Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
-
Two forms of ischemic optic neuropathy are:
-
Non-Arteritic (NAION) 95%
-
Arteritic (AAION). 5%
-
-
The main cause of AAION is vasculitis of the short posterior ciliary vessels supplying the optic nerve head.
-
large multinucleated monocytes infiltrate the small- and medium-sized arteries, causing obliteration of their lumen leading to ischemia.
Symptomatology:
AAION:
- Mean age of onset: 70 years
- Headache is the most common symptom.
- Rheumatic myalgia (poly myalgia rheumatica)
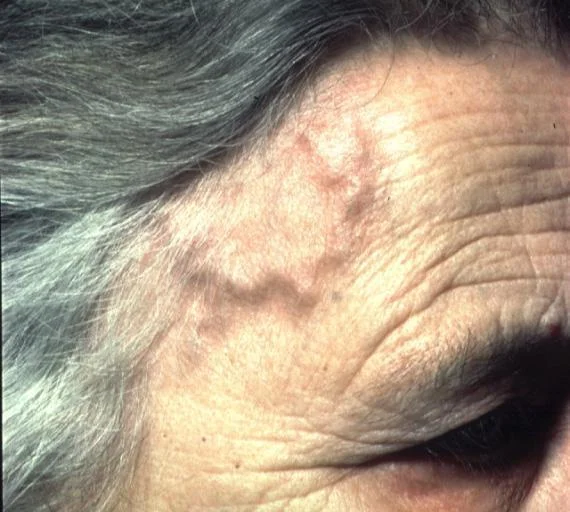
- Scalp tenderness
- Jaw claudication
- Malaise, anorexia, weight loss, low-grade fever
- Severe visual loss, developing over hours to days.
- Pallid disc edema (chalky white appearance of the disc)
- Disc of fellow eye: normal
NAION
-
Cause of NAION:
- Hypoperfusion or Non-perfusion of the optic nerve head.
-
Risk factors of NAION:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Smoking
Symptomatology:
- Mean age of onset: 60 years
- Patients present with Painless vision loss developing over hours to days.
- Visual loss is less severe than AAION.
- No systemic symptoms.
Signs:
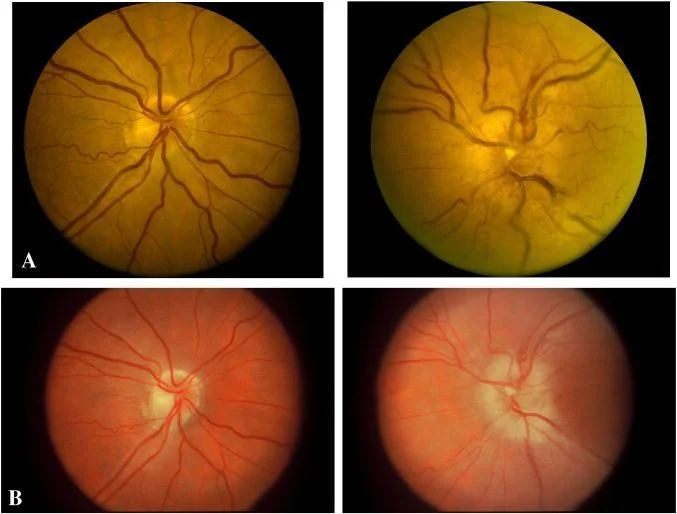
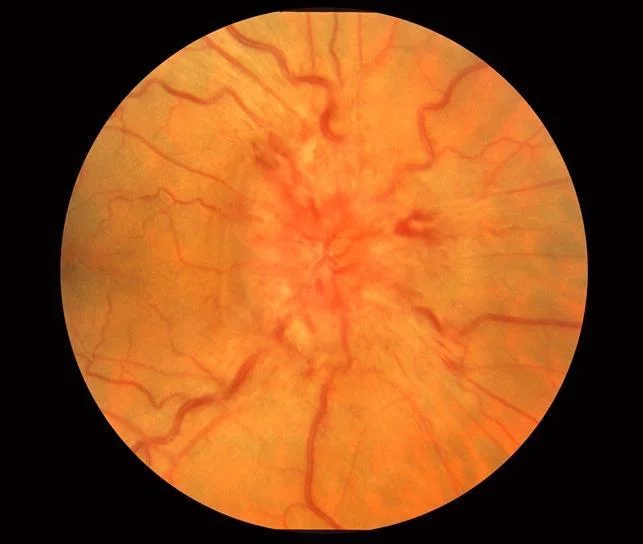
- Segmental or diffuse disc swelling, hyperemic or pale.
- Peripapillary retinal hemorrhages.
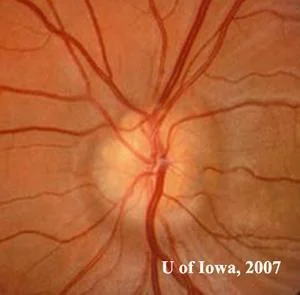
- Disc in fellow eye “disc at risk”: small, crowded, elevated with blurry margin
- Management:
-
AAION
- It is life and vision-threatening.
- High-dose (steroid) oral prednisone or intravenous methyl-prednisolone followed by a course of oral prednisone.
-
NAION:
- No proven treatment
- Optimize the medical condition.
-