ADHD – Core Features
- Age-inappropriate levels of inattention
- Difficulty sustaining attention with schoolwork, easily distracted.
- Impulsivity
- Not waiting for a turn, blurting out answers.
- Hyperactivity
- Fidgeting, squirming, talking excessively.
What is ADHD?
- A neurobiological condition
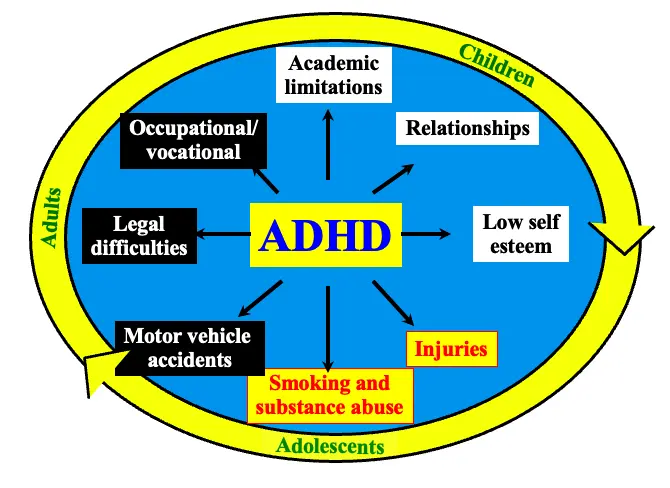
Conflicting Interactions with Peers and Family Members Academic underachievement

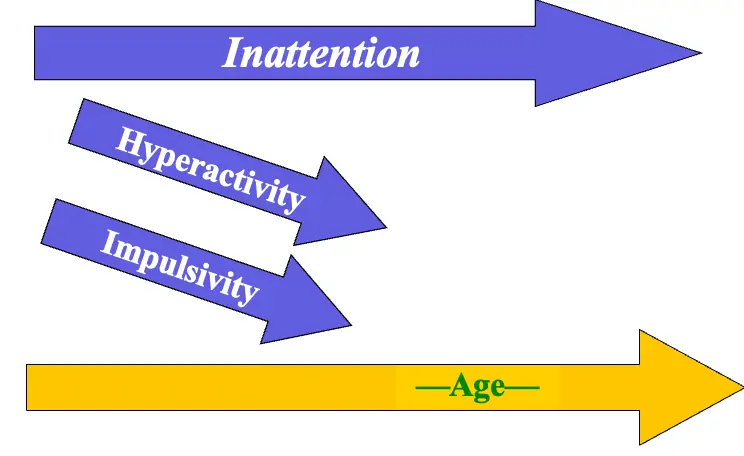
Symptom Evolution
- Hyperactivity
- Impulsivity
- Inattention
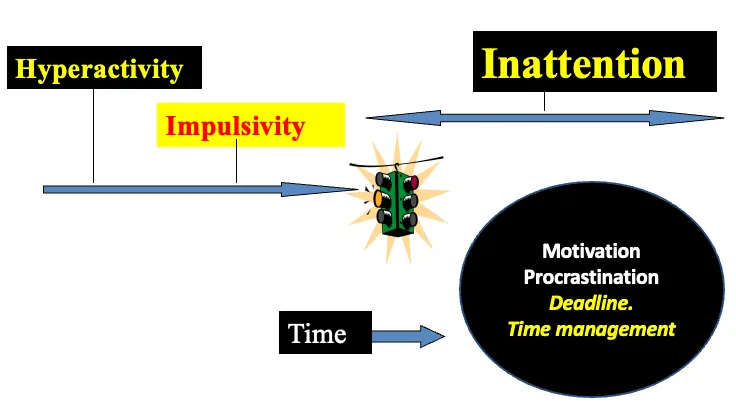
Time
- Motivation
- Procrastination
- Deadline.
- Time management.
