Surgery
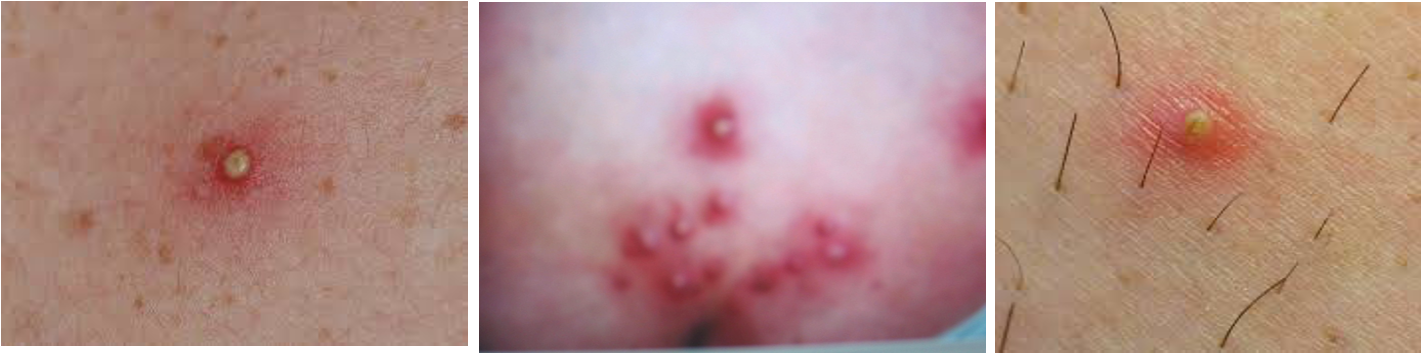
Folliculitis
Superficial Inflammation or infection of hair follicle. It’s usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
At first it may look like small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles
Treatment: Topically with Clindamycin1% or Erythromycin 2% applied 2 or 3 times a day to the affected areas
Dermatology
Folliculitis
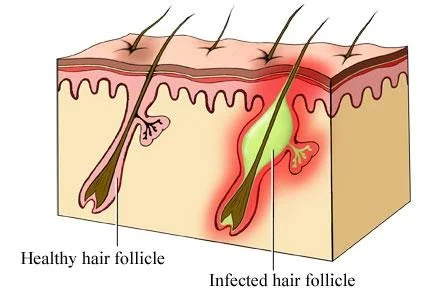
- Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicle.
- painless or tender pustule that eventually heals without scarring.
- usually with Staphylococcus aureus.
- Frequently seen in beard area, axillae or buttocks.
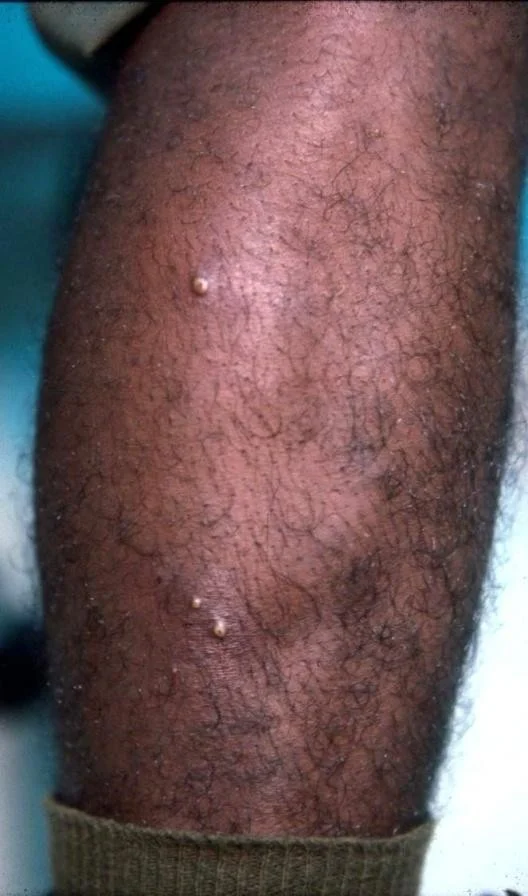
- Legs—Chronic folliculitis.
