PEDIGREE
When constructing a pedigree, ask about miscarriages, stillbirths, and consanguinity. Take details from both sides of the family and record dates of birth rather than current ages.
POLYGENIC, MULTIFACTORIAL OR COMPLEX INHERITANCE
Many factors are involved in causing a birth defect.
- A combination of genes from both parents, in addition to environmental factors, produces the trait or condition.
- Often one gender (either males or females) is affected more frequently than the other in multifactorial traits. For example, hip dysplasia is nine times more common in females than males.
Multifactorial inheritance characteristics:
- The higher the number of affected individuals in the family, the higher the recurrence risks.
- The recurrence risk is higher if the affected individual is a member of the less commonly affected sex (e.g., Autism is more common in boys than girls, but if a girl in the family has autism, it is twice as likely to recur in a sibling than if a boy is the one with autism).
- Recurrence risk is higher if the affected individual suffers the more severe form of the disease.
- Recurrence risk correlates with the prevalence in the general population.
Rickets Case Z
The mother of a 23-month-old dark skin infant expresses-1 concern that her son has bowing legs and he is not growing properly. He was exclusively breastfed until 11 months of age. He is a picky eater.
- ?Write two relevant questions, to ask the mother
- What specific signs you should look for during examination of ?this infant
- ? What are the important investigations
- What is the most likely diagnosis and give two differential ?diagnosis
- How you will treat this infant and how you will educate the mother ?to prevent this disease for future infants or recurrence
Answers
-
-:Ask the mother about the following
- Vitamin D supplement, sun exposure, family history of similar illness
- Muscle weakness, seizures, fractures
-
Growth parameter HT.WT
-
Frontal bossing, open AF
-
Wide wrists, Rachitic rosary, craniotabes, dental abnormalities
-
:C- Investigations
- X-ray of the left hand
- Serum level of Ca, phosphorus, Alkaline Phosphatase
- Vit D level, PTH
-
D- likely diagnosis :Nutritional rickets
-
: Differential diagnosis
- Vitamin D-dependent rickets
- Familial hypophosphatemia rickets
- E. treatment: Vit D
-
Prevention:
- Sun exposure
- Vit D Supplement
- Diet rich in vitamin D
- 3 abnormalities in X-ray
Rickets Case
28 month girl come to dr. complain of bowing and failure to thrive shh took brest feeding for 9 month then start feeding
Write two relevant question?
- Family history, diet, feeding, sun exposure, hypotonia, convulsions
What finding you will look to on examination?
- Rickety rosary, thick wrist joint, Harrison sulcus, SCOLIOSIS
Wriete important investigation?
- SERUM VIT D, ALP,CALCIUM,PHOSPHORUS, PTH, WIRST X RAY
Diffrential diagnosis?
- NUTRITIONAL RICKETS, VIT D RESISTANT, CELIAC DISEASE
Treatment ??and what advice the mother on future ?
- DIET, SUN EXPOSURE, VIT D SUPPLEMENT
Anemia Case Z
17-month-old boyl, presenting with pallor. Mom states his appetite is also poor and he is more irritable than usual. There is no history of splenectomy, gall stones at an early age, or other anemia in the family.
-
a- Write 3 relevant questions, to ask the mother?
- -diet
- -feeding
- -stool color
- Family history
-
b- What specific signs you should look for during examination of this infant?
- -lymphadenopathy
- -tachycardia, irritability koilonychias, beefy tongue, chelosis
- pallor in hand, systolic murmer
-
c- What are the important investigations?
- -cbc with deferential analysis
- -serum iron level,TIBC,SERUM FEERRITIN
- -stool
-
d- What is the most likely diagnosis and give two differential diagnosis?
- -iron deficiency anemia
- thalasemia major. -Sideroblastic anemia -Lead poisoning - Copper deficiency
-
e- How you will treat this infant and how you will educate the mother to prevent this disease for future infants or recurrence?
- Oral iron supplement 4-6mg
- Advices iron rich foods like animal protein and green vegetables
Feeding Issue
- Infant refusing to breast or bottle feed
- Received NG tube feeds for approx 2 weeks
- Wt gain rapidly picked up at 6 month
Pediatric Cases and Growth Charts
- a) what is the figure called ? GROWTH CHART
- B) comment on chart (female 10 yrs increase in height normal. Weight)
- C) Name 4 causes for it ?
- Familial
- Acromegaly
- Genetic
- Metabolic
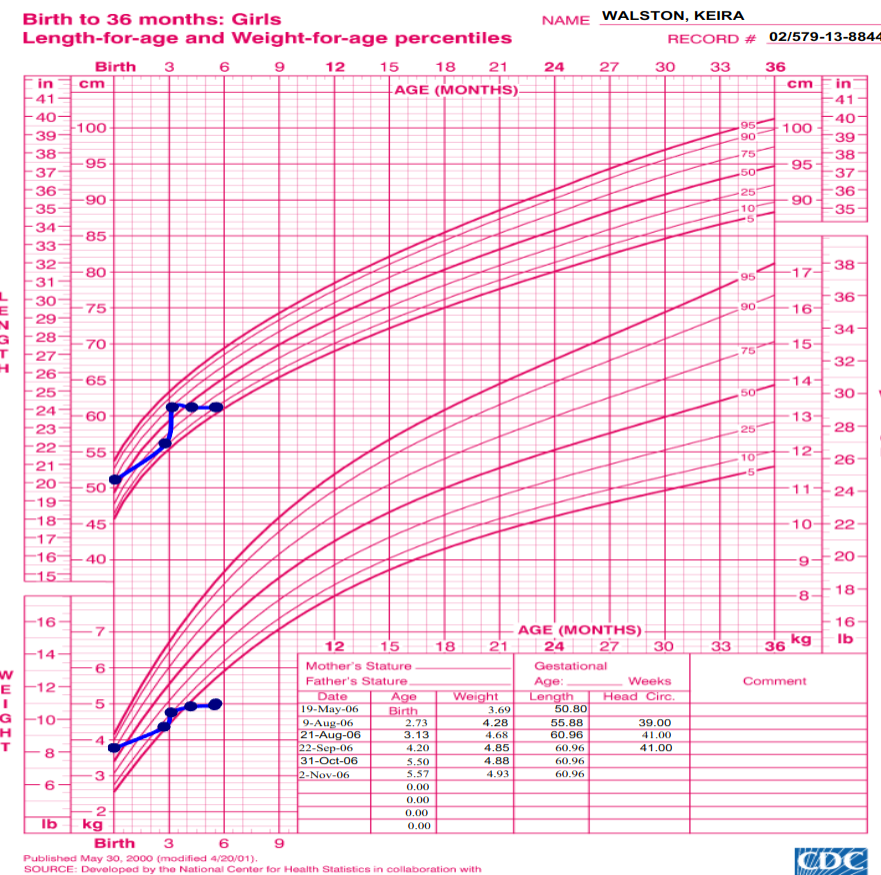
4 month old girl, well child visited clinic
- Mother complained about poor wt gain
- Same problem with first child
- Husband is unemployed
- Other development was normal
- Mom alleged that feeding was going well (breastfeeding)
- Wt = 5kg
- Went to ER at age 5 months
- Wt was “down”
- Infant transferred to a children’s hospital for inpatient stay
- Infant refusing to breast or bottle feed
- Received NG tube feeds for approx 2 weeks
- Wt gain rapidly picked up at 6 month
Growth Chart Image
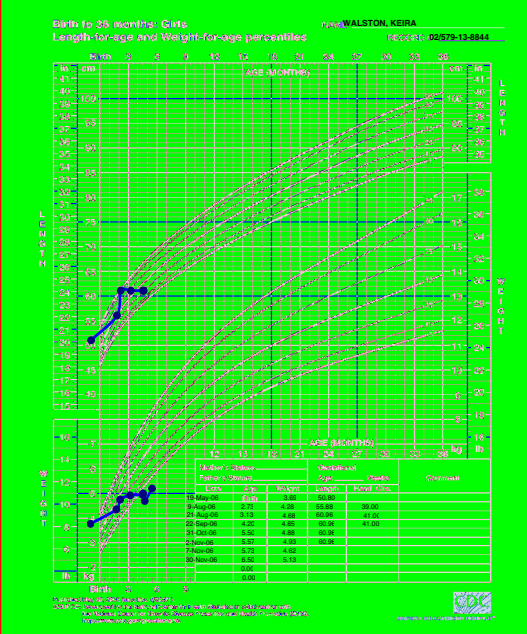
- ? Which type of growth chart is used for this infant
- ?Describe two abnormalities seen in the chart
- ? What is the likely cause of these abnormalities
-:Answers a. weight for age and height for age of girls from birth to 36 months b. Weight for age curve falls across two major percentile lines twice. e.Height for age curve falls across two major percentile lines twice c. Failure to thrive secondary to infant neglect (abuse).