ADHD: Course of the Disorder
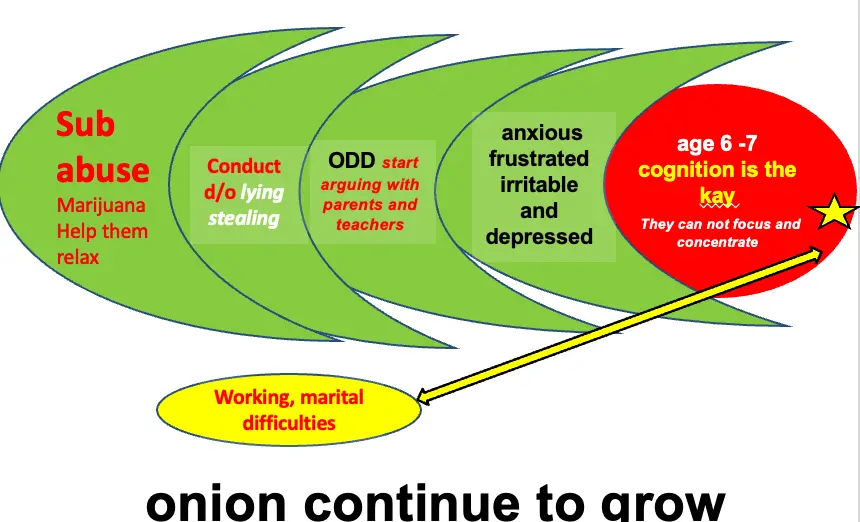
The Drug of Choice for ADHD Patients
- Marijuana
- Helps them relax.
So clear the layer of the onion, and get to the core of the illness.
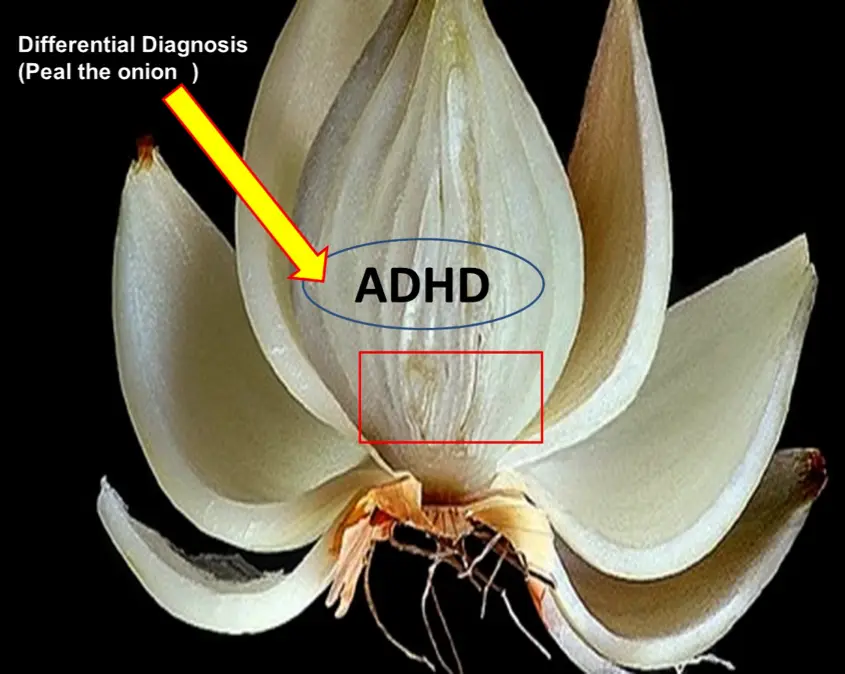
What is Wrong with You?
