Hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatoma)
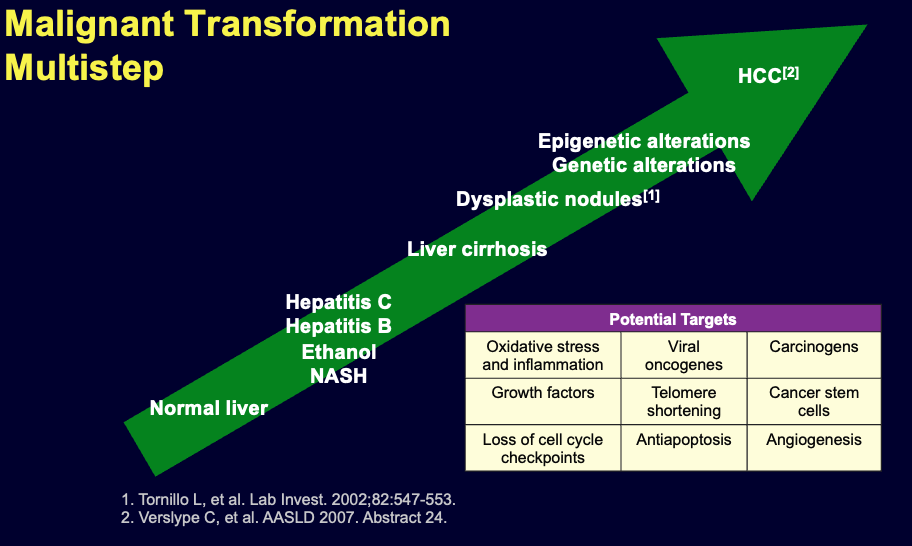
Risk factors
- Hepatitis b virus
- Hepatitis c virus
- Aflatoxin, derived from the fungus “Aspragellus flavus“
- Liver cirrhosis
Clinical features
Symptoms
- Asymptomatic in the early stage (even if 15cm tumor)
- Abdominal pain
- Sudden deterioration in the liver function due to extension of the tumor into the portal vein in patient with chronic liver disease
- Common presenting features involve progression of existing liver disease symptoms (abdominal pain, weight loss, abdominal distention, fever, spontaneous intraperitoneal hemorrhage)
- Jaundice is not common unless there is advanced cirrhosis
screen cirrhotic patient every 6 month and alpha fetoprotein
