanese male lethargic, in bed not connected to any device.
conscious alert man, well built, healthy, looks comfetable laying on bed, connected to vitals signs, no iv canulla, no oxygen, no foleys
In neck exam Agitation, nervousness or lethargy, myxedema,
“Now i will do focused examination after general apperance, should i do general examination?”
Is the patient well or unwell, comfortable or in pain, moving easily or lying motionless? e.g. peritonitis?
Writhing in agony, e.g. ureteric or biliary colic?
3) General Examination
dont touch patient until needed
-
Vitals
- Temperature
- Pulse: Tachycardia, bradycardia, water hammer pulse
- BP & RR
-
Hand: organized explaination from distal to proximal
- distal - nail, feature…
- no janeway.. no osler node…
- specific - cardiac, GIT, Resp
- no infection, no swelling, no deformitiy in dorsum
- no palmar erythema: liver cirrhosis, mitral stenosis , rheumatoid arthritis
- No janeway lesion: CVS
- Leukonechia kolionechia
- Clubbing (window test); Hypoxia; angiogenesis many causes— likely resp cvs, congenital heart diseases, malignancy
- Rheumatoid deformity w/ ulnar deviation - Z shape thumb, fixed not correctable - ((swan neck vs boutonniere??)), guttering.
- Sweaty; Hyper
- Thick: Depature contracutre???, hypothyroidism
- Dry: hypo
-
Clubbing - window test
-
Capillary refill
-
Pulse: (rate | rhythm | character | volume | comparison | radioradial delay)
- Dorsalis pedis
- Medial Malleolus
- Popliteal arteria
-
water hammer pulse
-
Vital signs - BP, RR, Temp, Pulse, saturation, - mention need to check
-
Face & Neck: head to neck
- general appearance
- Hair: normal hair distribution
- eye: no pallor/jaundice
- Nasal: no nasal discharge
- Mouth: oral hygiene, central cynosis, oral ulcers
- Neck: no obvious thyroid LN JVP, cyst, swallow - want me to examine?
-
Abdomen: general palpation -
-
Lower Limb: Edema - thumb
Edema Grading- GRADE I: edema from dorsum of foot & then behind medial malleolus bilateral;
- GRADE II: Tibial
- GRADE III: Pinching, catching fold of skin on thigh to check edema
- GRADE IV: Antero-Abdominal wall; peduea orange appearance, thick, red +++ Sacral edema; ascites ((generalized anasarca?))
Abdominal (liver): Water hammer, jaundice, Spider novae, gynecomastia
axilla acanthosis nigricans indicating GI Malignancy, Abdomen, Edema
4) Focused Examination
Abdomen Focused Examination
Abdominal Inspection
Go in-front patient check for
-
hernias (Cough)
-
Umbilicus (everted or inverted?)
-
Symmetrical
-
Hair distribution
-
pigmentation
-
Visible masses
-
Scars / Surgical / tattoos
- Renal transplant Scar - located at Appendix right iliac fossa
- Kocher scar
- Midline scar
-
Deformities
-
Distention; 5 S’s (normally mild convex)
-
Fluid; Ascites
-
Fat
-
Flatus; Gas
-
Fetus
-
Fibroid - Mass
-
-
Abdominal movement with respiration
- Male - Abdomino thoracic
- Female - intercostals stronger
- Obstruction (intestinal / Gastric) perlstatic movement
- Pulsation (tumour / )
- Hernia (Cough - Bulging appear)
- Positive expansile impulse
- Umbilicus (Position “Central, shifted; due tumor”, evert, invert, discharges; pus, urine, fistula, etc…, skin; hair distribution, scars, cushing, cullen’s sign, caput medusa “central Portal HTN” peripheral IVC obstruction)
-
Lower limbs: Edema, hernias…
Pitting Edema (CLD) - warm your hand before palpation - press with two sides at same time for bony prom of tibia, check patient eyes for any pain - comment findings
Visible Mass comment on LESION
Abdominal Palpation
Essure good technique (full hand relaxed on patient + good percussion)
Superficial Palpation Do you have any pain in abdomen - start far away from site of pain - look at the patient eyes to check any tenderness
Palpate 9 quadrants anti clock wise starting from left iliac or far away from pain site
- Tenderness
- Gaurding
- Palpable mass
Deep Palpation - after inspiration palpate the areas
- Organomegaly
-
Hepatomegaly - Edge + Tenderness + liverspan (percussion) (confirm with chest percussion, then reconfirm percussion on abdomen for dullness after palpation) - Edge (sharp round?) surface (nodular, smooth?) Liver span is normally 6 to 12 cm in the midclavicular line
-
Pyelomegaly - bimanual - (costo-vertebral angle)
-
Splenomegaly - Oblique growth (Renocolic; splenic flexture) (use tips of hand on direction oblique more to palpate the spleenomegaly from LRQ obliquely to spleen site) - not palpable in healthy, palpate in wave form from tip of finger after deep breath
-
