Common Benign Skin Growths CS-OSPE
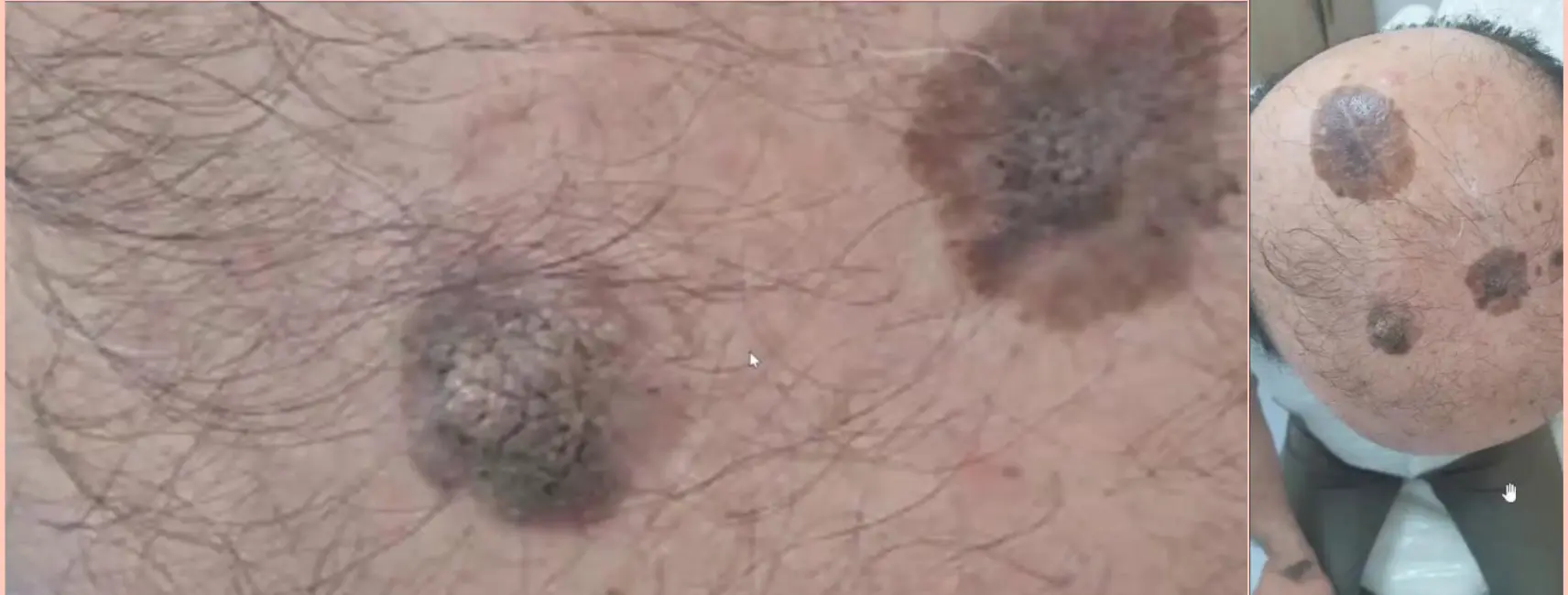
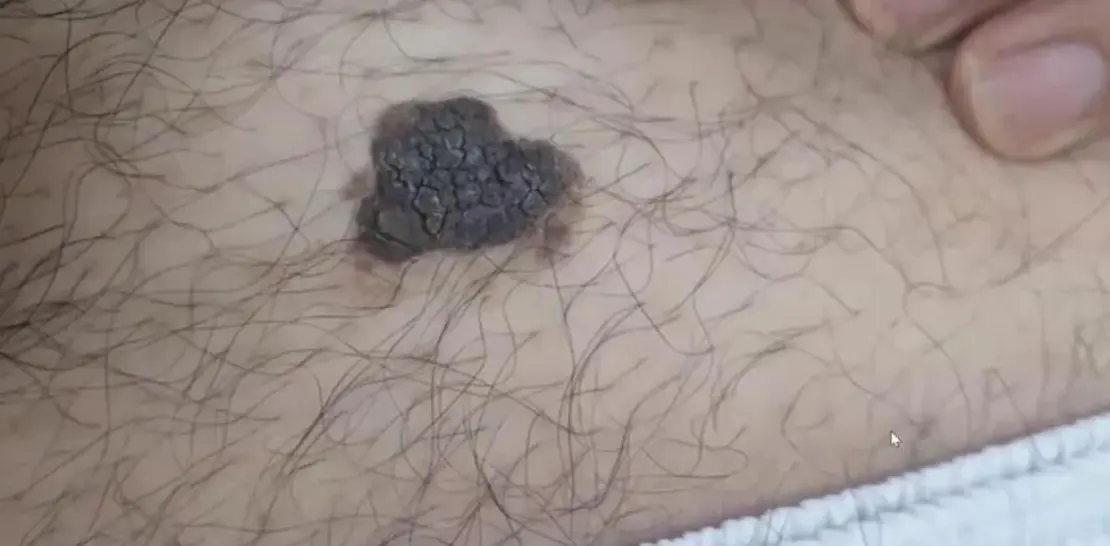
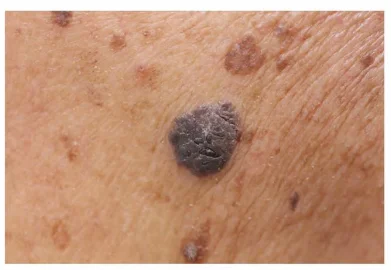