- Low self-esteem

Neurobiology of ADHD: Neuroanatomy and Neurochemistry
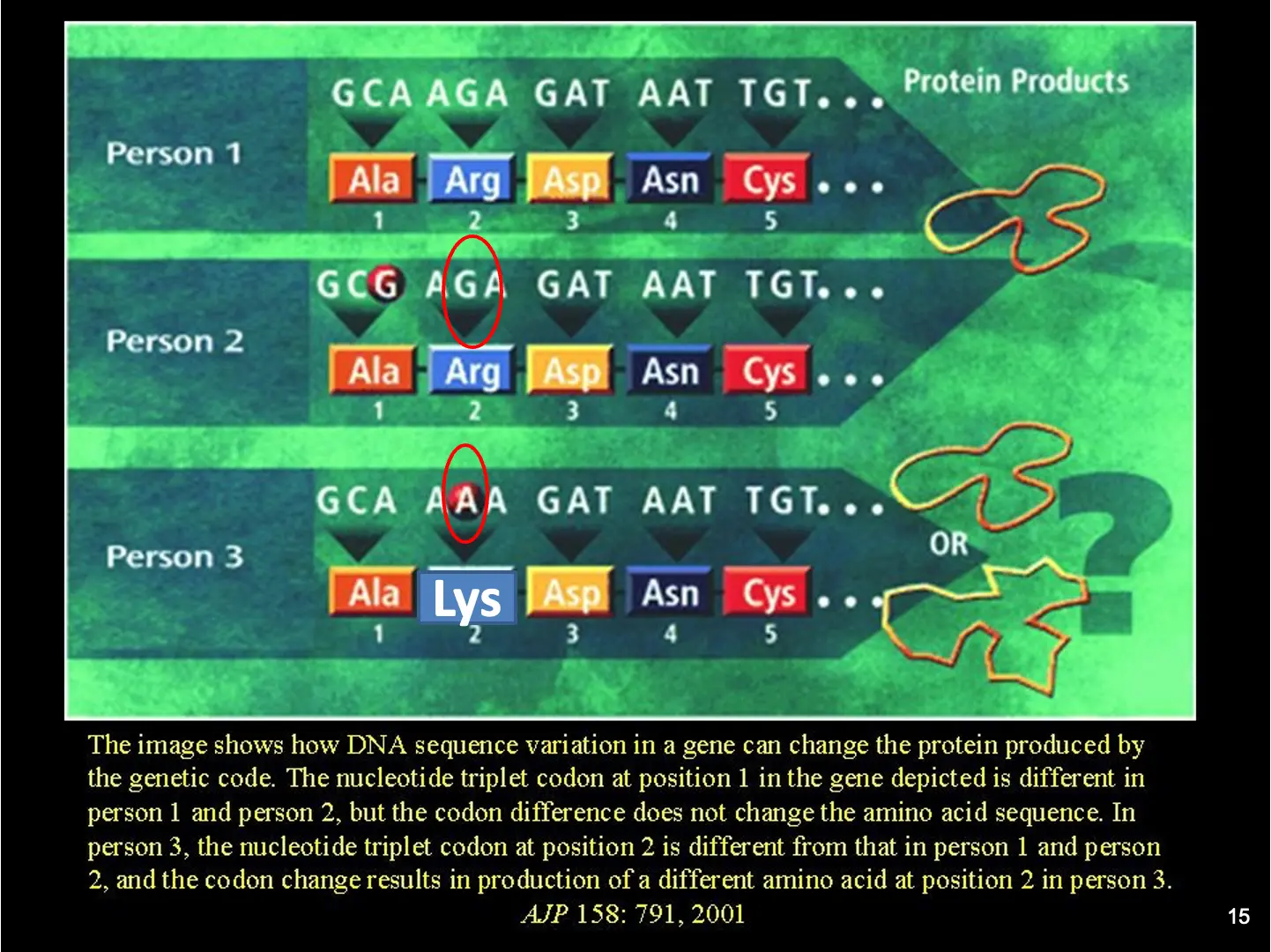
Genetic
- Mutations in dopamine receptor and dopamine transporter genes.
Other Biological, Non-Hereditary Factors
During Pregnancy
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Alcohol abuse
- Bleeding/infections
Associated with premature birth and low birthweight.
During Delivery
- Hypoxia (2%).
The Brain in ADHD Compared to Normal Controls
-
Smaller,
Hypoactive
&
Impaired functioning. -
Smaller Right Pre-frontal Cortex
-
Smaller Cerebellum
-
Decreased Volume: Basal Ganglia
Disruption of Attachment
- Results in difficulty with self-regulation, impulse & mood control.
- Behavior we see is an attempt to manage the deregulation and can be understood as.
Kids Manifesting a Clear Mismatch in Power
-
It’s helpful to think of these kids as being in a ‘cognitive wheelchair.’