Signs Examination may reveal features of established liver disease and hepatomegaly
Investigations
Lab tests: LFT is generally deranged. α-fetoprotein (AFP) is tumor marker which elevated in some patient with HCC and can be used as screening test in high risk patients (e.g. cirrhosis)
Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan and MRI can assess the site, size, diagnosis of the tumor and can help in planning the surgical resection. CT scan will show hypervascular tumor.
HCC CT FINDINGS
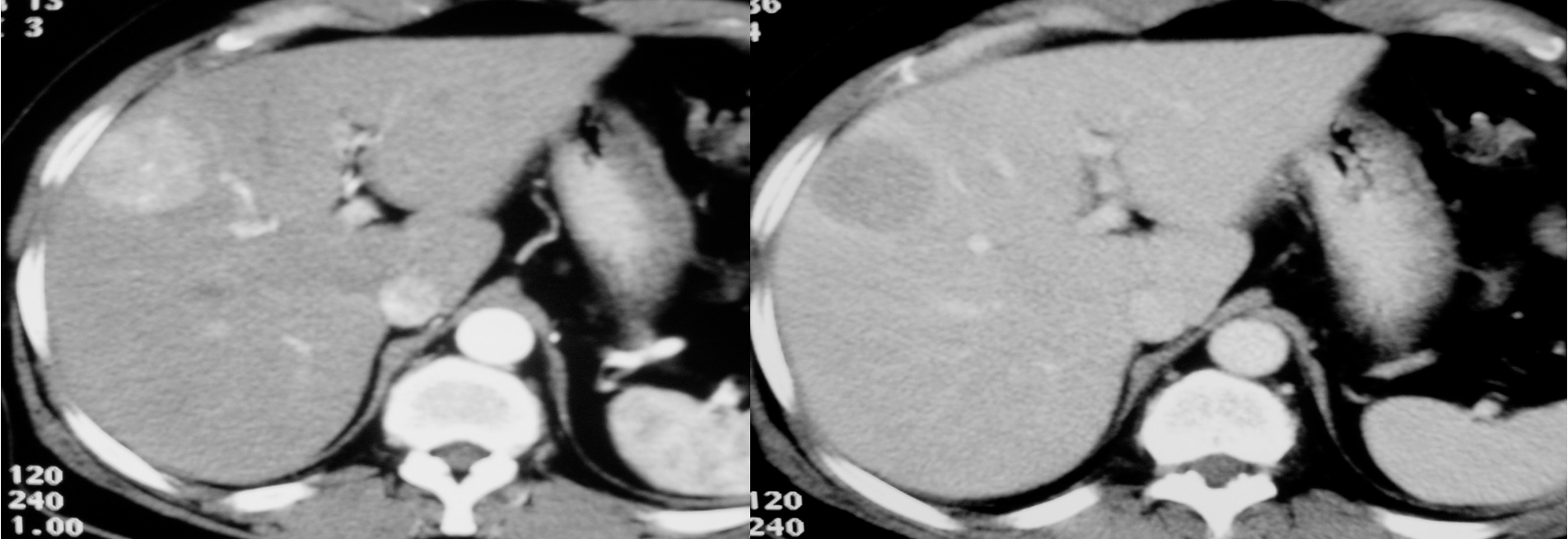 Arterial phase shows hypervascularity of the HCC tumor on right lobe - washing in
in venous its opposite - washing out
Arterial phase shows hypervascularity of the HCC tumor on right lobe - washing in