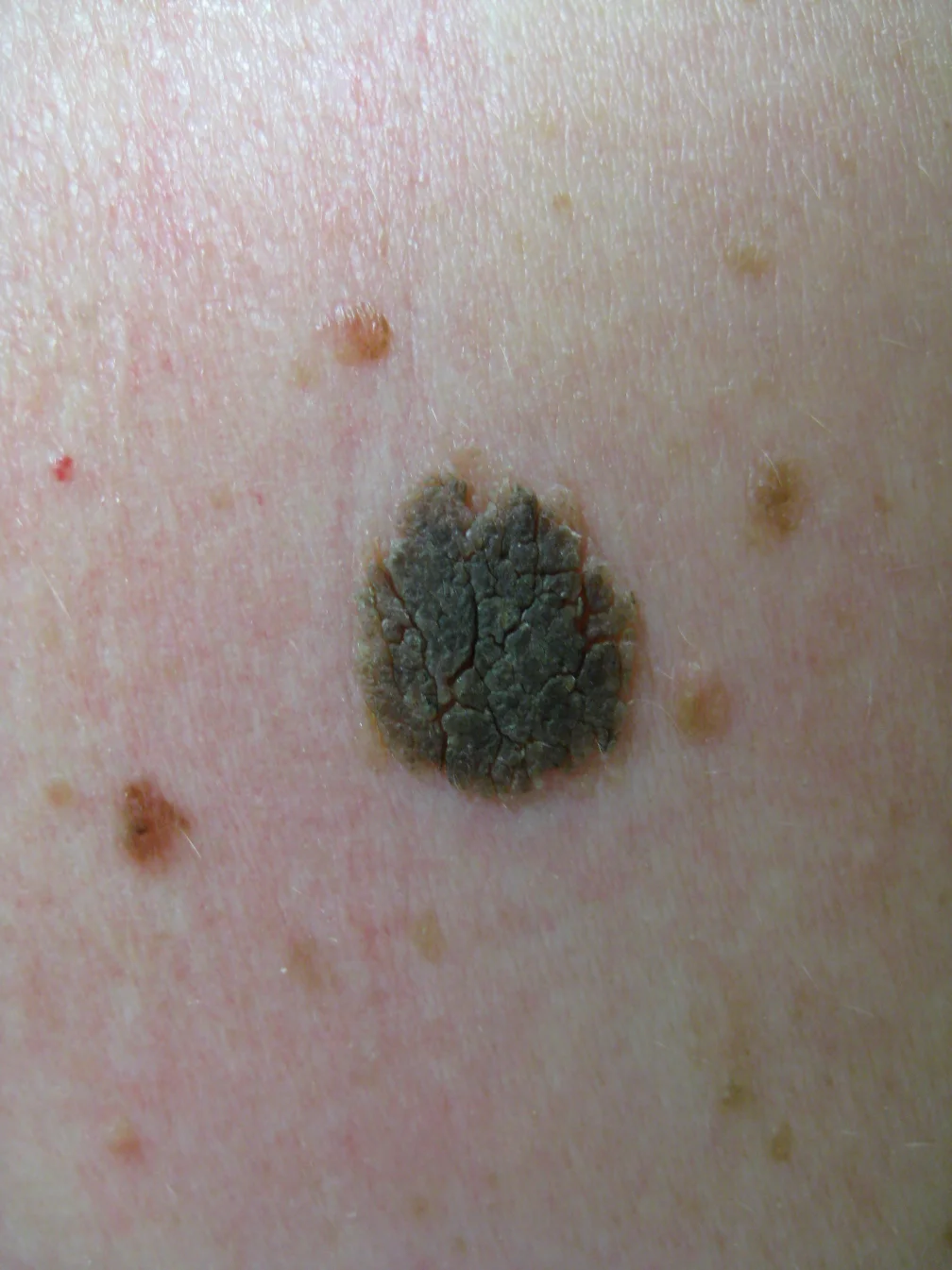
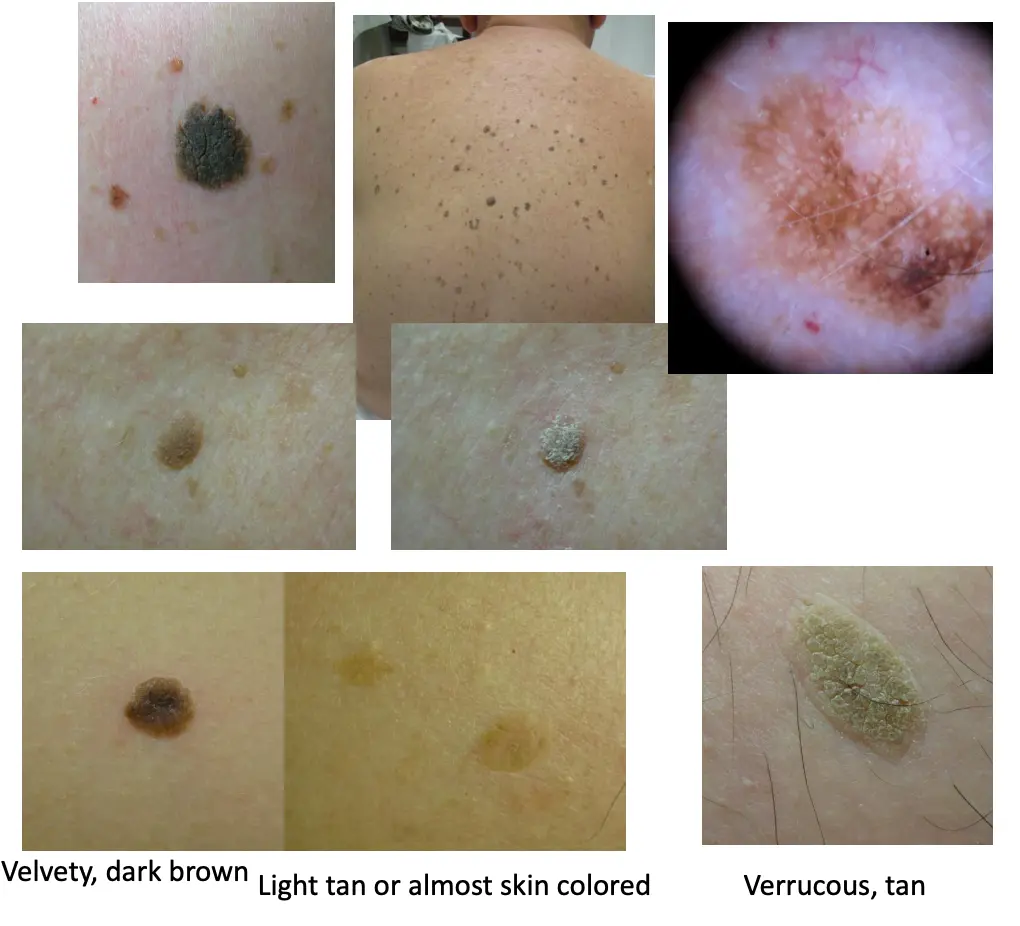
Seborrheic keratosis
Diagnosis: Z
- Seborrheic keratosis (SK, hyperkeratotic lesion). Characterized as verruca-like or Verrucous like, appearing at >40 years. Often multiple, may be a satellite lesion. The lesion sometimes itches and may bleed.