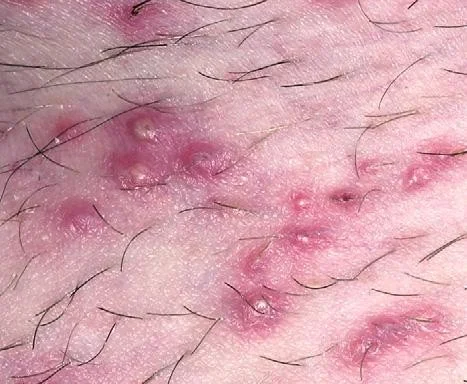
Treatment
- Superficial lesions – may respond to local antiseptics or persistent cases may need topical antibiotics.
- Widespread and severe folliculitis – oral flucloxacillin.
Types
- Superficial folliculitis
- Deep folliculitis (next)
- Furuncle and carbuncle
- Sycosis barbae
Folliculitis
- Folliculitis is a superficial bacterial infection of the hair follicles
- Presents as small, raised, erythematous, occasionally pruritic pustules less than 5 mm in diameter
- Genital folliculitis may be sexually transmitted
- Pathogens:
- Majority of cases are due to Staphylococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas folliculitis if there has been exposure to a hot tub or swimming pool.
- Pustules associated with marked erythema and scaling may represent genital candidiasis
Skin Exam Example
- Multiple follicular pustules with surrounding erythema in the right groin
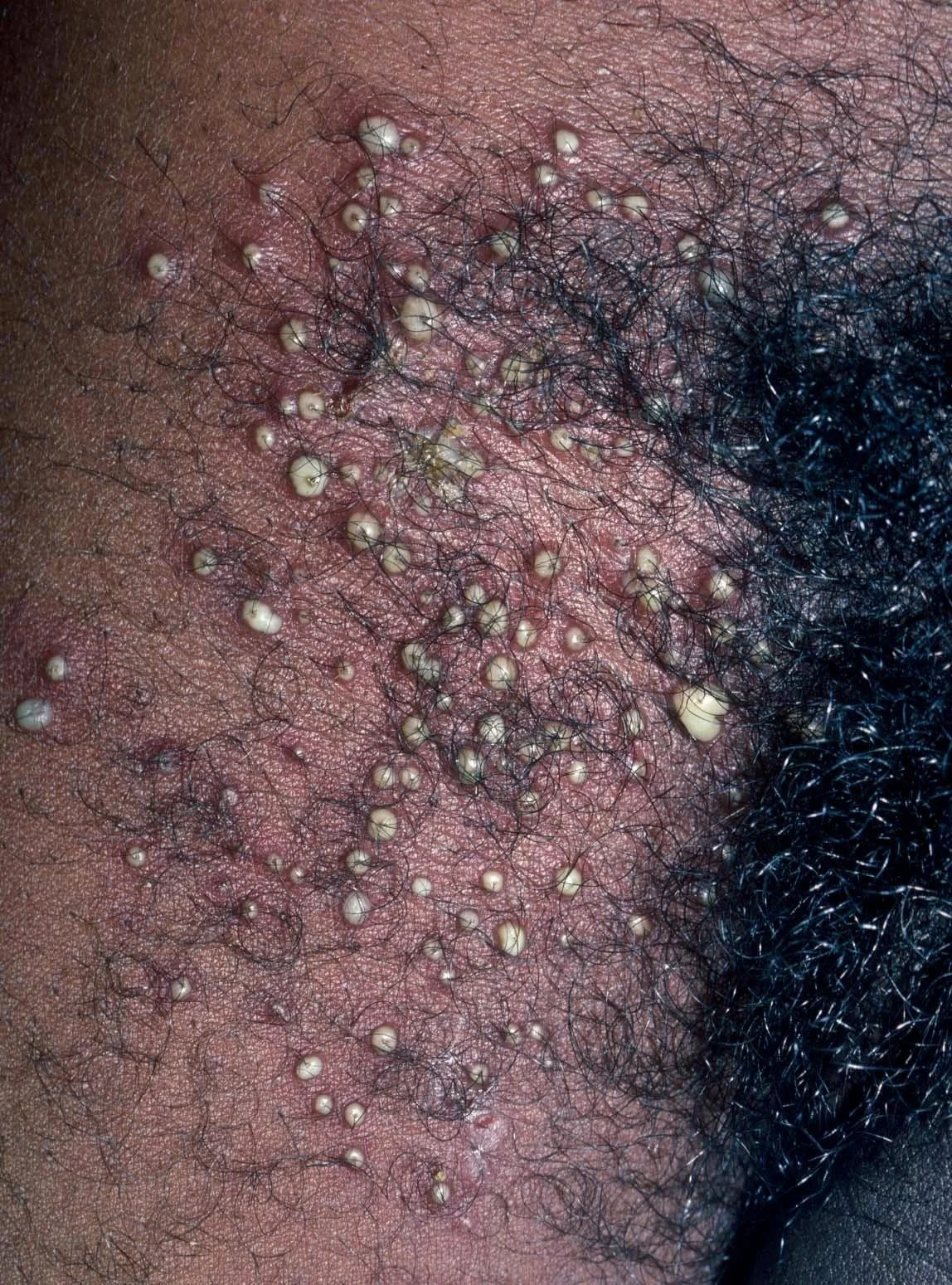
Management