Cholecystitis - Murphy’s sign (Catch breathing)
-
How to differentiate kidney, spleen
-
Spleen has notch, enlarges Diagonally/Oblique, moves with respiration, not palpable, under rib cage cant go above it
-
Kidney enlarges Vertically, largely unrelated, Palpable , Ballottable, does not move with respiration
Abdominal Percussion
-
Organomegaly (differentiating organs and extent),
- Spleen & Liver Dull
- Kidney is resonant; bimanual
Liver size Start below then above costal margin by cm or finger width
-
Fluid thrill & Shifting dullness Shifting Dullness Percussion from below sternum - until dullness from bladder - then becomes resonance, change position of hand to vertical by then https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Eog7addNRwc M ild to moderate ascites are usually on flanks - You can check by percussion -
-
dullness progressively getting more by flanks Light percussion middle midline for shifting dullness - Between 3rd and 1st space between umbilicus then percussion rest check for ressonance/Dullness
-
to assure its ascites or mass; keep hand same position by 20-30 seconds;
-
do the percussion again after shift other side, then after 10 seconds for viscera of fluids to descend - percuss to check… switching patient to other side; if mass it will be dull - if ascites the fluid directed downwards resulting in shifting dullness & resonance - reverse shifting dullness? Ascites? if huge Fluid Thrill
Fluid Thrill bilateral test flick, not advised Severe ascites, will resulted in … 1. main indicator by simple touch, with slight movement of abdominal region 2. Put hand on other side, and stimulate the abdomen from opposite side - (((whilst asking patient put their hand in midline))); to prevent transmission of fluid through anterior abdominal wall
Resonance tympanic,
AUsc Perstaltic movement, aneryusm,
Costophrenic percussion
Abdominal Auscultation
Peristaltic movement, aneurysm, bruit
-
Bowel sounds: Healthy persons may have no bowel sounds for several minutes (silent intestinal contractions). Bowel sounds are exaggerated (borborygmus), and increased in rate in mechanical intestinal. Absent (paralytic ileus),
-
venous hum: (indicate portal hypertension) - soft systolic murmur - large volume of blood flows in umbilical and paraumbilical veins in falciparum ligament (portosystemic shunt)
-
hepatic bruit: (indicating increase vasculature) - Heard over the liver, usually due to hepatocellular carcinoma, or vascular hepatic tumours
-
Aortic bruit: Just above the umbilicus
-
Renal bruit: Occurs in renal artery stenosis due to turbulent flow through a narrowed vessel
-
Succussion splash: Excess fluid in the gut, e.g. from pyloric stenosis, or advanced intestinal obstruction, may splash when the abdomen is shaken, or the patient rolled from side to side
5) Complete examination with
- Lymph nodes,
- lower limbs,
- Per Rectal examination,
- Per vaginal if female
- Melenas,
- Temperature,
- Sacral Edema
6) Summarize Findings
…
7) Differential, Impression, most likely diagnosis
Based on findings
8) Investigations
Surgical
- CBC
- Coagulation profile (INR, Prothrombin)
- LFT (metastases) & KFT (contrast)
- Electrolyte (calcium; malignant hypercalcemia)
- Albumin
Abdominal Investigations
…
9) Treatment/Management Plan
Depending on findings
Other notes
small bowel obstruction management ng tube to relieve gas ringer lactate for resuscitation antibiotic if he’s going into surgery as prophylactic
partial with fluid to - 24hr gastrography treatment
S/S vomiting nausea abdominal pain
most common cause
- adhesion
- hernia (strangulated if ischemia - the other classification wiithout) same presentation as pain -
Volvulus - strangulated ischemic- emergency most common due after surgery due adhesion
partial obstruction with flatus
complete obstruction without flatus may vomit stool in chronic cases
Mechanical
Functional paralytic illeus - common after pregnancy after electrolyte imbalance - ringer lactate
High grade obstruction may perforate
Low grade obstruction partial
strangulated
Non strangulated
pseudoobstruction same as paralytic illeus - antibiotic other medication may cause this morphine
inttescucupection
Tumour may cause obstruction
Toxic Megacolon 9cm diameter normal
most commonly transverse and ascending colon
mostly medical cases - cllostriduim deficille may result due anitbiotic usage
management stop all antiboitic iv fluid change position
when will it be surgical?
surgical failed medication for 3 days detriotrated perforated
removal of all colon.