SURG
Spleen
-
Aetiology: Blunt/ Penetrating injury
-
Blunt trauma: most frequently injured organ
-
Injury to left side- chest, flank, or abdomen
-
Left lower chest & upper abdomen:
- Pain, Bruising, Tenderness
-
Diagnosis:
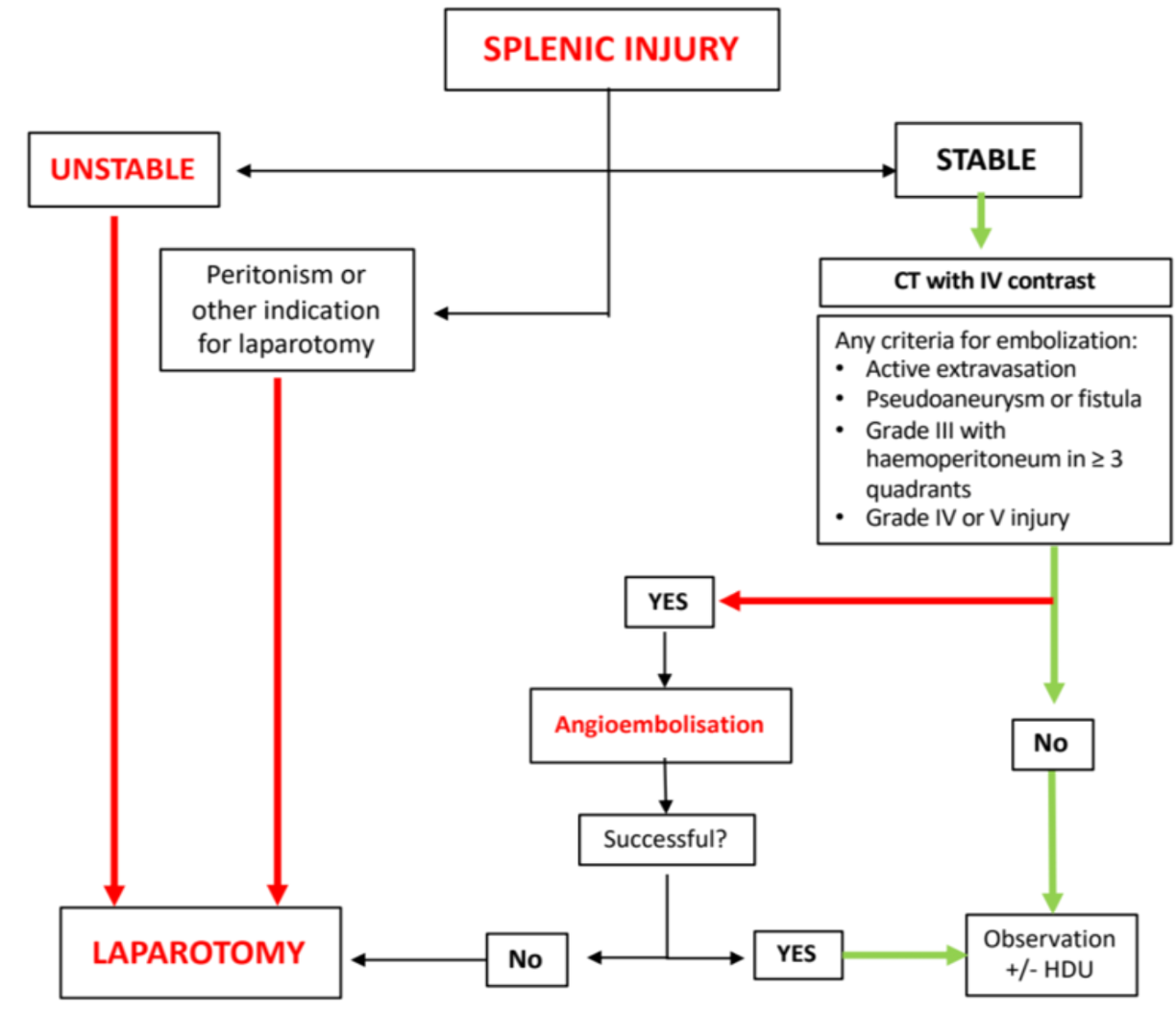
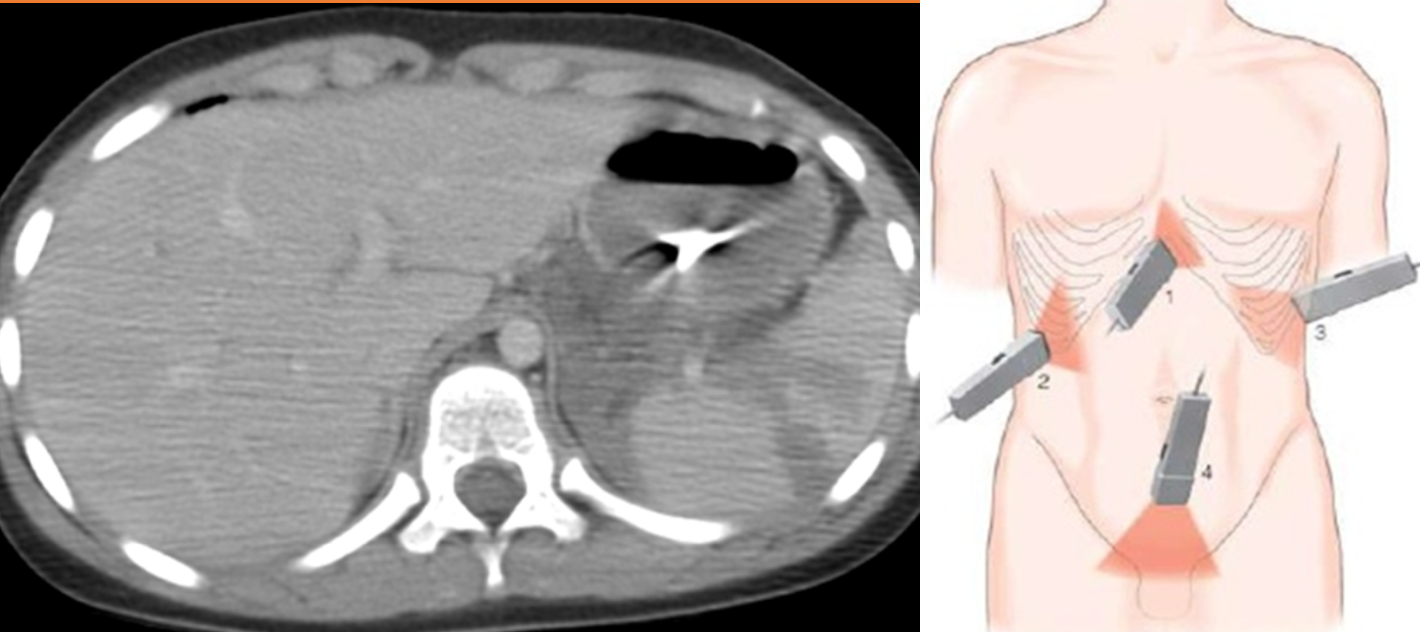
- FAST - unstable patients
- FAST + CT-stable patients
-
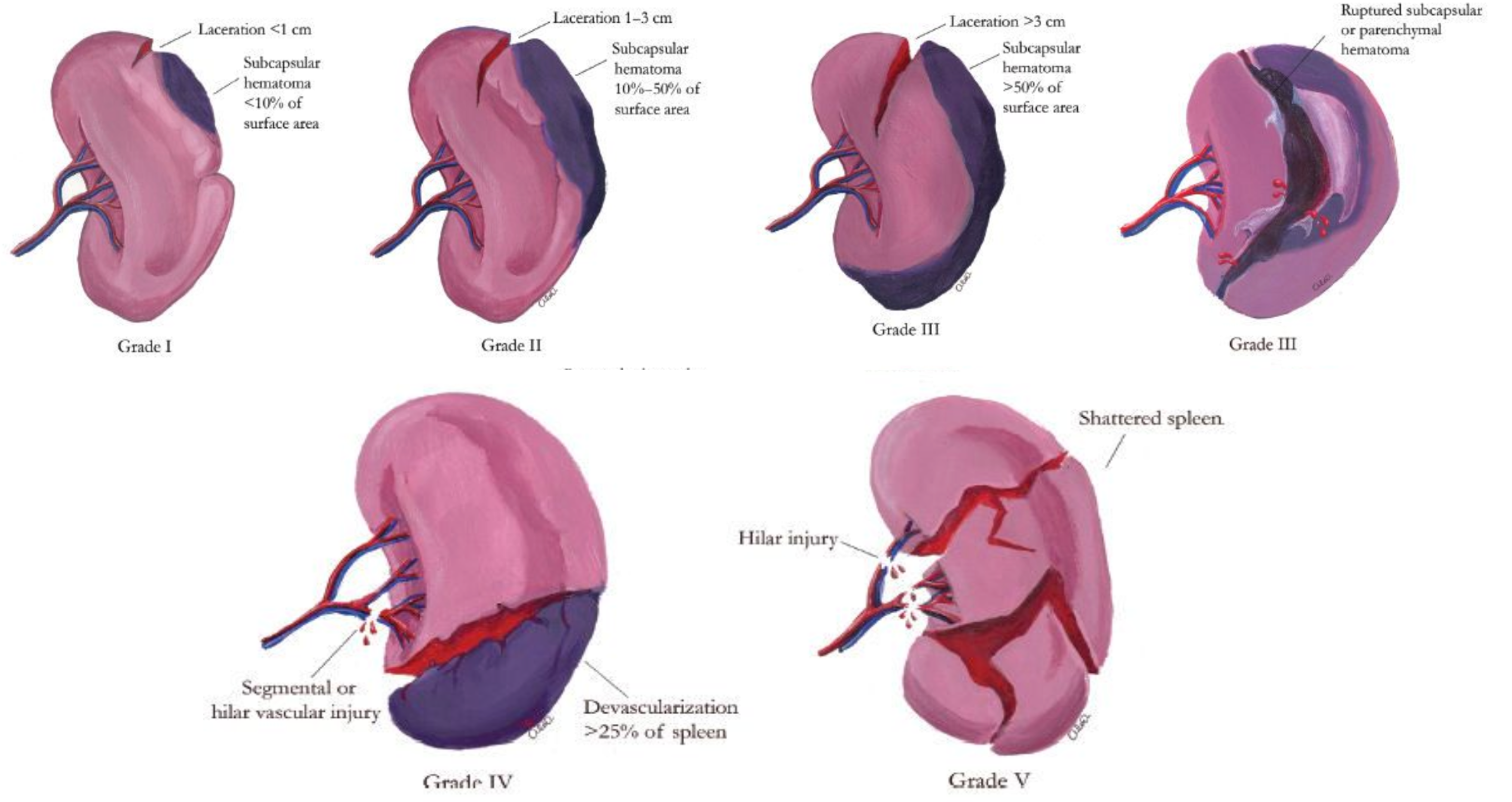
American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) splenic injury scale