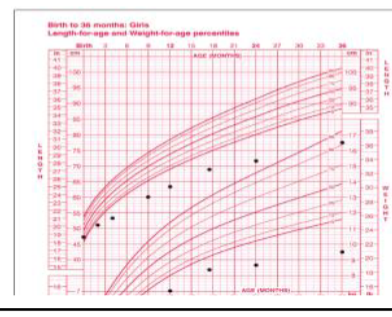 Growth Chart:
Growth Chart:
- What is the diagnosis? Gluten Sensitivity Disease
- What is the next step investigation? Endosomal Antibodies
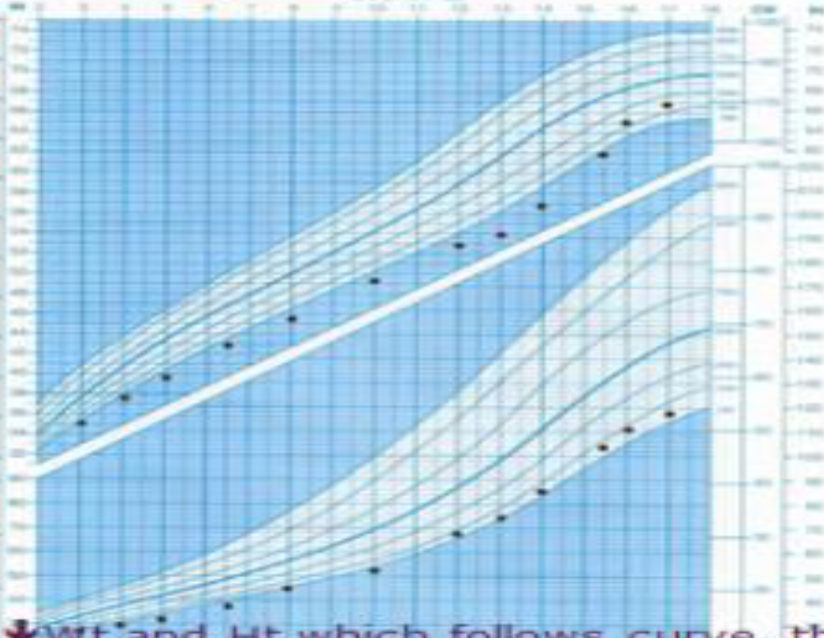
Marasmus Growth Chart
Growth Chart about Marasmus
- 1. what is the Diagnosis ?
- Marasmus
- 2. Cause af Malnutrition?
- Decrease Caloric Intakes
- 3. Interpritation about Growth Chart
 Growth Chart (Boy):
Growth Chart (Boy):
- Description: Growth Chart for boy shows Failure To Thrive, both weight and height decreased or affected, which eventually improved, maybe due to IUGR
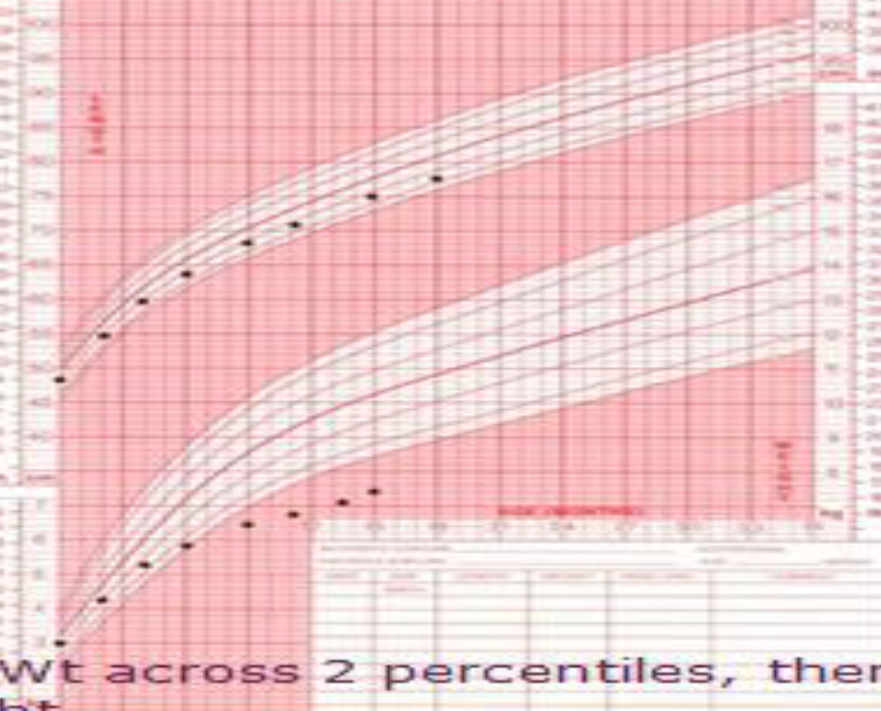 Growth Chart (Girl):
What is observed in the growth chart? Weight crosses 2 centiles, then height follows a normal deviation.
Growth Chart (Girl):
What is observed in the growth chart? Weight crosses 2 centiles, then height follows a normal deviation.
What is the likely diagnosis? Failure to Thrive.
 Growth Chart (Boy):
Growth Chart (Boy):
- Description: Growth Chart for boy shows Failure To Thrive, both weight and height and Head circumference decreased or affected due to Congenital Abnormality.