in venous its opposite - washing out
diagnostic for HCC gold standard- doesnt need biopsy
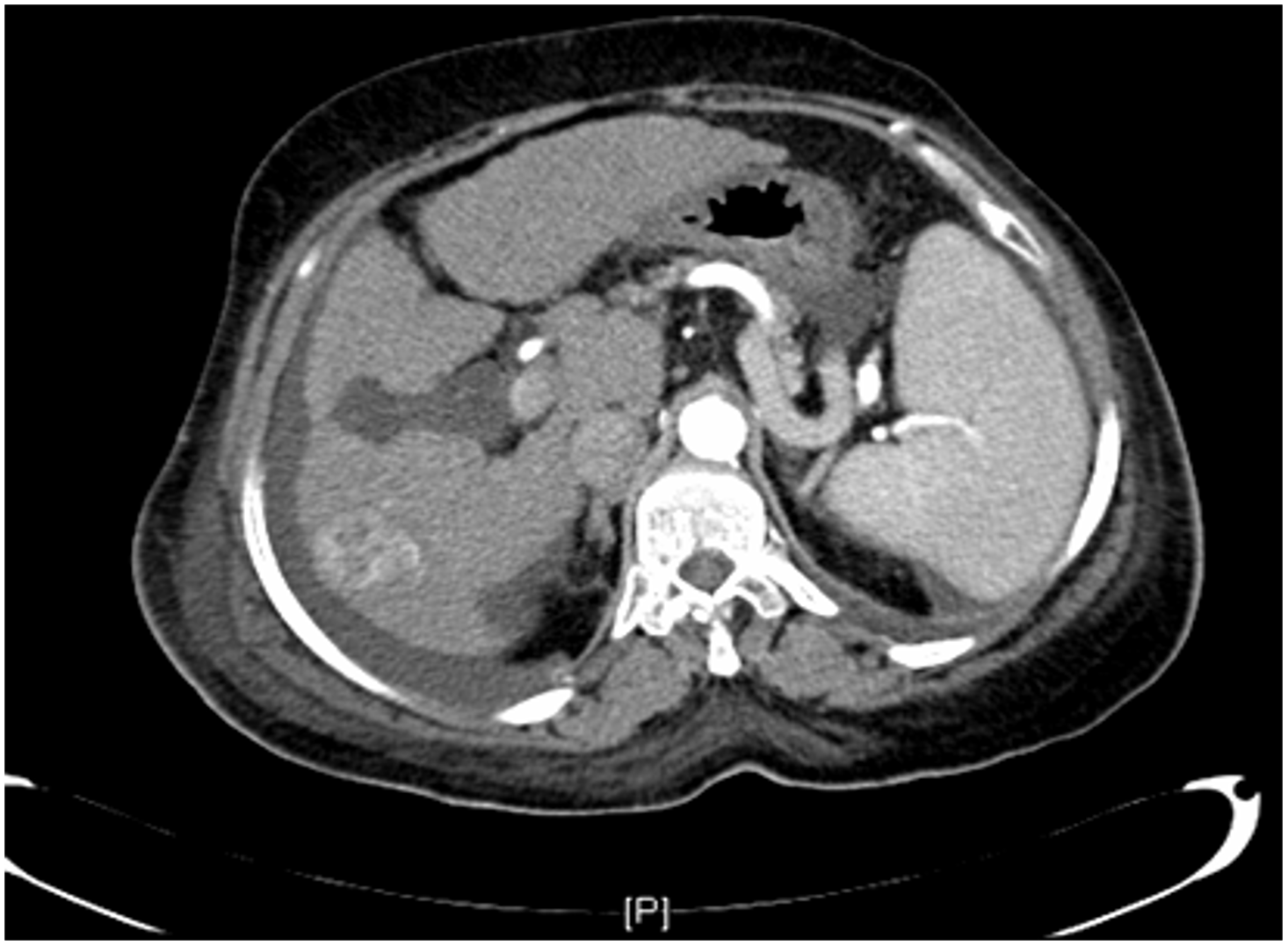 irregular margin, liver shrink, ascites present
irregular margin, liver shrink, ascites present
CT scan : Huge hepatocellular carcinoma in the right lobe of the liver

Biopsy
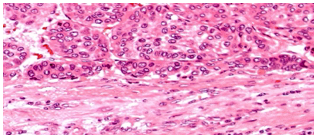
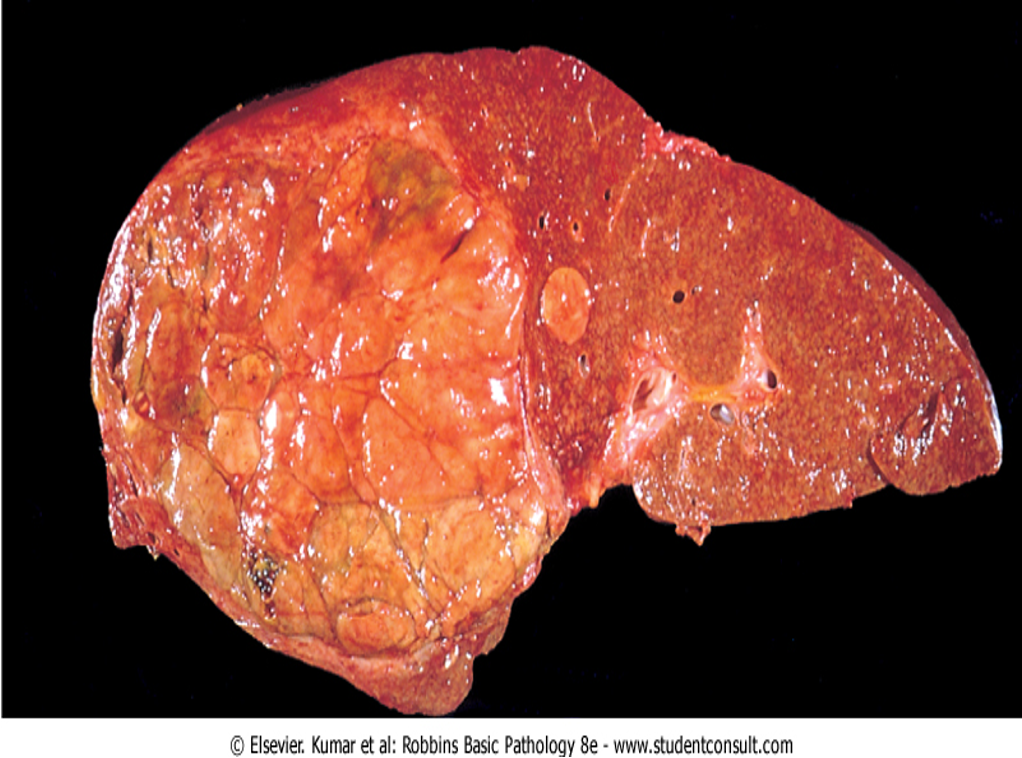
Gross HCC - Liver Cirrhosis (HBV – HCV)
 cirrhotic, tumour round homogenous on right lobe
cirrhotic, tumour round homogenous on right lobe
Huge hepatocellular carcinoma in the right lobe of the liver
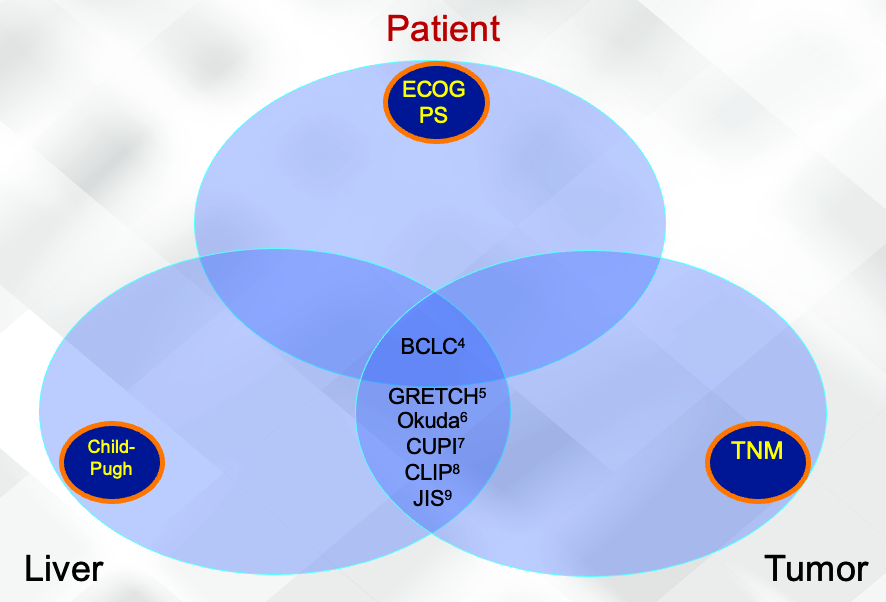
HCC Staging is Multifaceted
Staging is used for prognosis and to guide treatment1 Y Staging HCC1