Trauma
Splenic injury
- Most frequently injured organ in blunt trauma
- History of injury to the left side of the chest, flank, or left upper part of the abdomen
- Bruising, pain tenderness- lower chest and upper abdomen on left side
- Diagnosis: - Z
- CT in hemodynamically -stable patients
- FAST or exploratory laparotomy in an unstable patients
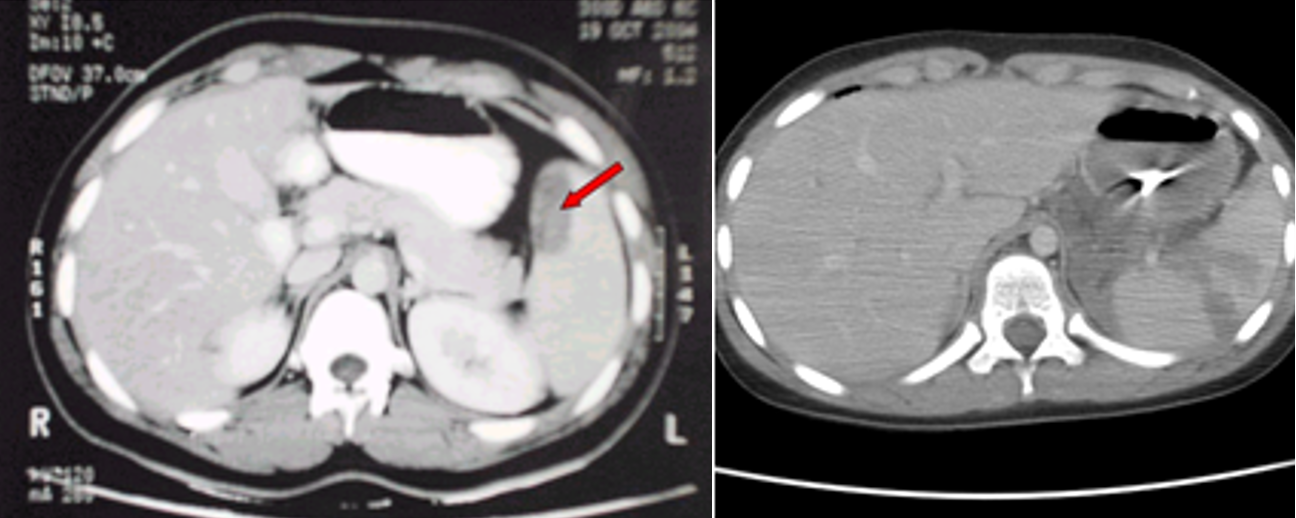
(Image: Splenic injury (CT scan))
Splenic injury: I-Non-surgical management (70%)
- Hemodynamically stable.
- FAST, CT scan.
- No other intra-abdominal injury requiring operation
- ICU admission for continuous monitoring.
- Serial hemoglobin.
- Repeated abdominal assessment.
- If hypotension develops - for surgery.
Splenic injury: II- Surgical management
- Hemodynamically unstable
- FAST: splenic injury, free fluid (hemoperitoneum)
- Surgery- splenectomy
- Polyvalent pneumococcal vaccine (pneumovax)