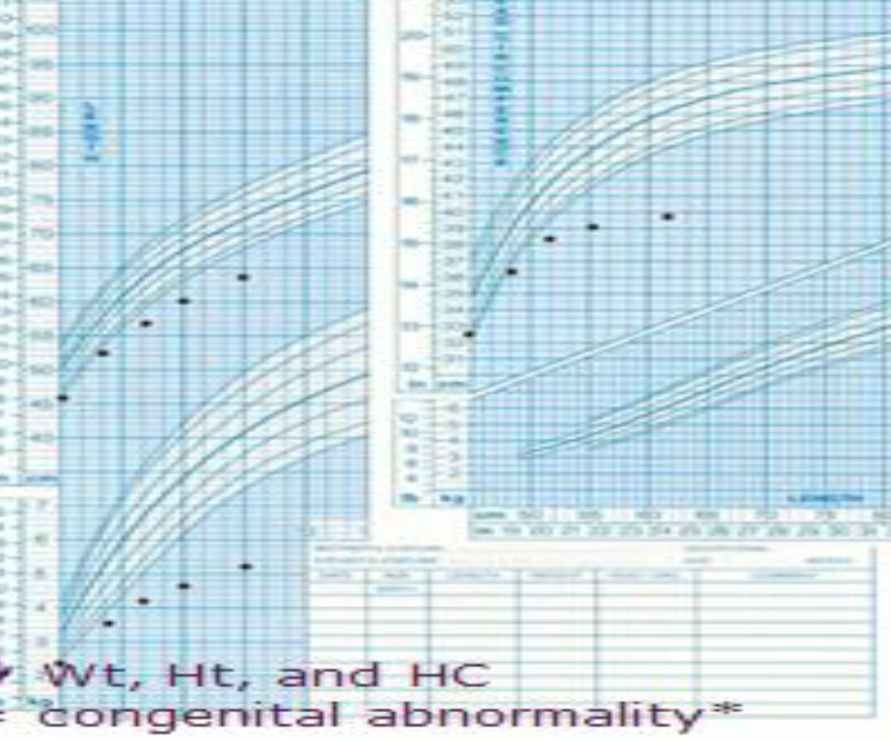
 Growth Chart (Girl):
Growth Chart (Girl):
- Description: Growth Chart for Girl form the start she was normal then went to failure to thrive then was managed and improved then went to failure to thrive again.
- Diagnosis: Recurrent failure to thrive
 Station 7: Growth Chart
Station 7: Growth Chart
- Growth chart
- What is the diagnosis? Gluten Sensitivity Disease
- What is the next step investigation? Endosomal Antibodies
Case Study: Growth Chart

Questions
- Describe the growth chart?
- The chart displays stature-for-age and weight-for-age percentiles for girls aged 2 to 20 years.
- It includes curves representing different percentiles (e.g., 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 90th, 95th).
- The plotted points indicate the individual’s measurements over time.
- Name 2 associated diseases?
- Growth hormone deficiency
- Chromosomal abnormality
Case Study: Constitutional Delay of Growth
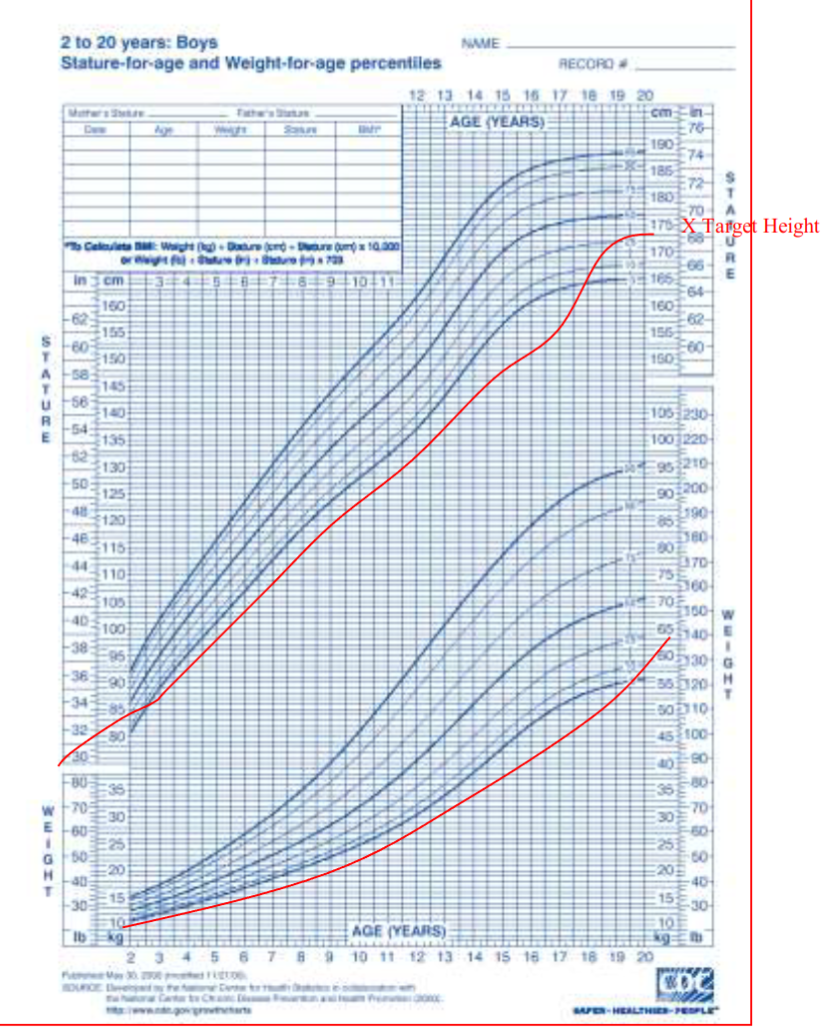
Questions
- A-What is the diagnosis?
- Constitutional Delay of Growth
- B-What is the bone age to chronological age?
- Delayed
- C-Puberty (early, appropriate, delayed)?
- Delayed
- D-how to reassure the parent through the growth chart about there child?!!!!!
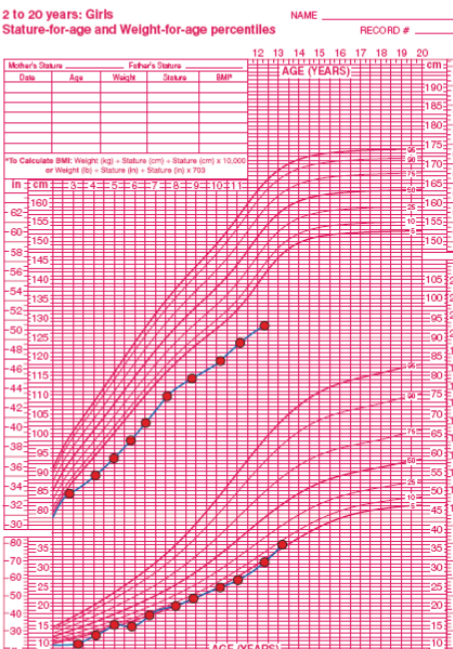
Case
This is growth chart of 13 years old describe? This patient has short stature and failure to thrive give 4 possible cause ? Chronic disease, Malnutrition, Chromosomal abnormality, Growth hormone deficiency
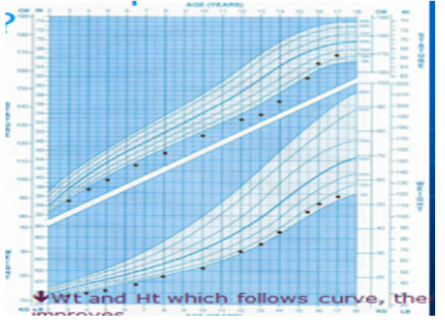
Case
Description: Growth Chart for boy show Failure To Thrive, both weight and height decreased or affected which eventually improved maybe due to IUGR
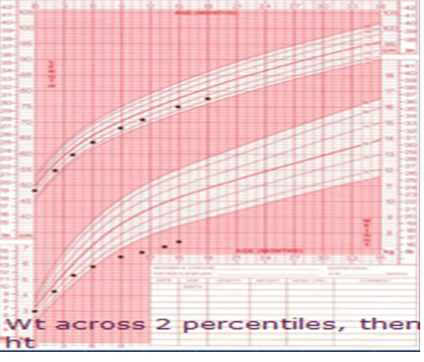
Case
Description : Growth Chart for Girl show failure to thrive weight across 2 percentile the height
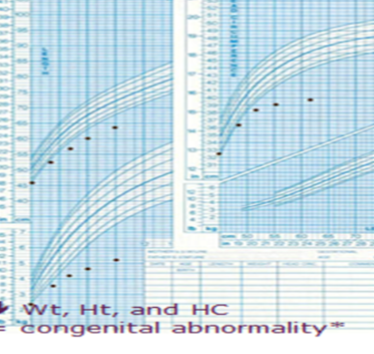
Case
Description: Growth Chart for boy show Failure To Thrive, both weight and height and Head circumference decreased or affected due to Congenital Abnormality.