- Thoroughly cleanse the affected area with antibacterial soap and water 3x/day
- Superficial pustules will rupture and drain spontaneously
- Oral or topical antibiotics
- Deep lesions of folliculitis represent small follicular abscesses and should be drained
More Examples
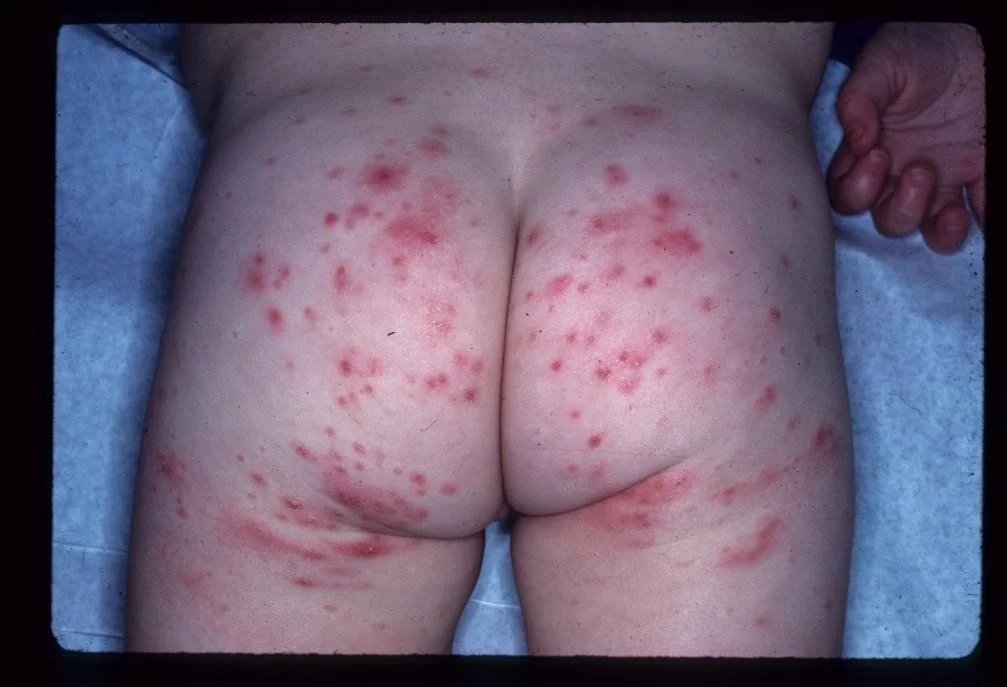
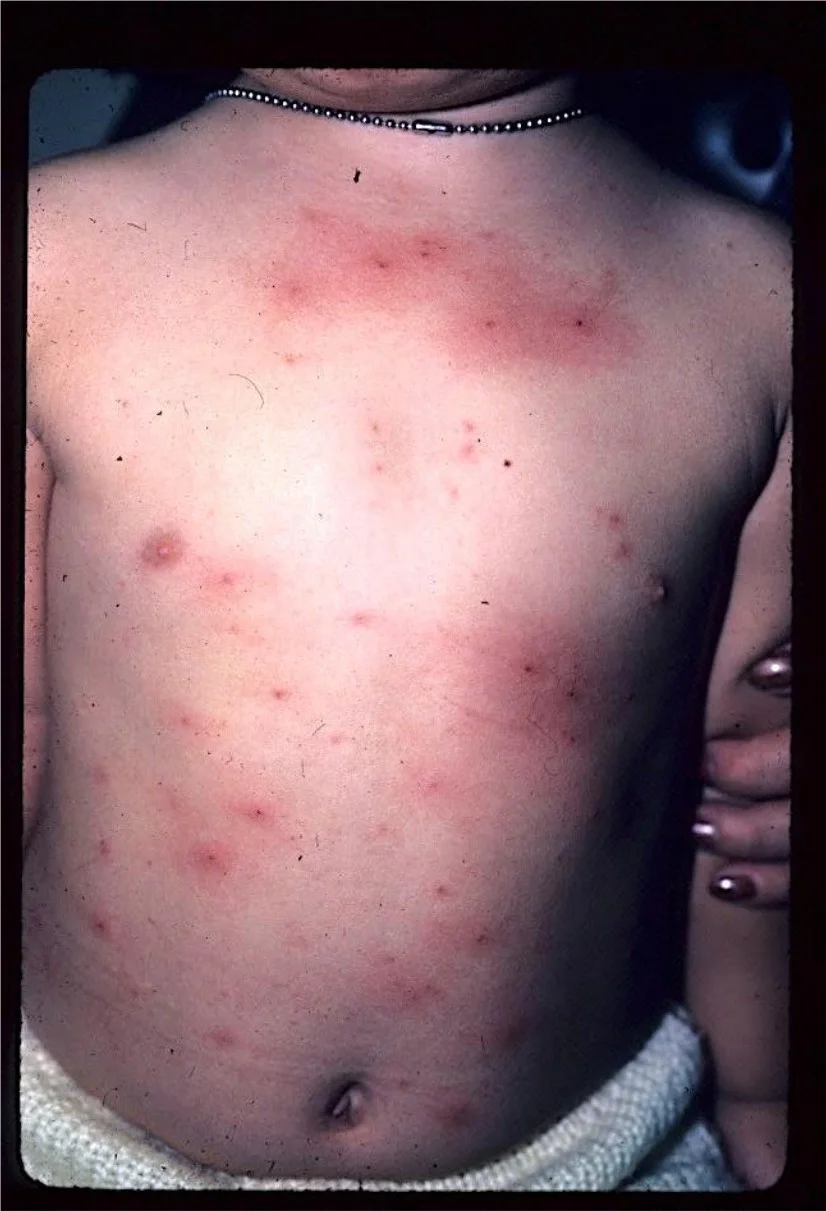
Case Four
History
- Mr. Y is a 19-year-old man who presents to dermatology clinic with two weeks of multiple “pimples” in his groin. He is concerned he has an STD.
