Definition of Anemia
- Reduction of red cell volume or hemoglobin concentration below the range of normal values for age.
- Lack of (or impaired) RBCs in the body, resulting in a decreased flow of oxygen to the organs. It is marked by one of the following:
- Hematocrit <41% in men or <36% in women
- Hemoglobin <13.5 g/dL in men or <12 g/dL in women
Classification
I. Aetiological II. Morphological
Aetiological Classification
- Due to inadequate production
- Due to blood loss
- Due to increased destruction
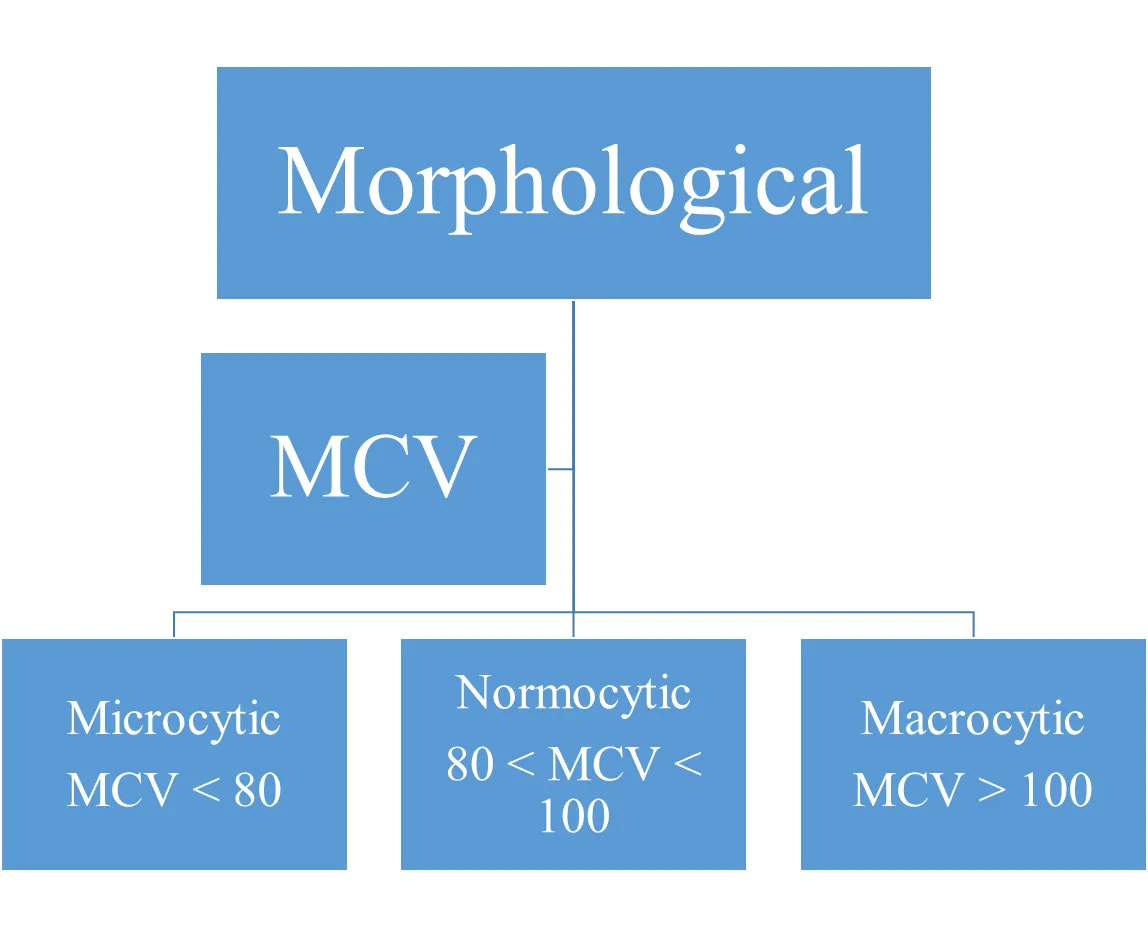
Morphological Classification
- MCV
- Microcytic
- MCV < 80
- Normocytic
- 80 < MCV < 100
- Macrocytic
- MCV > 100
- Microcytic
Laboratory Diagnosis Z
-
HB level and RBC’s count
-
Hematocrit; or packed RBC’s volume (the ratio of the volume of RBC’s to the volume of whole blood)
-
Red blood cells indices:
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) =
(Ht/ RBC’s count = normal 75-100 fimitoliter)-
If >100 → macrocytic anaemia
-
If <75 → microcytic anaemia
-
If 75-100 → normocytic anaemia
-
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH):
Average quantity of HB per individual red cell
(HB/RBC’s count Normal 26-32 picogram) -
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC):
- Average concentration of HB in a volume of packet RBC’s =
- HB/Hematocrit =
- Normal 32-36 %
-
Both MCH and MCHC are used to determine the content of HB in RBC’s.