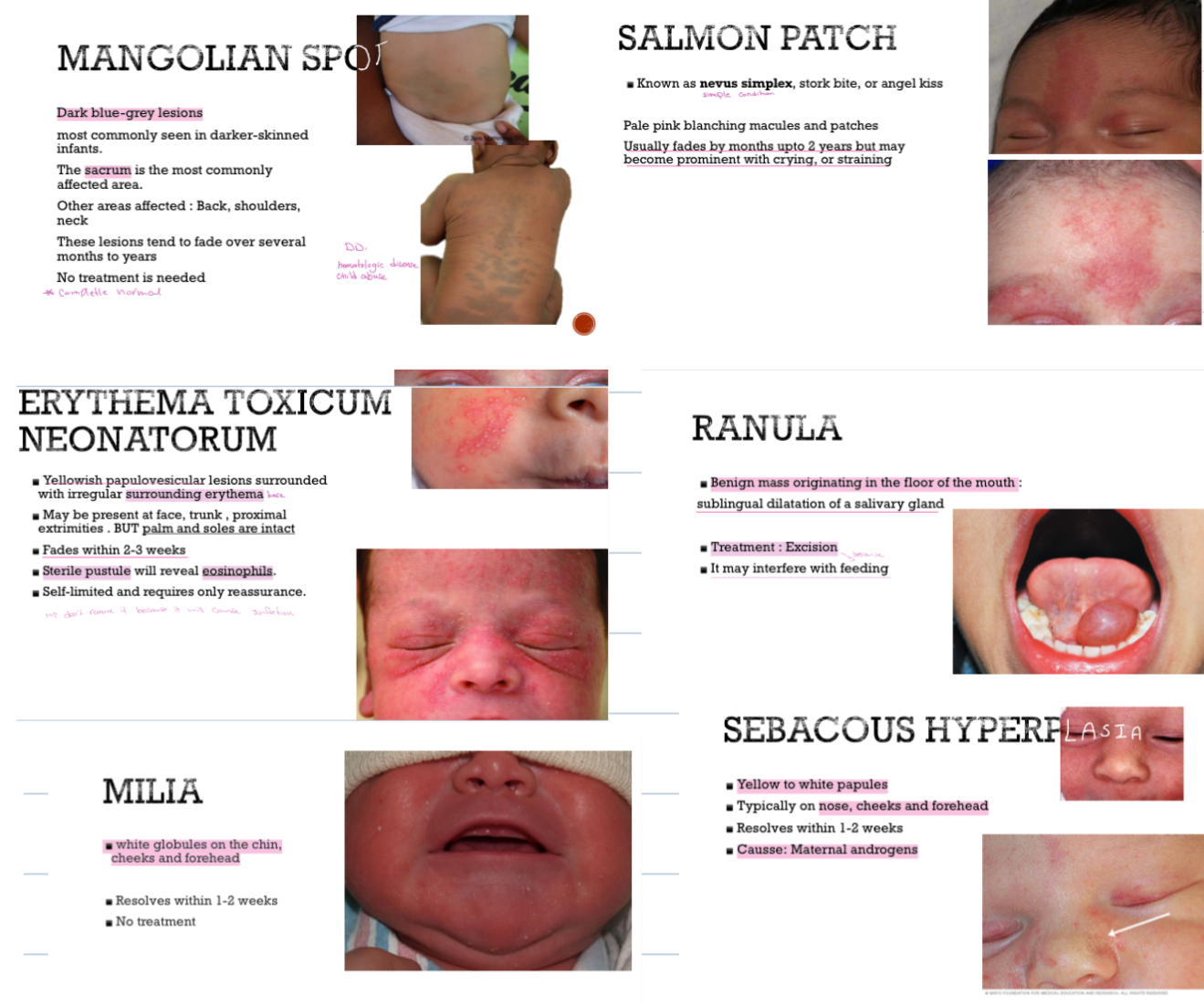
- Mangolian Spot
- Salmon Patch
- Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum
- Ranula
- Milia
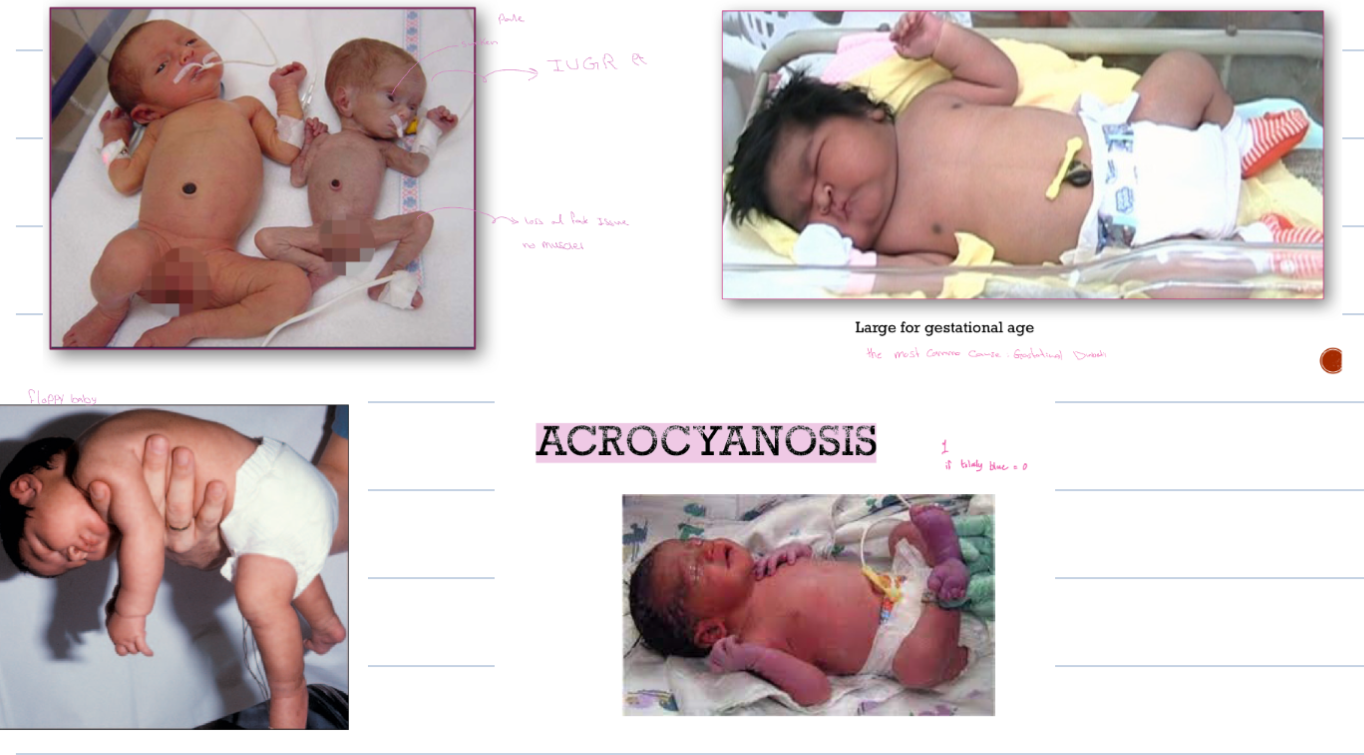
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia
- Acrocyanosis
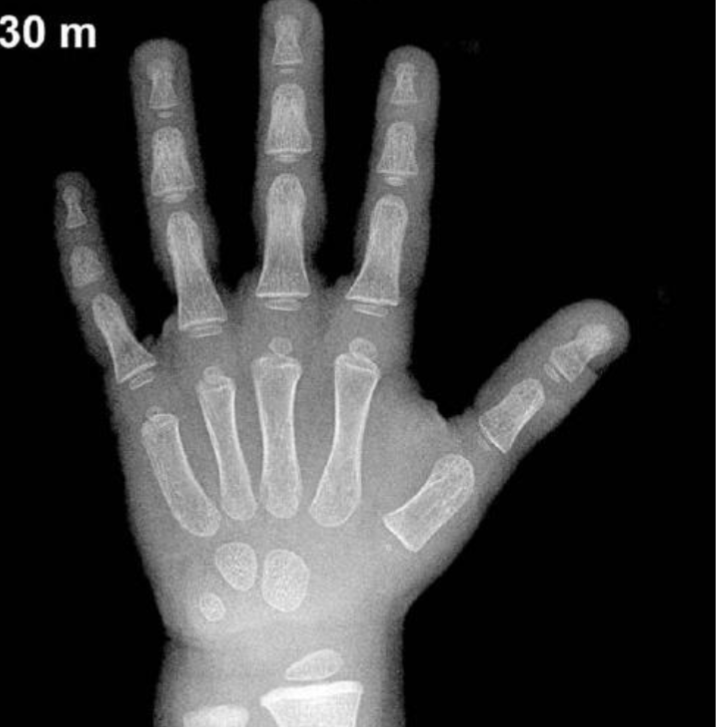
Case
The bone age of this boy is 30 month (2y 6 month), but the chronological age is 5 years. give 2 cause of delayed bone age? 1.Hypothyroidism 2.Constitutional growth delay