- When asked, he reports occasionally shaving his pubic hair
- Sexual history reveals one female partner in the last year
Skin Exam
- Multiple follicular pustules with surrounding erythema in the right groin
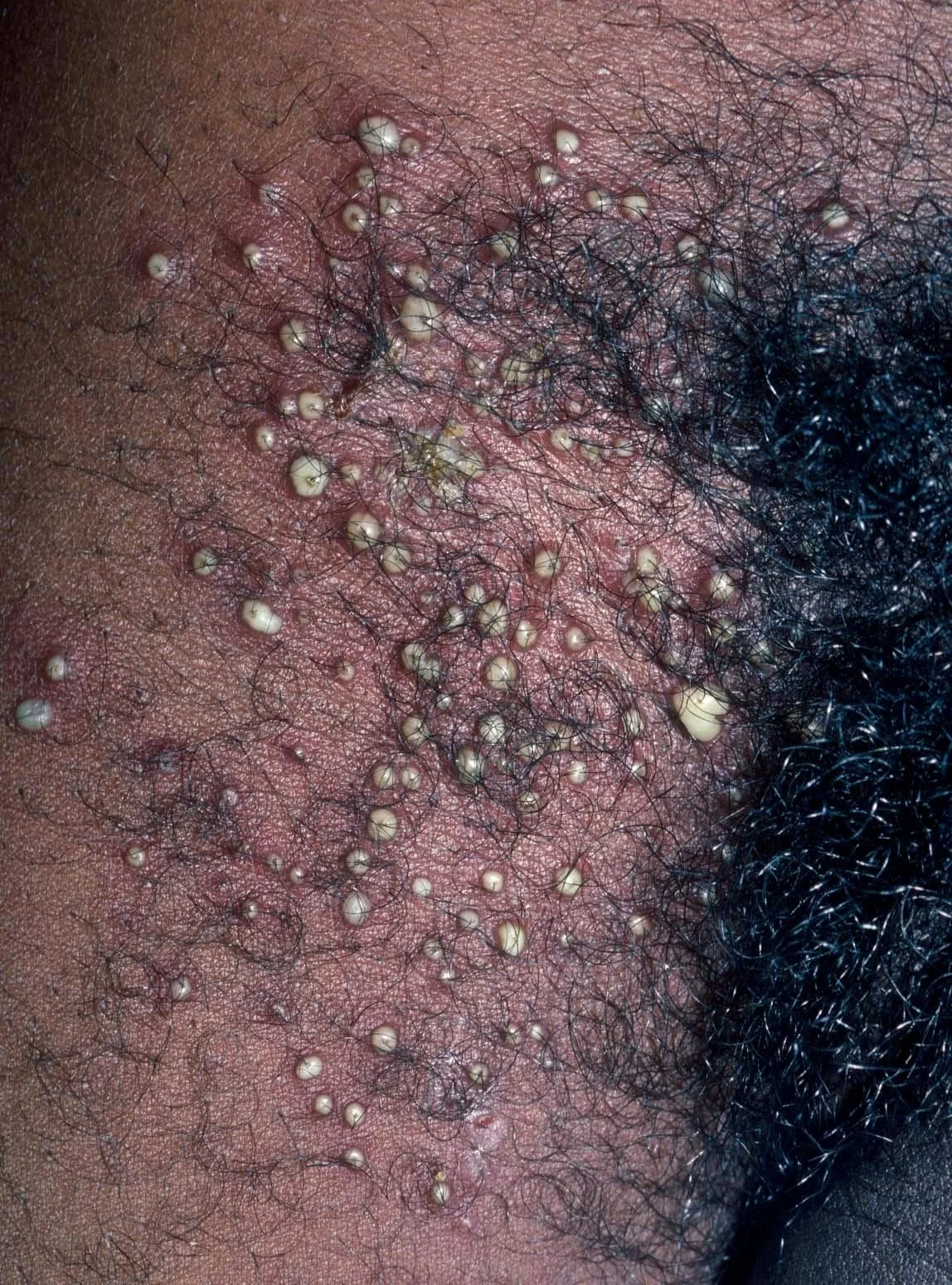
Question 1
- Which of the following recommendations would you provide Mr. Y? a. Prescribe oral antibiotics b. Stop shaving that area c. Wash the area (antibacterial soap may be used) d. All of the above
Question 1 - Answer
Answer: d
- Which of the following recommendations would you provide Mr. Y? a. Prescribe oral antibiotics b. Stop shaving that area c. Wash the area daily (antibacterial soap may be used) d. All of the above
Folliculitis
- Folliculitis is a superficial bacterial infection of the hair follicles
- Presents as small, raised, erythematous, occasionally pruritic pustules less than 5 mm in diameter
- Genital folliculitis may be sexually transmitted
- Pathogens:
- Majority of cases are due to Staphylococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas folliculitis if there has been exposure to a hot tub or swimming pool.
- Pustules associated with marked erythema and scaling may represent genital candidiasis
Management
- Thoroughly cleanse the affected area with antibacterial soap and water 3x/day
- Superficial pustules will rupture and drain spontaneously
- Oral or topical anti-staphylococcal agents may be used
- Deep lesions of folliculitis represent small follicular abscesses and should be drained