Benign or malignant condition?
- Benign, but if rapid appearance or in young: red flag for GIT cancer (especially if eruptive, to rule out Leser-Trélat sign)
Pathology:
- Superficial epidermal growths
Description:
- Usually papular, but may appear macular. Color is variable, wart-like have a stuck-on quality, like a piece of wax. (Example: May be seen on the back of a forty-six-year-old man).
Differential Diagnosis:
- Warts
- Dermatosis papulosa nigra
Confirmatory Tests & Dermoscopy:
- Picking or scratching the lesion. It may crumble, flake, or lift off, revealing that superficial waxy character.
- Use dermoscopy to look for:
- White spots (pseudocyst)
- Keratin pseudocysts (spot test by dermoscopy > you will see: keratin pseudocysts)
Management/Treatment (Tt):
- Full history
- Examination
- Education (If picked off or curetted, SK will leave a pink moist base with minimal bleeding)
- Cryotherapy Z
- Electrodessication (with or without Curettage) Z
- Laser Z
- Curettage Z
- Shave removal / Shave excision
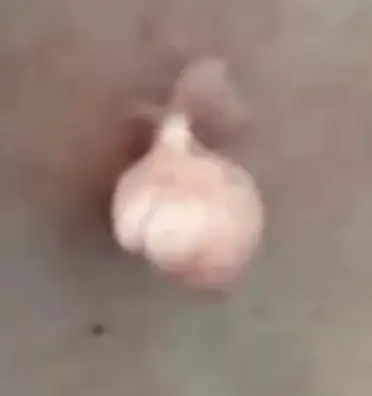
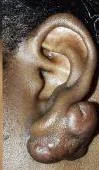
Skin Tag
Risk factors:
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Family history
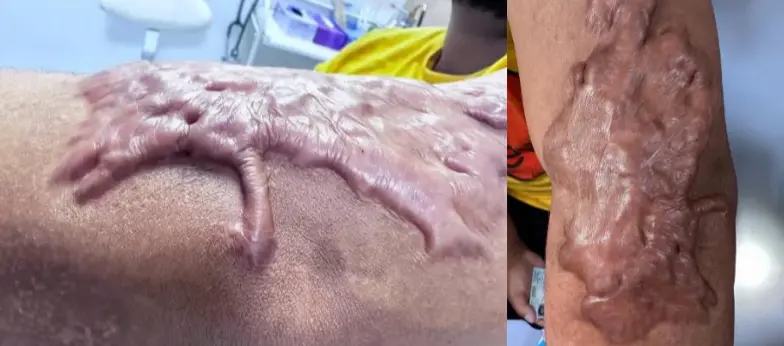

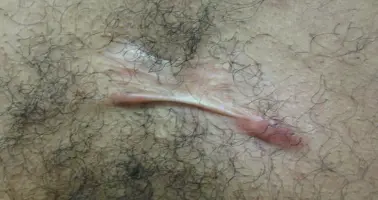
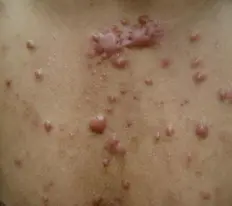
Keloid
Diagnosis: Keloids Pathophysiology: Fibroblast proliferation Z Complications: Basal cell carcinoma Treatment notes: Intralesional corticosteroid in tight areas. But in large lesions, not recommended (because it will get systemic absorption). So, only inject painful areas.