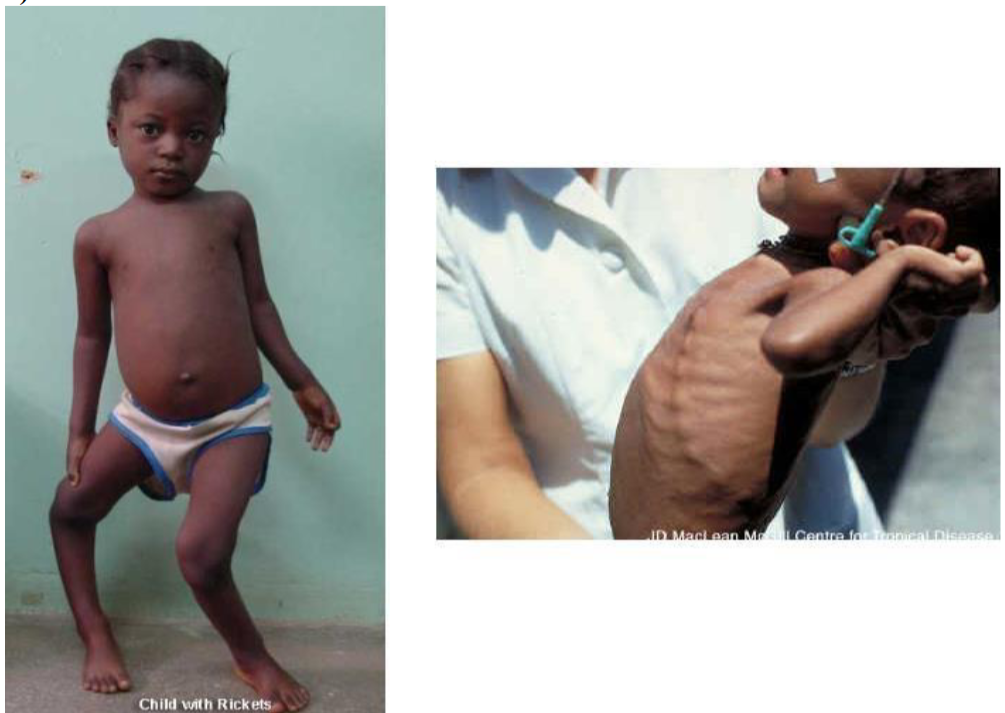
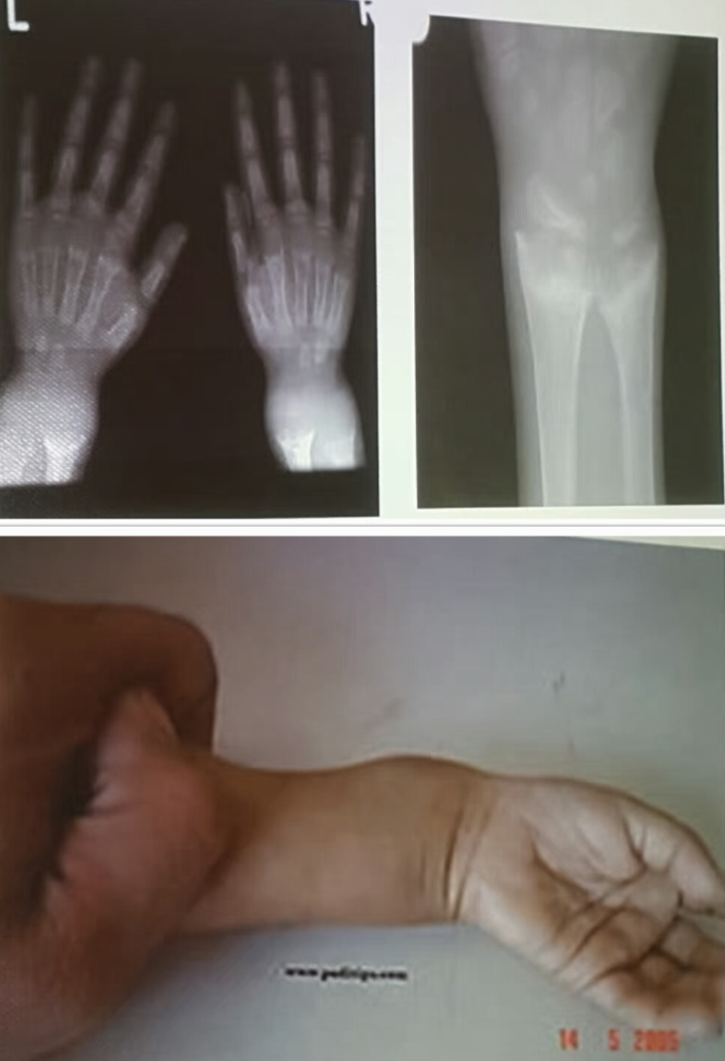
Child with Rickets - 18-month-old infant has bowing legs and is not growing properly. He was exclusively breastfed until 11 months of age.
- Mention 2 abnormalities sign in this pictures?
- Rachitic rosary (Knobby deformities)
- Leg bowing
- What is your diagnosis?
- Rickets
- Q2. What are other relevant investigations?
- a. Total iron binding capacity (TIBC).
- b. Serum level of Ca, phosphorus, Alkaline Phosphatase.