— Ross Greene -
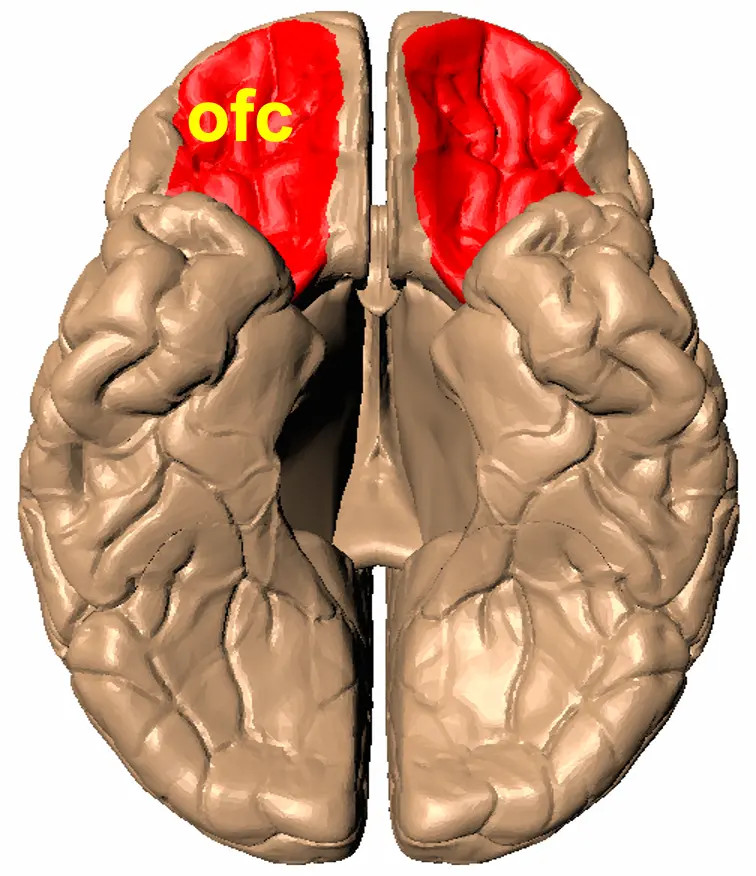
Strong emotion-generation
- Amygdala
- Orbital PFC
Less developed emotion regulation centers.


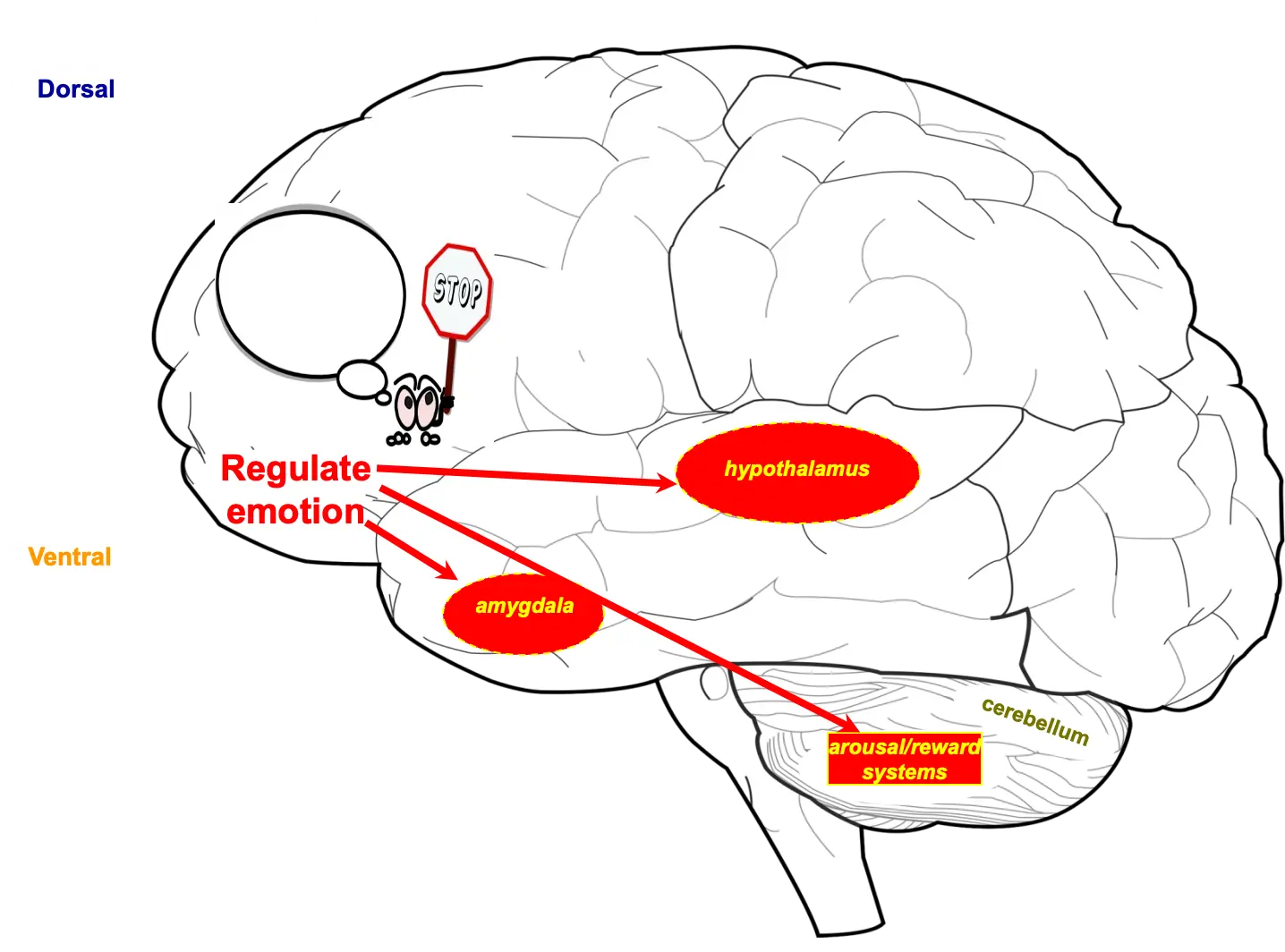
Regulate Emotion
- Amygdala
- Hypothalamus
- Arousal/reward systems
- Cerebellum