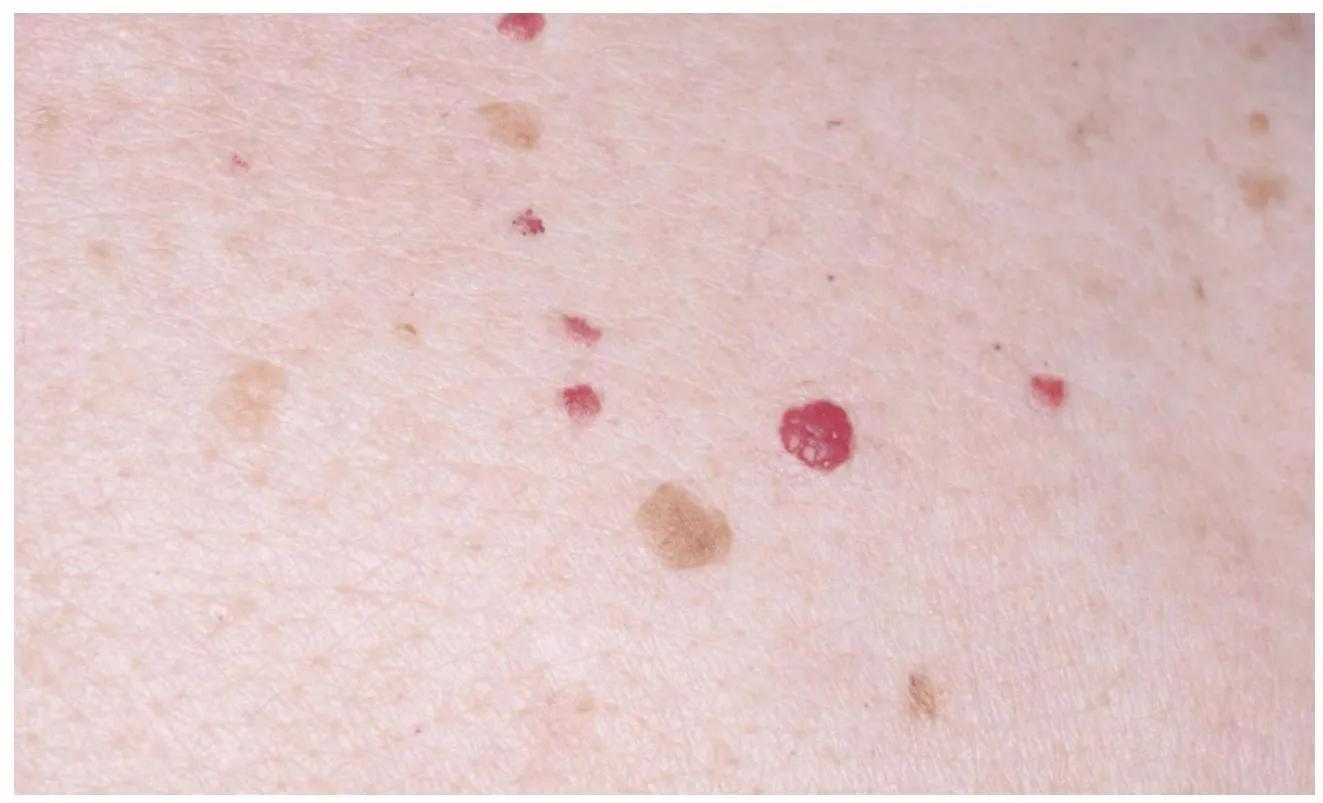
Cherry angioma
Description: Typically presents as multiple non-pruritic, painless lesions (e.g., appearing in the chest of a 45-year-old man). Diagnosis:
- Cherry angioma
Prognosis:
- Good - Benign tumor in blood vessels, no chance to be malignant
Management/Treatment:
- Cryotherapy
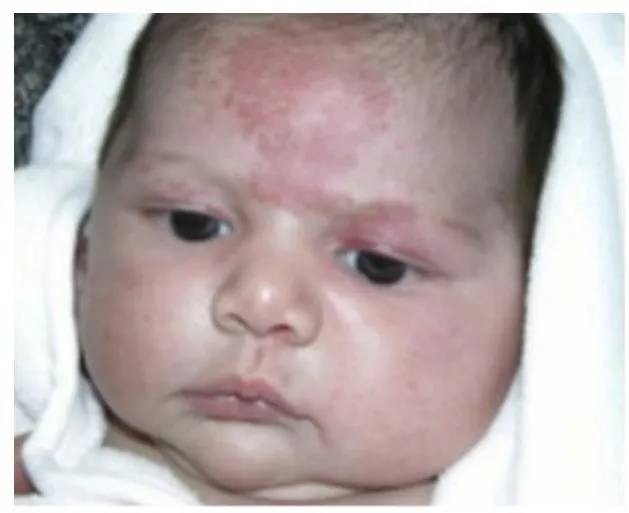
Nevus simplex
Treatment?
- No need treatment
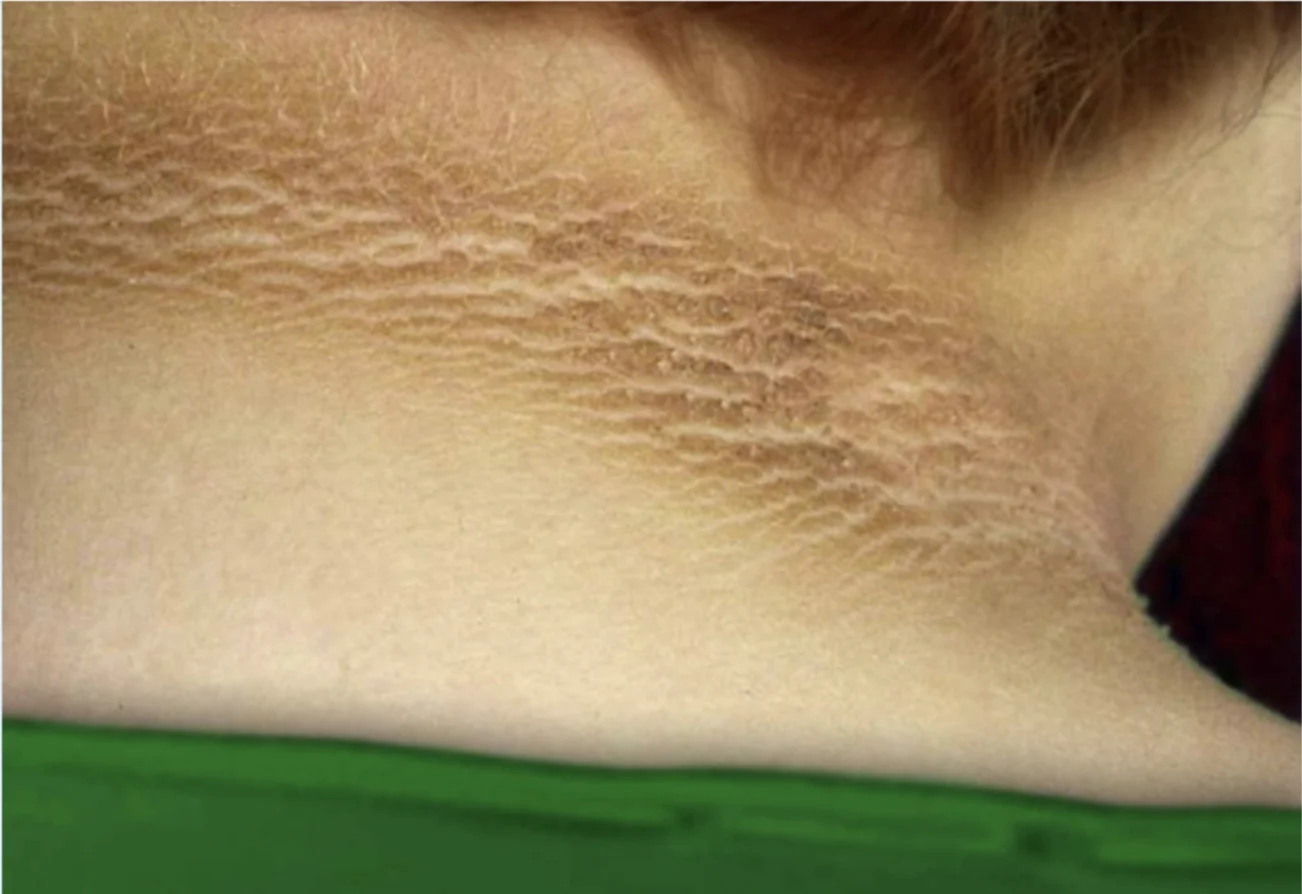
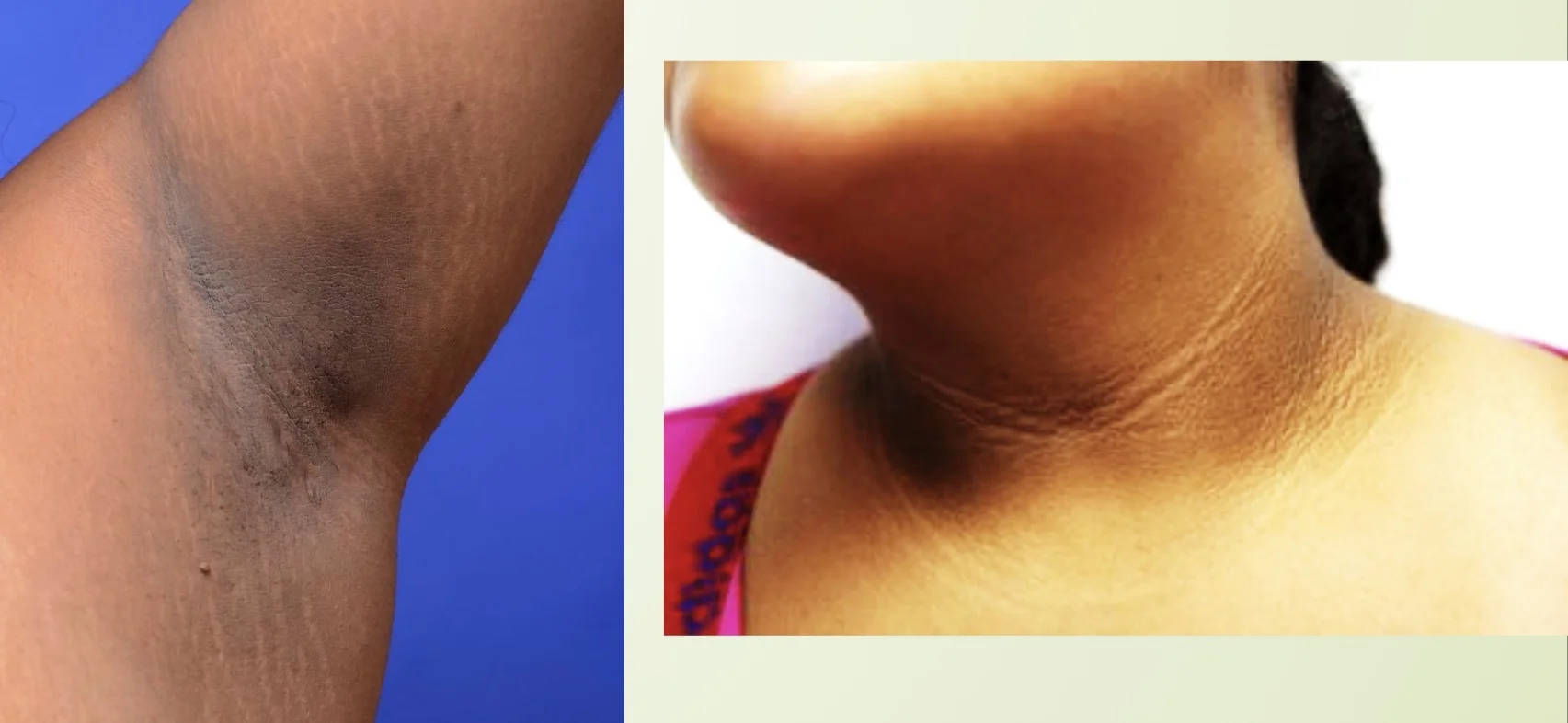
Acanthosis Nigricans
Scenario: This obese diabetic patient developed discoloration on his nape. Scenario: A 54 Y/O female presents with asymptomatic black discoloration in axillae and neck. Her BMI is 40. What is the name of this condition?