- c. Vit C level
- d. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). What are the findings in the X-ray images? Widened metaphysis, osteopenia, cupping, and wide, frayed appearance.
Rickets: Craniotabes
very weak and fragile bone
HARRISON SULCUS

Case Study: Marasmus Z
Infant was delivered by c/s due to fetal distress at 40 weeks gestation. His birth weight was 2.1 kg. He developed severe, difficult to control hypoglycemia. What is the diagnosis?
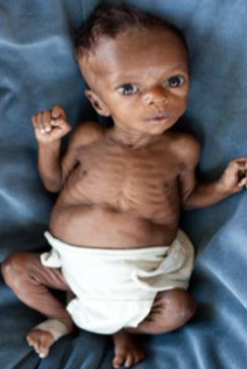
Questions
- Diagnosis?
- Marasmus
- Describe?
- Wasting, wild eyes, abdominal distention, senile monkey face
- Cause?
- Caused by malnutrition, Large VSD
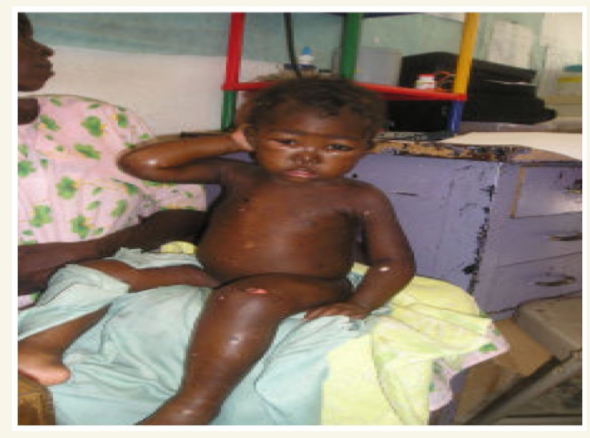
Q5A-B Q3-A: Most likely the diagnosis? A: Kwashiorkor. Q3-B: Describe? A:
- Muscle wasting.
- Edema.
- Depigmentation.
- Dermatoses.
- Hypopigmentations,
- Hyperpigmentations,
- and skin peeling.
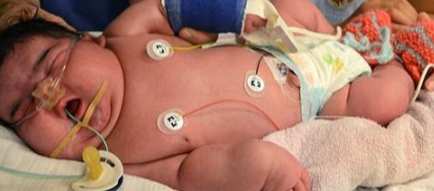
Severe hypoglycemia and hypocalcemia Z
- The mother had no antenatal care
- Diagnosis? Macrosomia
- Complication? RDS, polycythemia, CHD, shoulder dystocia
- Birth injuries
- Respiratory distress
- Sacral agenesis
- Large for GA
- Respiratory distress, polycythemia
- Congenital malformations
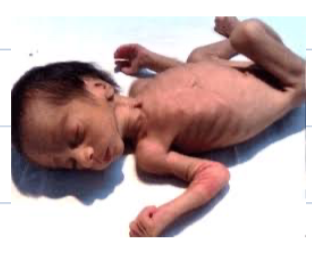 Diagnosis: IUGR / due placental insuffencies
Complication : cardiovascular disease-malnutrition
Diagnosis: IUGR / due placental insuffencies
Complication : cardiovascular disease-malnutrition
Case Study: Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)
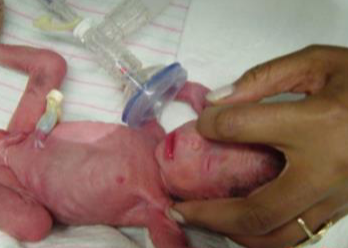
Questions
- 40 weeks of gestation, 2.1kg, Can’t control the hypoglycemia? Diagnosis??
- IUGR (Intrauterine growth retardation)
- Mention 2 acute associated symptoms?
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Cyanosis
- Failure to thrive
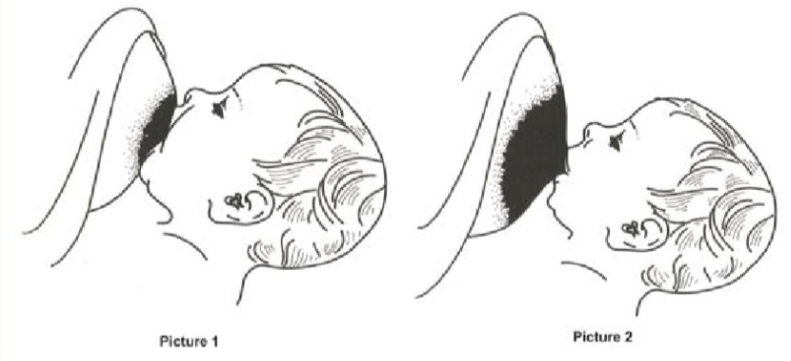
Q1A-B Q1-A: Which one of the pictures is considered as good breast attachment? (Pic1 or Pic2)? A: picture 1 Q1-B: name 2 complications of bad attachment? A:
- Breast Abscess.
- Mastitis.
- Breast engorgement.
- sore or fissured nipple.
Case Study: Formula vs. Breast Milk
Questions
- A- give important deference between formula and breast milk?
- Protein is more in formula, carbohydrate and immunoglobulin are more in breast milk
- B- give one electrolyte difference between formula or breast milk?
- Potassium, sodium is more in formula
- C-vitamin D is more in which formula or breast milk?
- Vitamin D is more in formula
- D-one related complication to formula milk?
- Increase chance of obesity, DM, decrease immunity …
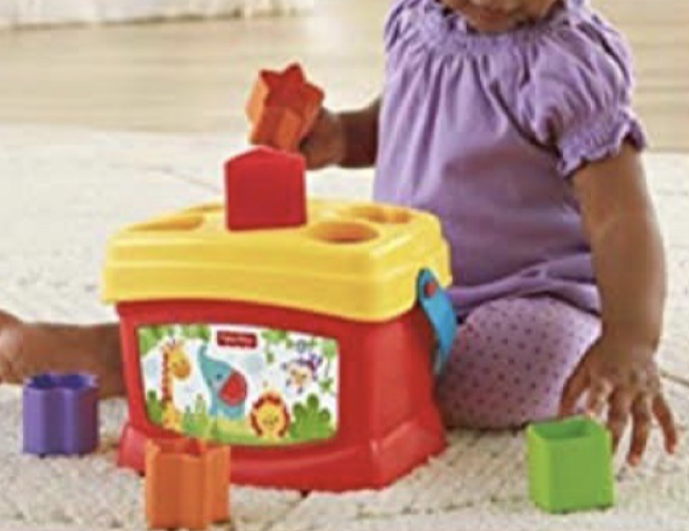 Q2. At what age child start developmental milestones noticed in the picture:
a. 7-8 months.
b. 1-2 year.
c. 11-14 months.
d. 4-5 months.
I put 8-12 month
It’s According to what Milestone
you wrote
Q2. At what age child start developmental milestones noticed in the picture:
a. 7-8 months.
b. 1-2 year.
c. 11-14 months.
d. 4-5 months.