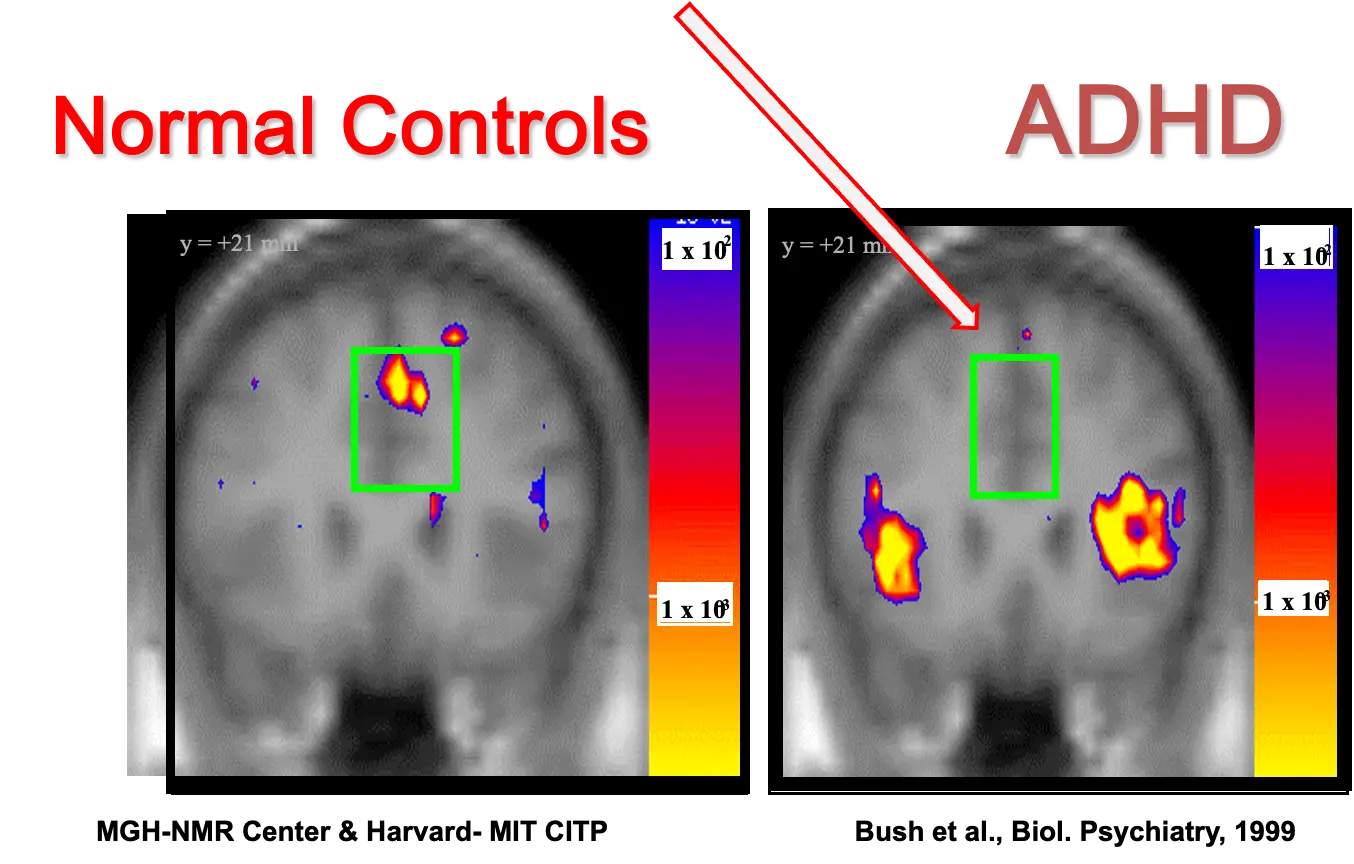
Anterior Cingulate (Cognitive Division)
Fails to Activate in ADHD
Organizing
- Prioritizing
- Controlling impulses
- Self-awareness
- Initiating and ending activities
Cognition
- Sustain attention
- Problem solving
- Short term memory
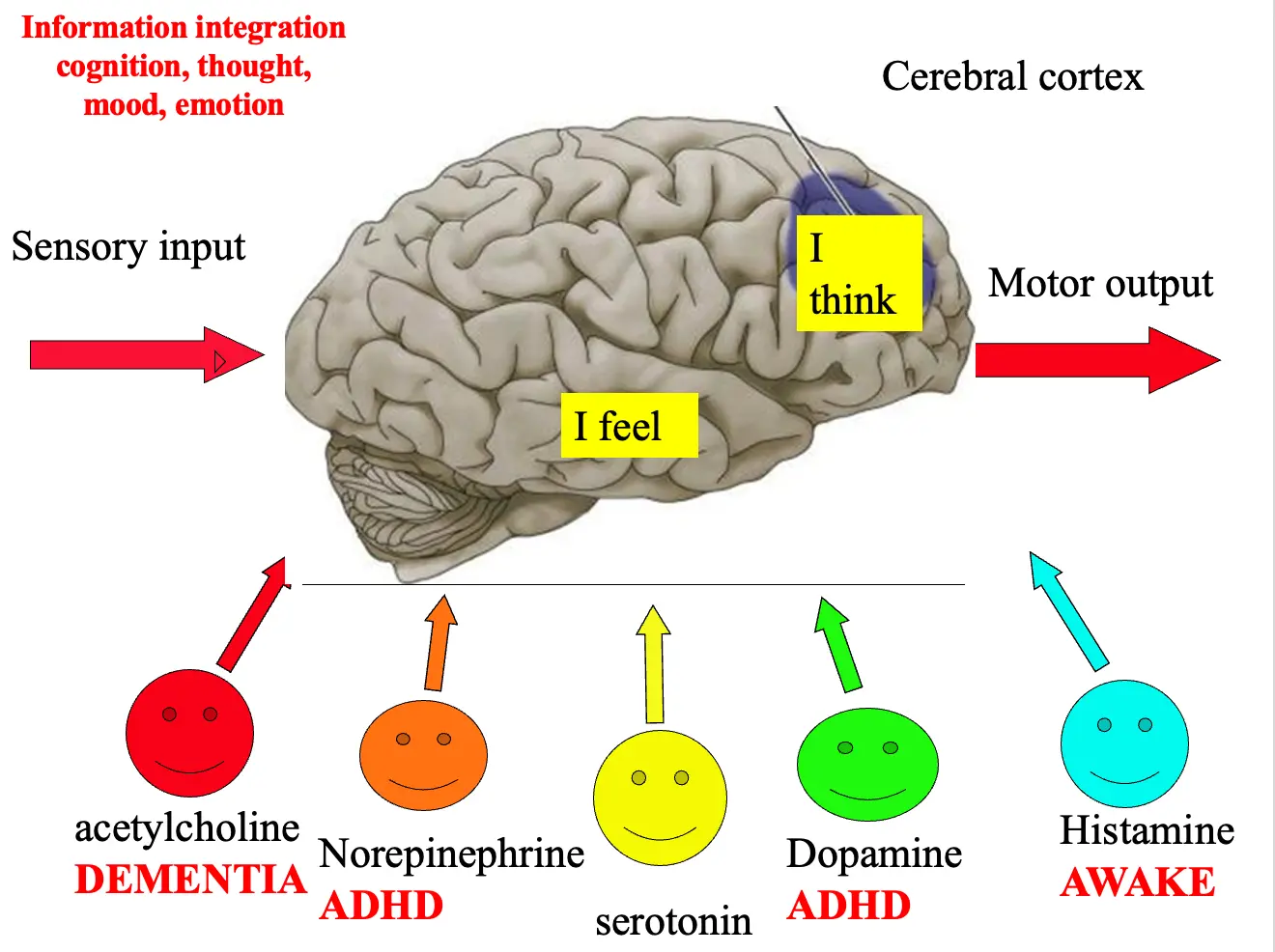