- A. If normal MCH and MCHC =
- Normocytic anaemia - B. If low MCH and MCHC =
- Hypochromic anaemia
- A. If normal MCH and MCHC =
-
-
Peripheral blood smear (film)
-
Reticulocytes count
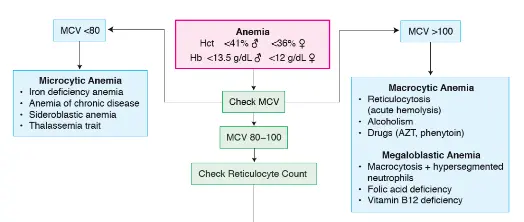
MCV < 80
Microcytic Anemia
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Anemia of chronic disease
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Thalassemia trait
MCV 80–100
Check Reticulocyte Count
MCV > 100
Macrocytic Anemia
- Reticulocytosis (acute hemolysis)
- Alcoholism
- Drugs (AZT, phenytoin)
Megaloblastic Anemia
- Macrocytosis + hypersegmented neutrophils
- Folic acid deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
Data Interpretation
- Orange Box
- Gray Box
- Blue Circle
Sample CBC
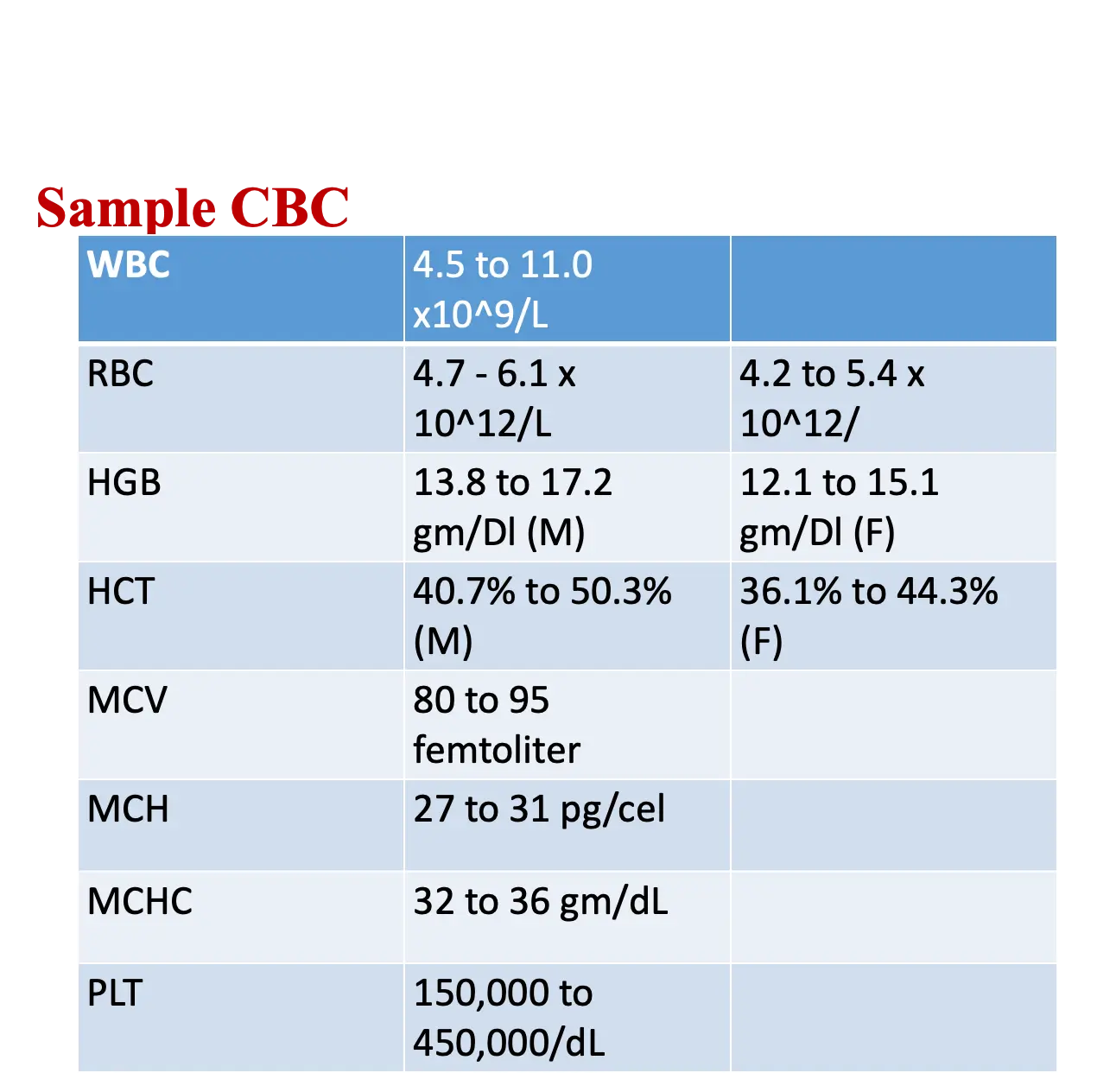
- WBC: 4.5 to 11.0 x 10^9/L
- RBC:
- 4.7 - 6.1 x 10^12/L
- 4.2 to 5.4 x 10^12/L
- HGB:
- 13.8 to 17.2 gm/DL (M)
- 12.1 to 15.1 gm/DL (F)
- HCT:
- 40.7% to 50.3% (M)
- 36.1% to 44.3% (F)
- MCV: 80 to 95 femtoliter
- MCH: 27 to 31 pg/cel
- MCHC: 32 to 36 gm/dL
- PLT: 150,000 to …
Differential
- Segs: 48% (51-72%)
- Lymphs: 40% (8-35%)
- Monos: 6% (1-9%)
- Eos: 4% (0-9%)
- Baso: 2% (0-2%)
Fe Panel
-
Serum Iron
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Decreased
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: Decreased
- Sideroblastic Anemia: Increased
- Thalassemia Minor: Normal
-
Serum Ferritin
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Decreased or Normal (early)
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: Increased
- Sideroblastic Anemia: Increased
- Thalassemia Minor: Normal
-
Transferrin/ TIBC
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Increased
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: Decreased
- Sideroblastic Anemia: Normal
- Thalassemia Minor: Normal
-
% Saturation
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Decreased
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: N/Decreased
- Sideroblastic Anemia: Increased
- Thalassemia Minor: Normal