- Most patients have underlying liver disease
- Key prognostic indicators are not clearly defined
- Prognostic indicators vary during the course of disease
Factors affecting staging systems 2,3 Y
- Tumor stage
- Liver function
- Health status
- Impact of treatment
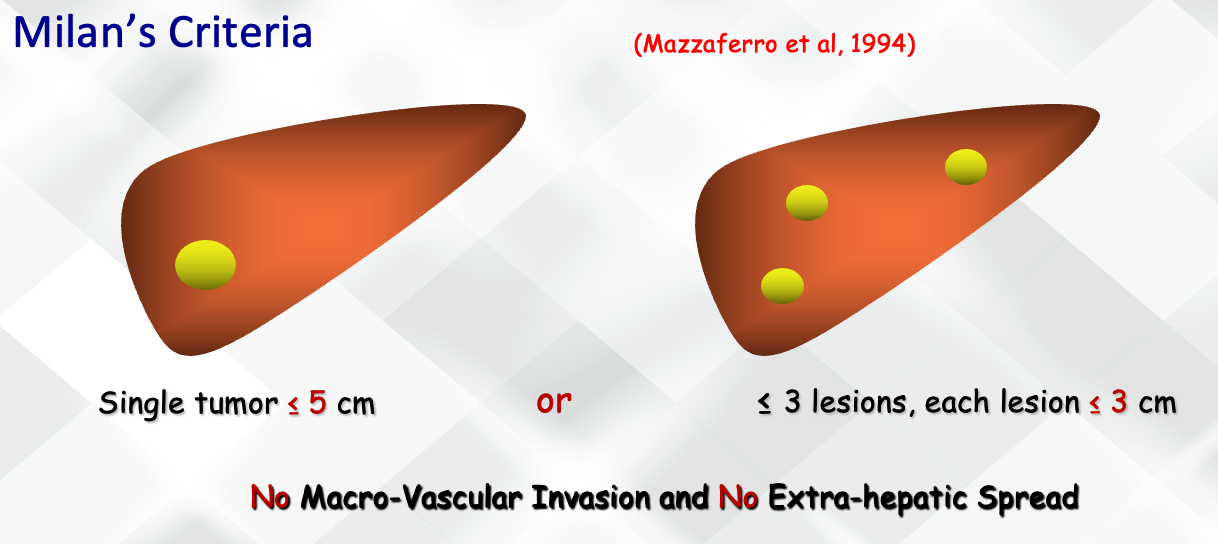
Liver Transplantation for HCC “Patient Selection”
No Macro-Vascular Invasion & No Extra-hepatic Spread
Milan’s Criteria
- Single tumor ≤ 5 cm or
- ≤ 3 lesions, each lesion ≤ 3 cm
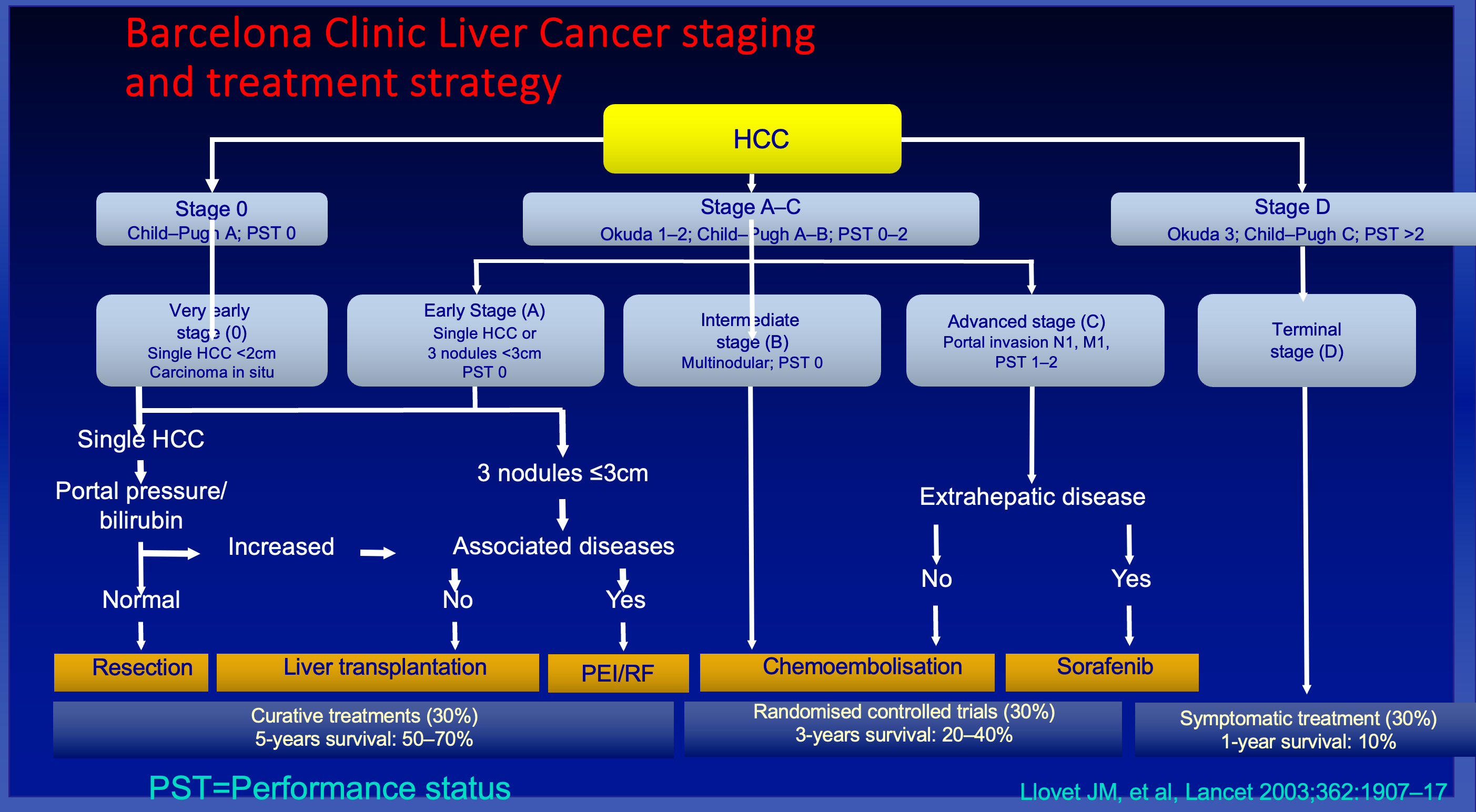
Y Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging and treatment strategy
HCC
Stage 0 Child-Pugh A; PST 0
- Very early stage (0)
- Single HCC <2cm
- Carcinoma in situ
Stage A-C Okuda 1-2; Child-Pugh A-B; PST 0-2
- Early Stage (A)
- Single HCC or
- 3 nodules <3cm
- PST 0
- Intermediate stage (B)
- Multinodular; PST 0
- Advanced stage (C)
- Portal invasion N1, M1,
- PST 1-2
Stage D Okuda 3; Child-Pugh C; PST >2
- Terminal stage (D)
Single HCC
Portal pressure/bilirubin
- Normal
- Resection
- Liver transplantation
- Curative treatments (30%)
- 5-years survival: 50-70%
- Increased
- 3 nodules ≤3cm
- Associated diseases
- No
- PEI/RF
- Yes
- Chemoembolisation
- Randomised controlled trials (30%)
- 3-years survival: 20-40%
- Chemoembolisation
- No
- Associated diseases
- Extrahepatic disease
- No
- Yes
- Sorafenib
- Symptomatic treatment (30%)
- 1-year survival: 10%
- Sorafenib
- 3 nodules ≤3cm
PST=Performance status
Llovet JM, et al, Lancet 2003;362:1907-17