- Acanthosis Nigricans
What is the other benign skin growth this patient may develop?
- Skin tags
What is the clinical test or investigation that confirms the diagnosis?
- Insulin level
may indicate GIT carcinoma
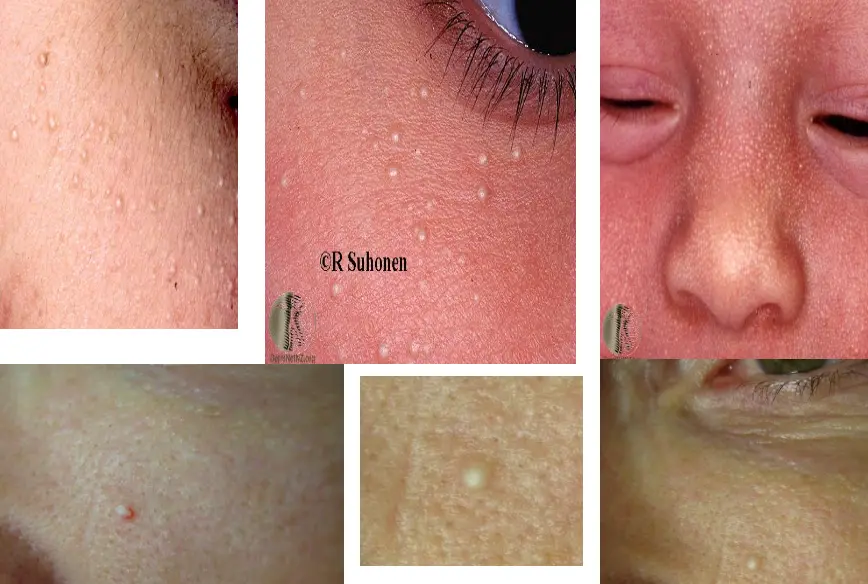
Milia
What is the diagnosis?
- Milia.
What are the clinical presentations?
- 1-2 mm white to yellow subepidermal papules.
- They are fixed and persistent.
What is the treatment?
- Grooving the surface.
- Cryotherapy.
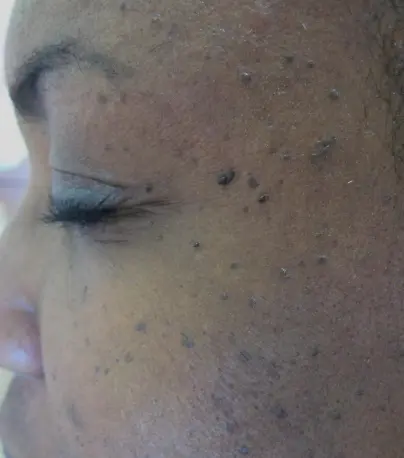
Dermatosis papulosa nigra
What is the diagnosis?
- Dermatosis papulosa nigra.
How does Dermatosis papulosa nigra present clinically?
- Multiple, small, hyperpigmented papules.
- They are typically sessile to filiform and smooth-surfaced.
- Arise in individuals with darker skin types.
- Usually found on the cheeks and temples.
What is the recommended treatment?
- Light electrodessication.