I put 8-12 month
It’s According to what Milestone
you wrote

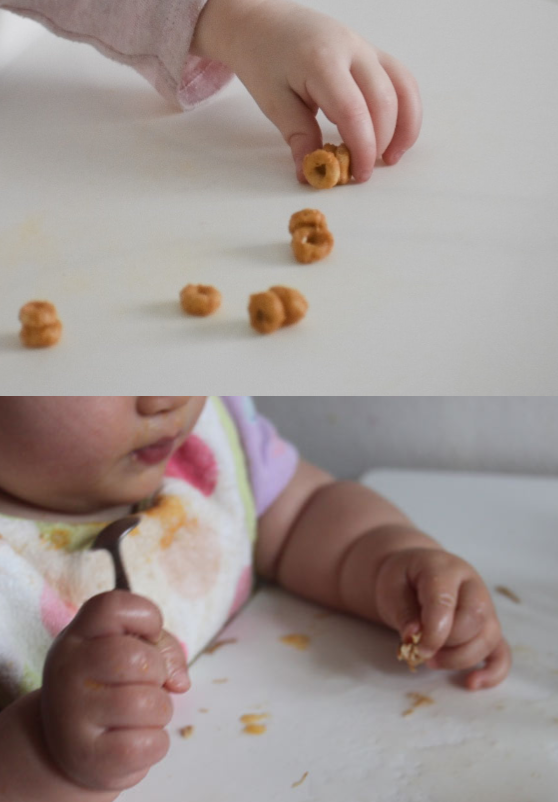
- Fist? 4-5 months
- Four finger grip? 6-8 months
- Pincer grip? 1 year to 1.5 years

Case Study: Moro Reflex Z
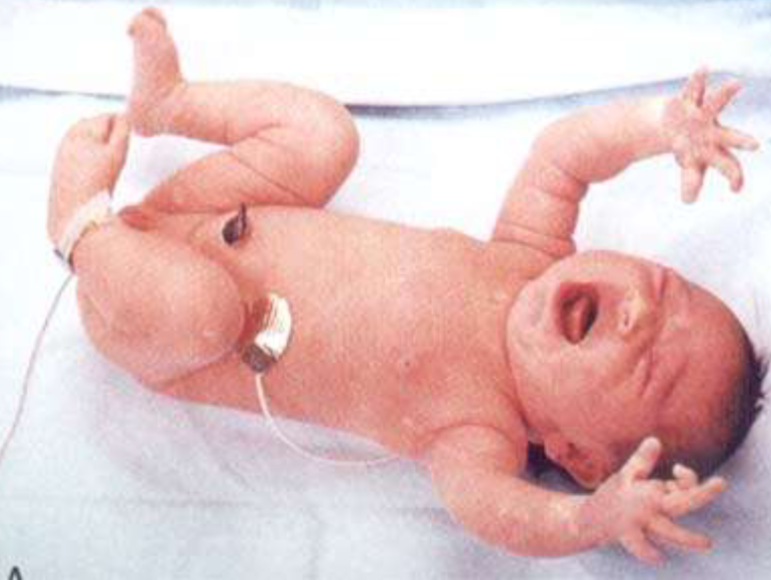
Questions
- A-What is the name of the reflex?
- Moro reflex
- B-when does this reflex disappear?
- 4-6 months
- C-if it is asymmetrical give one diagnosis?
- Erb palsy
- D-if it is absent in both sides give one diagnosis?
- CP cerebral palsy


Range of age : 9 months
- Mention 2 developmental milestone aspect in this picture?
- Gross motor: sitting without any support
- Fine motor: grasp
- Communication/Social: smile
- What is the likely syndrome?
- Down syndrome (trisomy 21 )
Pedigree:
- What is the mode of inheritance? Autosomal Dominant
- What is the possible diagnosis? Neurofibromatosis Type 1
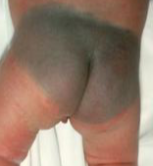 Blue-Black Spot on Buttocks:
Blue-Black Spot on Buttocks:
- What is the diagnosis? Mongolian Spot
- What is the management? Assure the mother
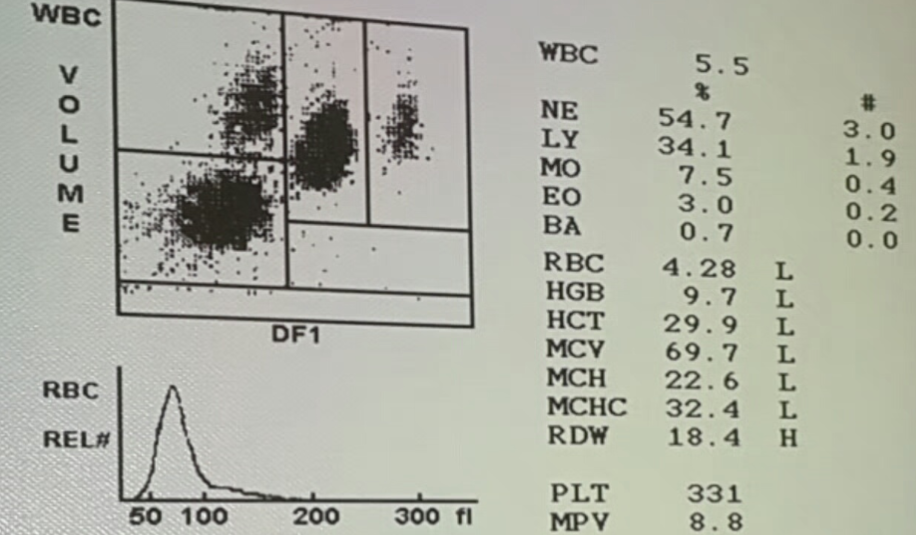 What are the findings in the blood analysis? Microcytic hypochromic red blood cells.
What are the findings in the blood analysis? Microcytic hypochromic red blood cells.
What is the likely diagnosis? Iron deficiency anemia.
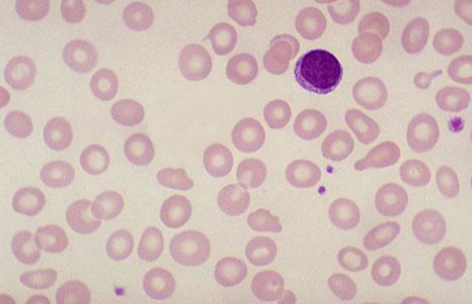 (RP)
(RP)
- Diagnosis? Peripheral blood film shows hypochromic microcytic cells in severe iron deficiency anemia.
- In which kind of rickets this finding will appear? Vitamin D dependent type 2
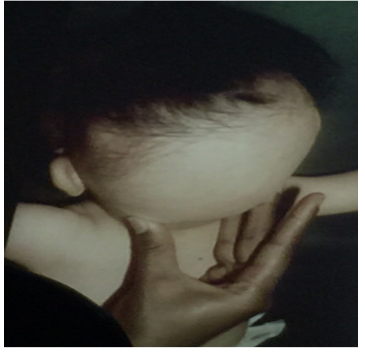
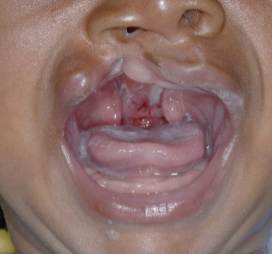
Diagnosis: Cleft lips and palate
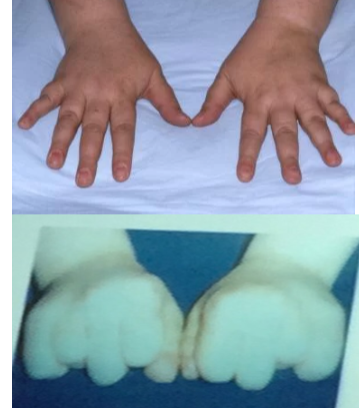
Patient with hypocalcemia
- What is the most likely diagnosis? Pseudohypoparathyroidism showing shortened fourth metacarpals.