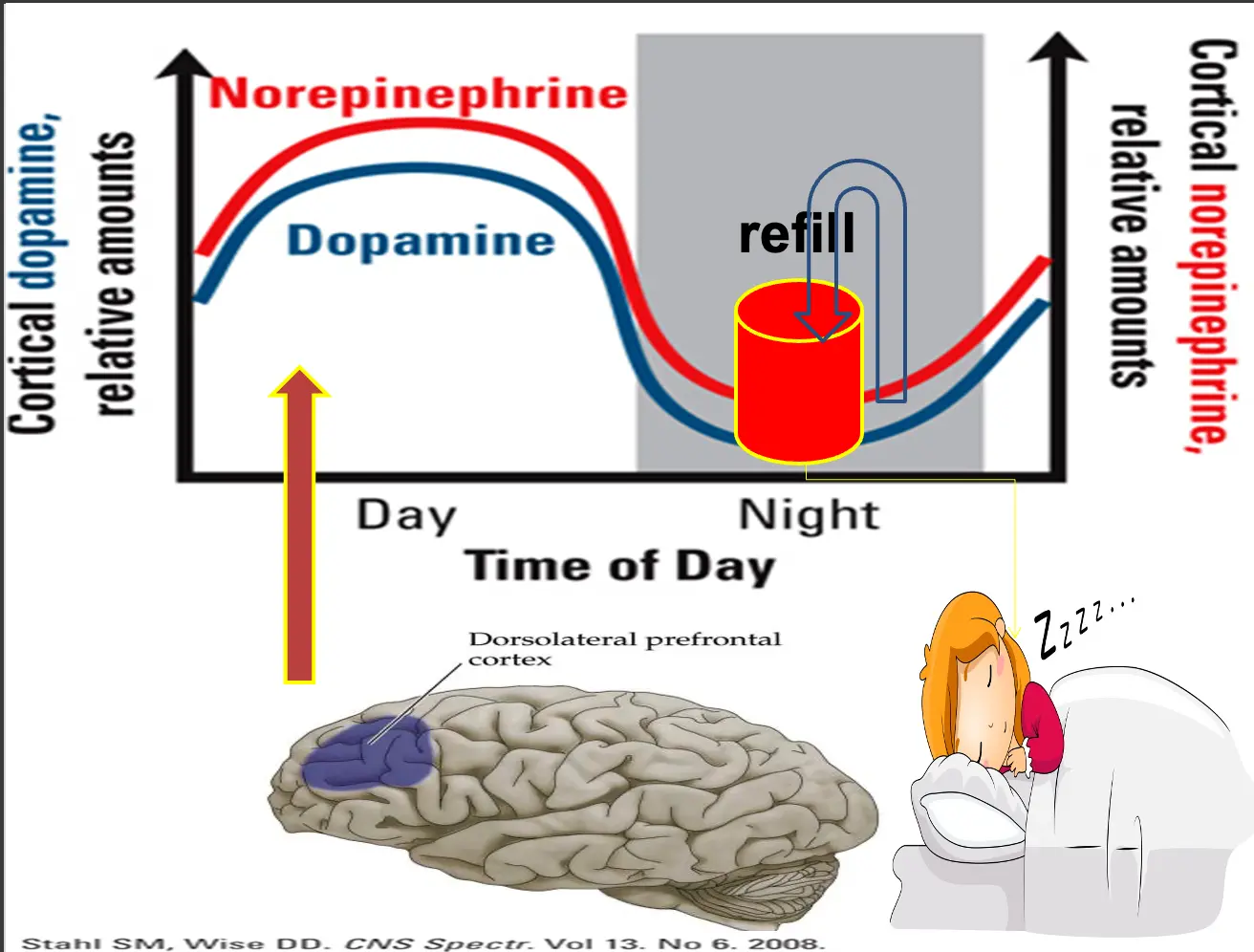
- Dopamine
- Make us do the right things
- Problem-solving, adaptation, coping with changes, attention.
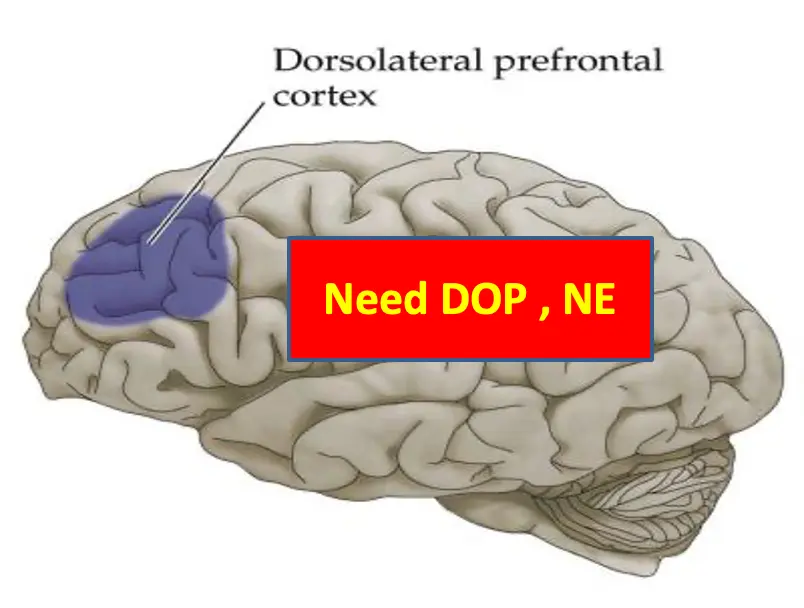
Need DOP, NE Working memory, and very complex functions, such as planning activities.

ADHD - Treatment
- Stimulant medications – Ritalin, Dexedrine.
- Reduced impulsiveness and hyperactivity and improved attention.
- NARI, atomoxetine.
Treatment
- Parents and teachers must be advised on how to cope with hyperactive children.
- Nootropic drugs and mild doses of antipsychotics are sometimes prescribed.
- Stimulant drugs such as methylphenidate sometimes have the paradoxical effect, according to theory, that stimulants act by reducing the excessive, poorly synchronized variability in the various dimensions of arousal and reactivity seen in ADHD.
- Stimulants are the drugs of first choice.