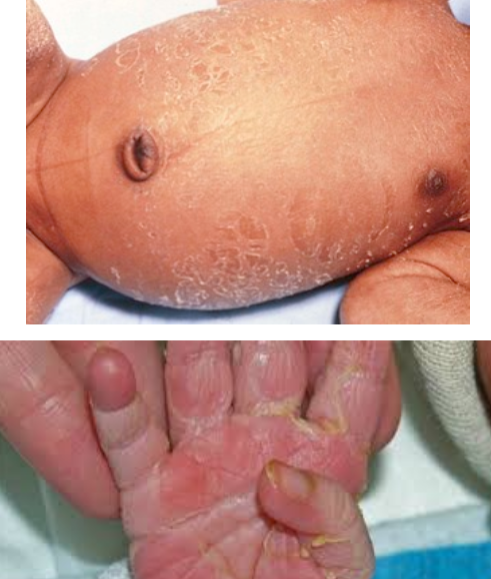
Diagnosis: Skin peeling
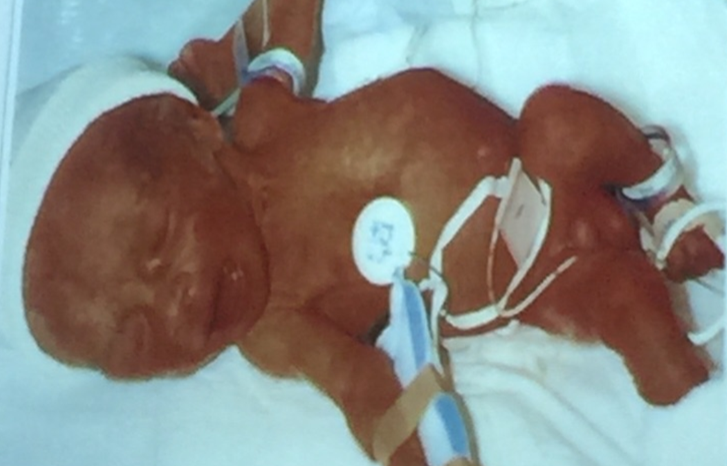
- Cause? Post term
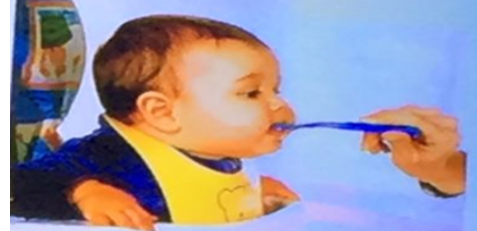
Milestone
- Milestone? Sitting with support.
- Age? 6.
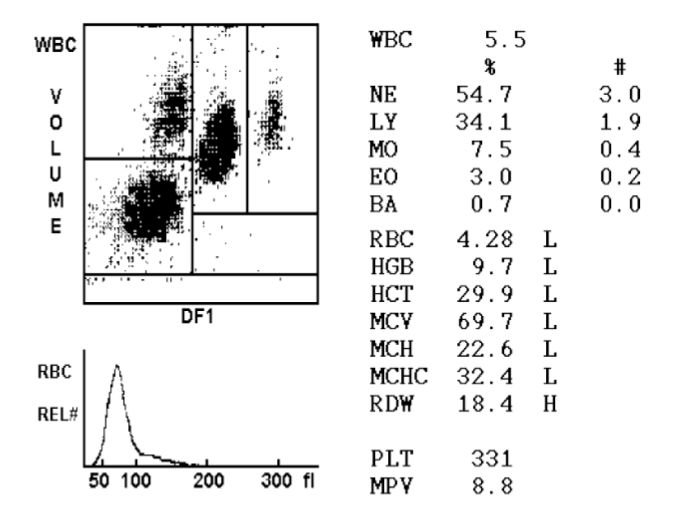
Case
What is abnormality ? Peripheral blood film show hypochromic microcytic cells with high RDW Diagnosis? IDA
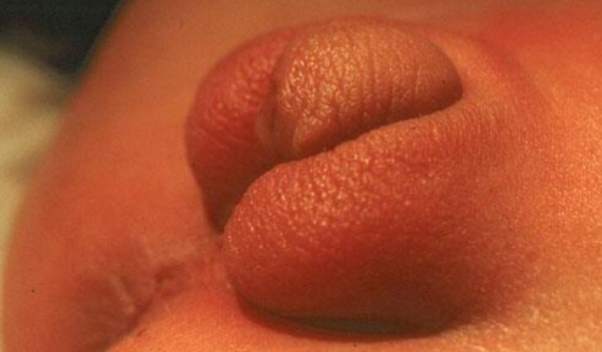
Case
A 3-week-old infant is admitted with vomiting of 5 days’ duration. Physical examination reveals a rapid heart rate, evidence of dehydration, and ambiguous genitalia. Serum electrolytes are Na+ 120 meq/L, K+ 7.5 meq/L, HCO3 – 12 meq/L, BUN 20 mg/dL. In addition to intravenous fluid replacement with normal saline, administration of which of the following would be most important? Hydrocortisone
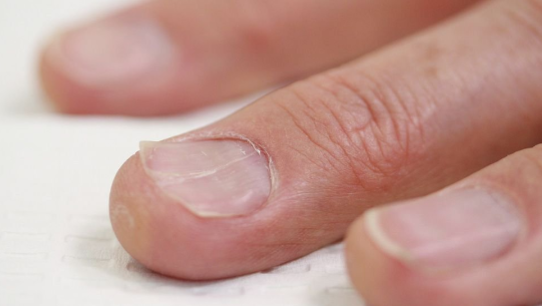
Case
What is this sign ? Koilonychia Usually associated with ? Iron def anemia
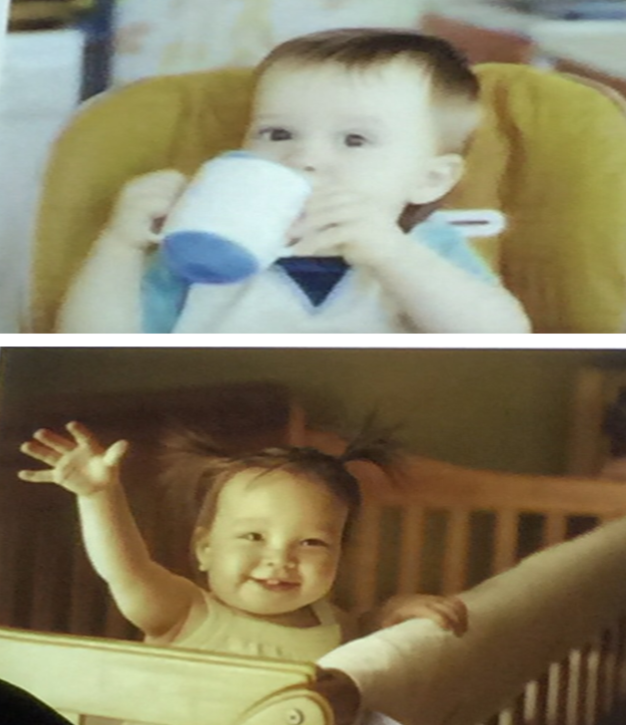

Case
1st Milestone ? Uses cups and spoons Age ? 12 month 2nd milestone ? Stand with support Age? 9 month

Case
Q1. What are the abnormal findings in the lab results? low serum phosphatase , high parathyroid hormone, high alkaline phosphatase Q2, What other investigations are required ? Vitamin D and 25OH Q3.What is the likely diagnosis? rickets